-
編集者のコメント
This review describes the importance of comminution and classification processes to produce battery materials and battery electrodes, and to recycle production scrap and end-of-life battery cells. It shows how comminution and classification processes are integrated into the production of various active materials, such as spheronisation of natural graphite, grinding of nano-sized silicon and dispersion of calcined lithium metal oxides, and into the processing of electrode slurries using planetary mixers, extruders or stirred media mills. The use of mills and classifiers in the recycling of battery materials and the mechanochemical synthesis of solid sulphide electrolytes is another important topic.
-
編集者のコメント
Solution processing is one of the important methods in the synthesis of functional materials. This method can create various compositions and control their crystal structure, particle morphology, and size. It is expected to lead to the development of new functionality of materials. This paper introduces the relationship between powder particle morphology and material functionality, explains the various environmental response functionalities of transition metal oxides synthesized by the environmentally friendly liquid-based method, and indicates that the morphology control associates material science with art. It arouses the reader's interest and implies further potential in developing future functional materials.
-
40 巻 (2023) p. 172-185Performance Testing for Dry Powder Inhaler Products: Towards Clinical Relevance もっと読む編集者のコメント
Dry powder inhaler formulations have garnered interest as a way to deliver drugs directly to the lungs in a stable, solid dosage form. Developing generics of brand-name dry powder inhalers is essential to their widespread availability but requires careful consideration in characterizing bioequivalence. This review highlights the standard characterization methods frequently employed as well as physiologically relevant measures that may aid in bioequivalence decisions. The necessity of considering in vivo relevance while performing in vitro testing is highlighted, assisting the field in shifting to physiologically relevant characterization methods.
-
編集者のコメント
