-
Volume 28 (2020) Pages 109-117Effects of Adhesive Force Distribution by Admixing Smaller Particles on Improving Particle Flowability Read moreEditor's pick
The particle flowability can be improved by admixing particles smaller than the original particles (main particles). However, the details of this improving mechanism are not yet fully understood. In this article, it was investigated that the effects of adhesive force distribution at each of contact points due to admixing particle coating on improving the flowability by DEM simulation. As a result, non-uniform adhesive force distribution had a larger discharge flow rate. This result suggested that the adhesive force distribution at each of contact points would also contribute to improving the flowability in a smaller particle admixing system.
-
Volume 28 (2020) Pages 88-92Production of PLGA Nanoparticles and Its Application to Drug Delivery Systems Read moreEditor's pick
Nanomedicines have attracted attention in the field of drug delivery technology. The size of nanomedicine plays important role in the biodistribution and its performance, such as antitumor effect and gene silencing activity. Therefore, development of size control techniques for nanomedicines is strongly desired. In this article, we report a precise size control method of poly lactic-co-glycolicacid(PLGA) nanoparticles encapsulated anti-tumor drugs using a microfluidic device.
-
Editor's pick
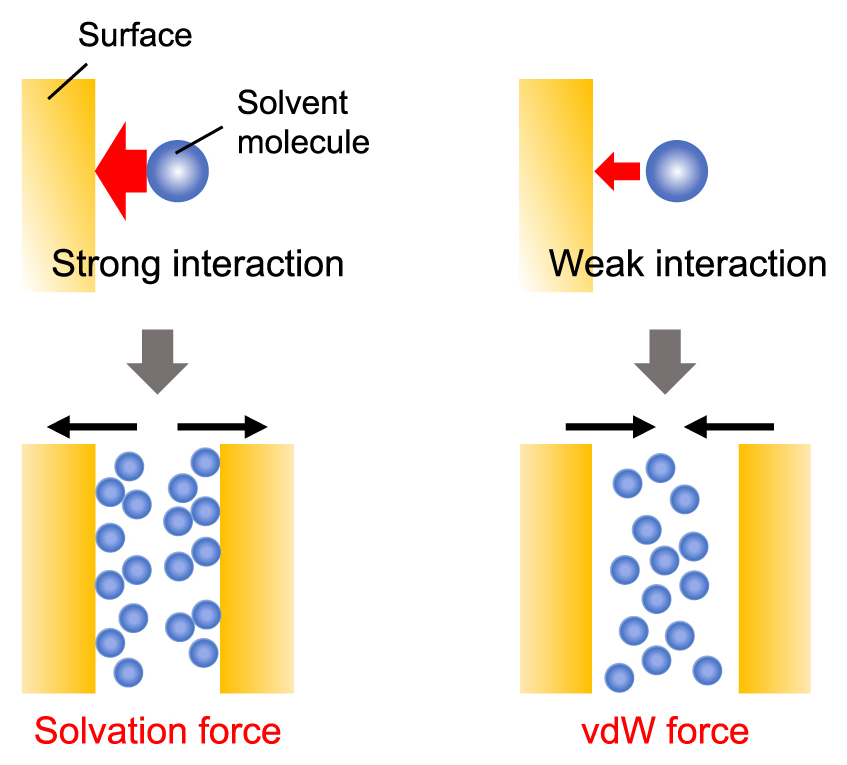
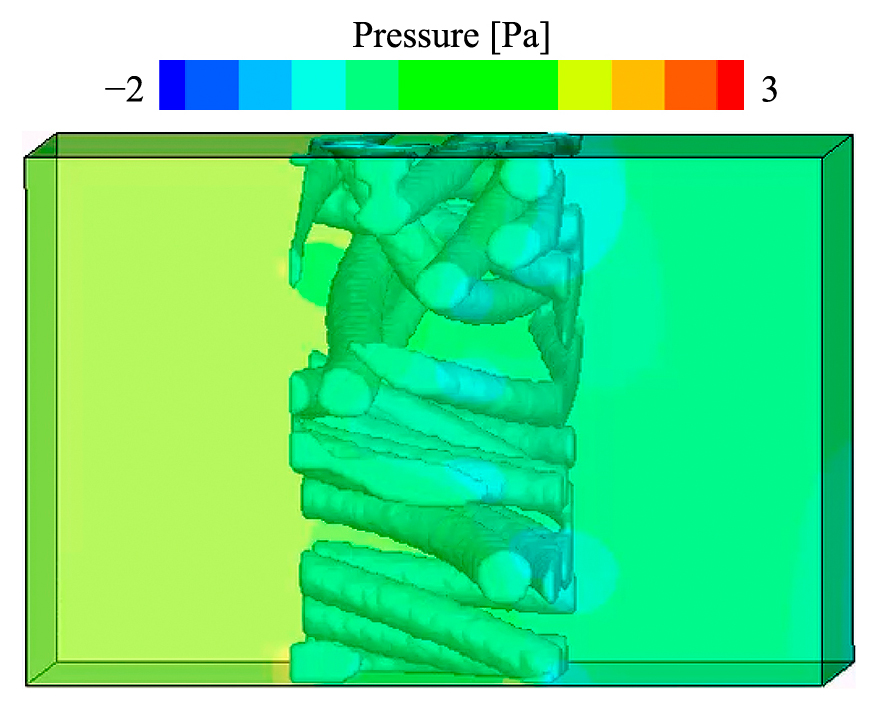
Since particle suspensions in organic solvents are used in various industries, characterizing the stability of suspensions in organic solvents is significant for handling such suspensions. However, the interaction forces between particles, which dominate suspension stability, in non-aqueous solvents have not been understood well. In this study, the author conducted the direct force measurements between solid surfaces in different organic solvents using atomic force microscopy and revealed that the affinity between surface functional groups and solvent molecules affect significantly the interaction forces. This will provide a novel insight to the stability characterization of particle suspensions in organic solvents.
-
Volume 28 (2020) Pages 124-128Crystal Structure Engineering of Powders for Visible-Light-Active Photocatalysts Read moreEditor's pick
One of the major challenges in the last decades has been how to provide sufficient energy to the world’s population. It is nowadays clear that fossil fuels, which currently supply about 85% of our necessary energy, will be unable to satisfy the increased energy demand in the future. In this article, authors have proposed an interesting approach for designing a pn junction semiconductor photocatalyst. Results show that a nano-level combination of n-type BiVO4 and p-type BiOX enhances the photocatalytic activity as compared to each semiconductor.
-
Volume 28 (2020) Pages 44-48Fabrication of Colored Magnetic Powder Using Magnetic Polymer Network Read moreEditor's pick
Since iron oxide magnetic particles exhibiting excellent magnetism are dark brown materials, it was difficult to prepare colored magnetic particles based on iron oxide magnetic particles. This article describes the creation and properties of colorless and full-color magnetic particles based on a polymer doped with holmium, a lanthanide with low colorability and a strong magnetic moment.
-
Volume 27 (2019) Pages 81-86Mechanistic Insight into Protein Corona Formation on Nanocarbon Materials Read more
-
-
Volume 27 (2019) Pages 53-57Fabrication and Application of Functional Soft Particles Using Red Blood Cells as Template Read more
-
Volume 27 (2019) Pages 121-125Synthesis of SnTiO3 Nanoparticles Using Supercritical Fluids Read more
-
Volume 27 (2019) Pages 19-24Numerical Analysis of Filter Collection Coordinated with Imaging Read more