Delve into the forefront of rare earth permanent magnet research with this insightful paper. With electric vehicles driving demand for higher-performance magnets, the quest for advanced structural control in powder metallurgy processes is paramount. Discover how innovative approaches in chemical synthesis have led to the development of submicron-sized Sm-Fe-N powders with remarkable coercivity. Explore the evolution of grain boundary control techniques and the emergence of low-thermal load consolidation methods like spark plasma sintering, crucial for enhancing remanence in next-generation magnets.
-
編集者のコメント
Spray drying emerges as a pivotal method in pharmaceutical manufacturing, offering versatility across various delivery routes. Its capacity to engineer particles enhances drug efficacy and stability, vital for global distribution, notably for vaccines. Despite complexities in formulation design, this review elucidates practical steps and essential background knowledge crucial for successful spray-dried microparticle formulation. It navigates through estimating solute concentration during drying, solidification kinetics, and the role of stabilizers, providing invaluable insights for practitioners striving to optimize particle properties for therapeutic delivery.
-
編集者のコメント
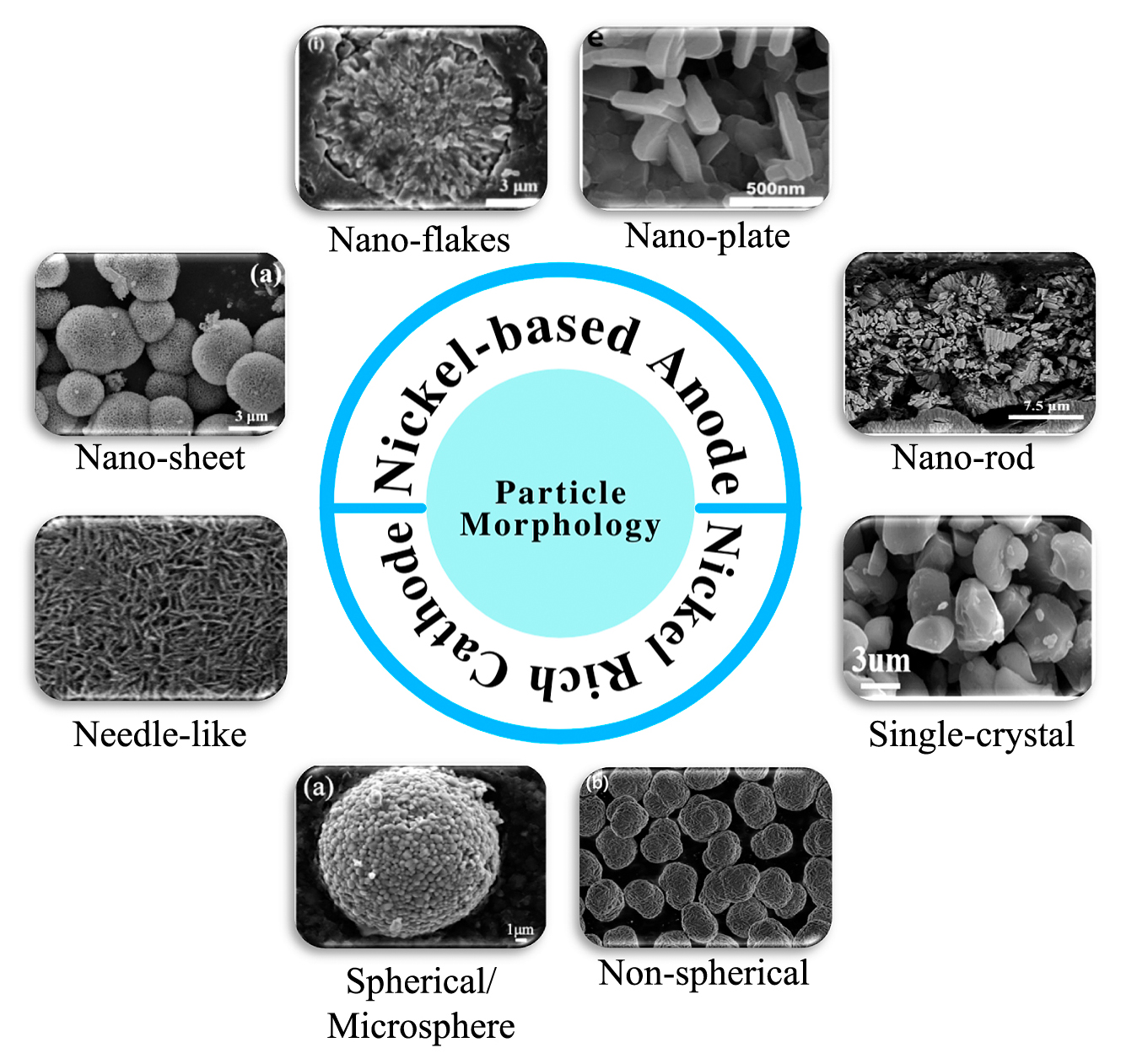
Nickel is set to play a pivotal role in the next chapter of energy storage. Over the next decade, nickel-based Li-ion batteries are expected to dominate the battery market for both energy storage systems (ESS) and electric vehicles. One of the key features of nickel-based active materials is their morphology; the shape and size of the particles can affect the electrochemical performance of the active materials. Both nickel-containing anode and cathode materials with excellent morphology have been reported to have high capacity, excellent cycle stability, and rate-ability. These key performance metrics demonstrate the promising future for the development of a clean and sustainable energy industry.
-
編集者のコメント
Pharmaceutical dry powders with desired aerosol properties are required for efficient pulmonary drug delivery. Thin-film freezing (TFF) followed by lyophilization is a particle engineering technology that produces highly porous, brittle, powder matrices with excellent aerosol properties and high drug loading. In this review article, the authors describe the TFF technology and discuss the physical and aerosol properties of TFF powders as well as factors affecting those properties. Finally, the authors provide a comprehensive review of published literature for applying the TFF technology to prepare aerosolizable dry powders of protein-based pharmaceuticals for pulmonary delivery.
-
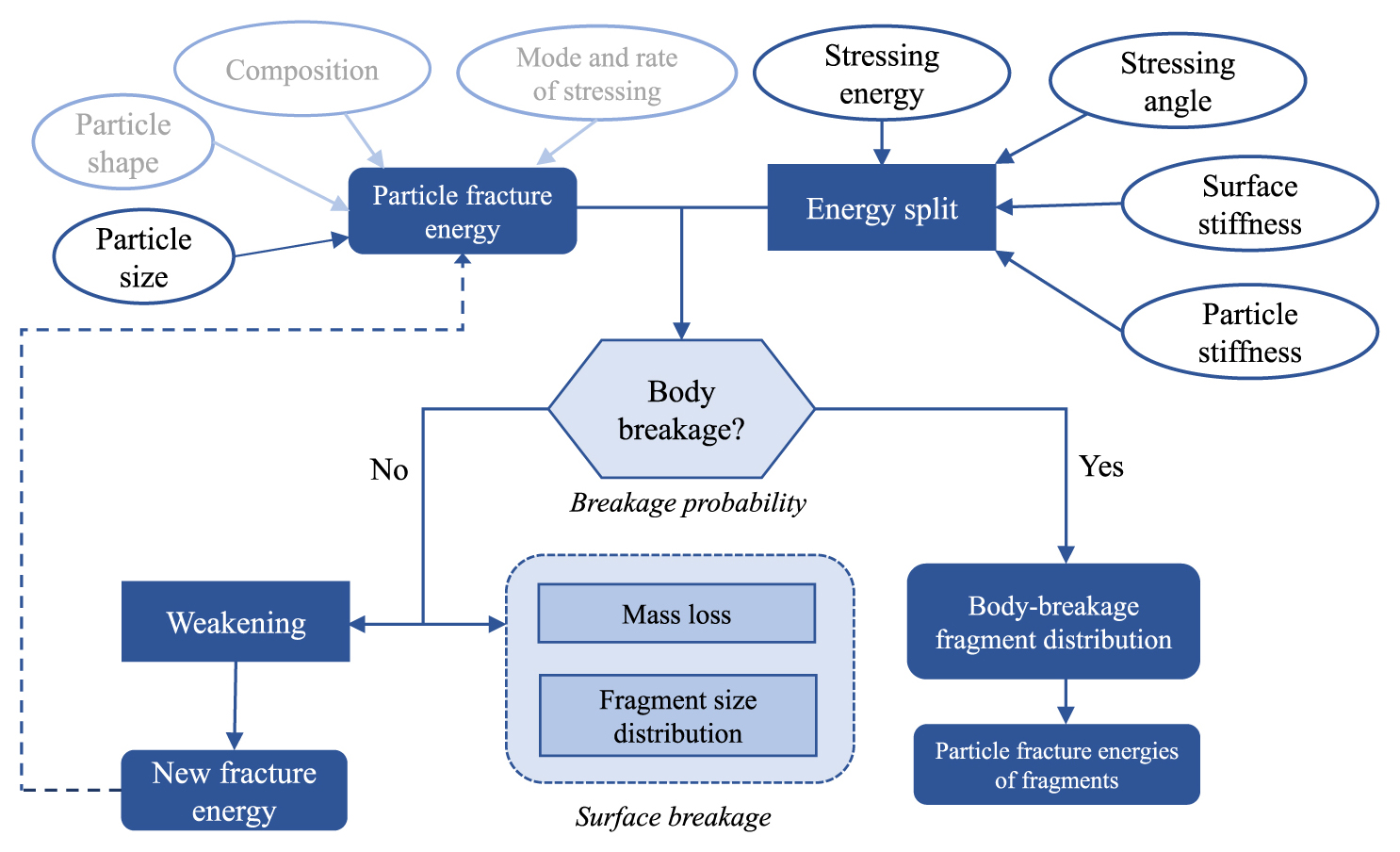
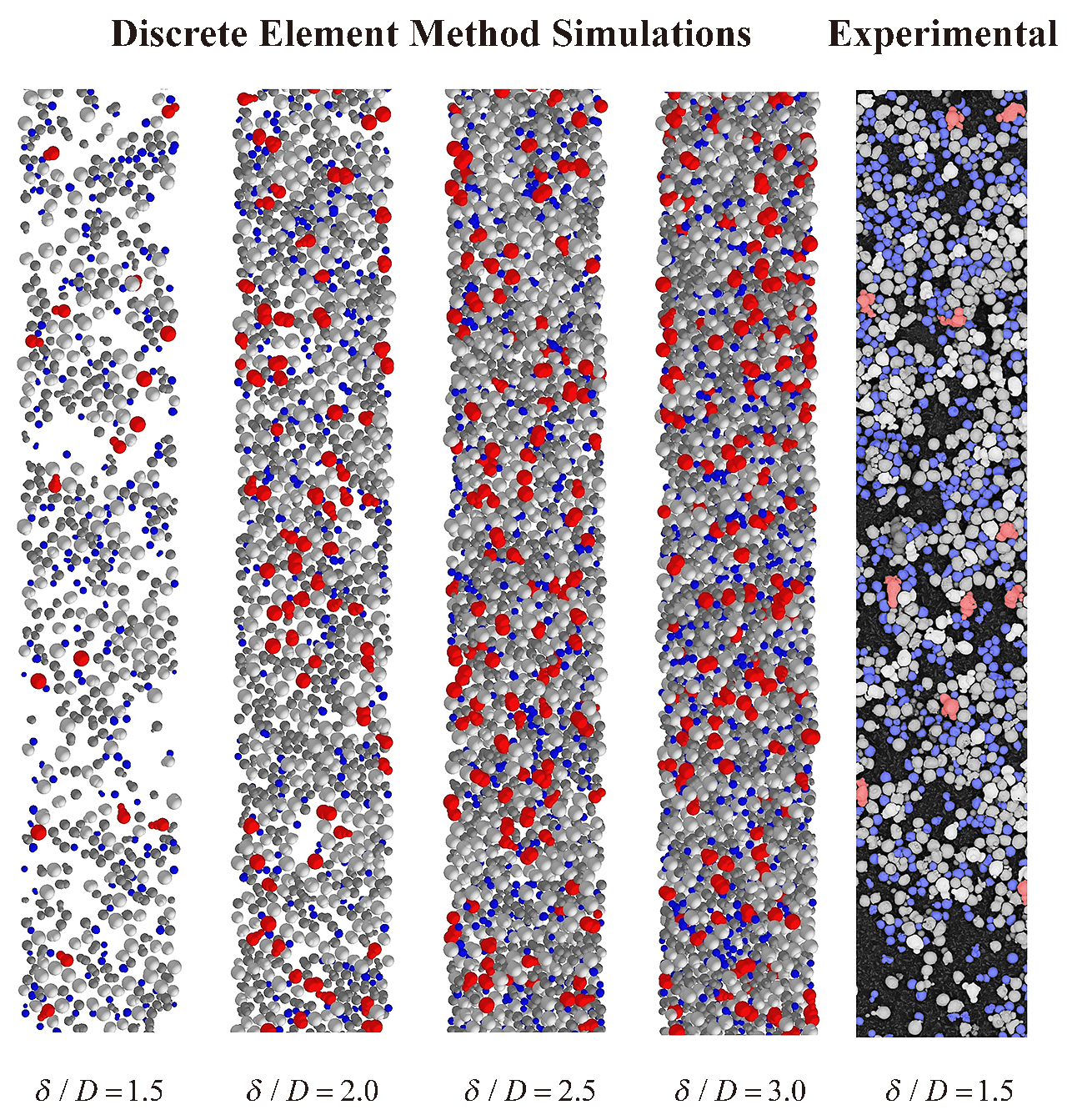
39 巻 (2022) p. 62-83Review and Further Validation of a Practical Single-Particle Breakage Model もっと読む編集者のコメント
Single-particle breakage studies were, in the not-so-distant past, only of academic interest, since no tools were available to transfer the microscale information they provide to deal with problems in industry. Fortunately, the discrete element method (DEM), along with properly-formulated population balance models, not make it possible to carry information from single particles to predict the performance of crushers, mills and handling systems that may cause their mechanical degradation. The work critically analyzes one model that has been found quite powerful in this task.
-
39 巻 (2022) p. 251-261Biodegradable PLGA Microsphere Formation Mechanisms in Electrosprayed Liquid Droplets もっと読む編集者のコメント
Delivery systems using nanoparticles and microparticles composed of biodegradable polymers such as polylactic glycolic acid have attracted much attention in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic fields to the delivery of active ingredients into the body. This paper describes a novel microparticle preparation method using fine-charged droplets as reaction fields generated by electrospray. This method is unique and impactful because tailored PLGA microspheres with various sizes and different structures such as porous and solid structures can be prepared by controlling the process conditions. The formation mechanism of particles with different sizes and structures within the droplets is also explained.
-
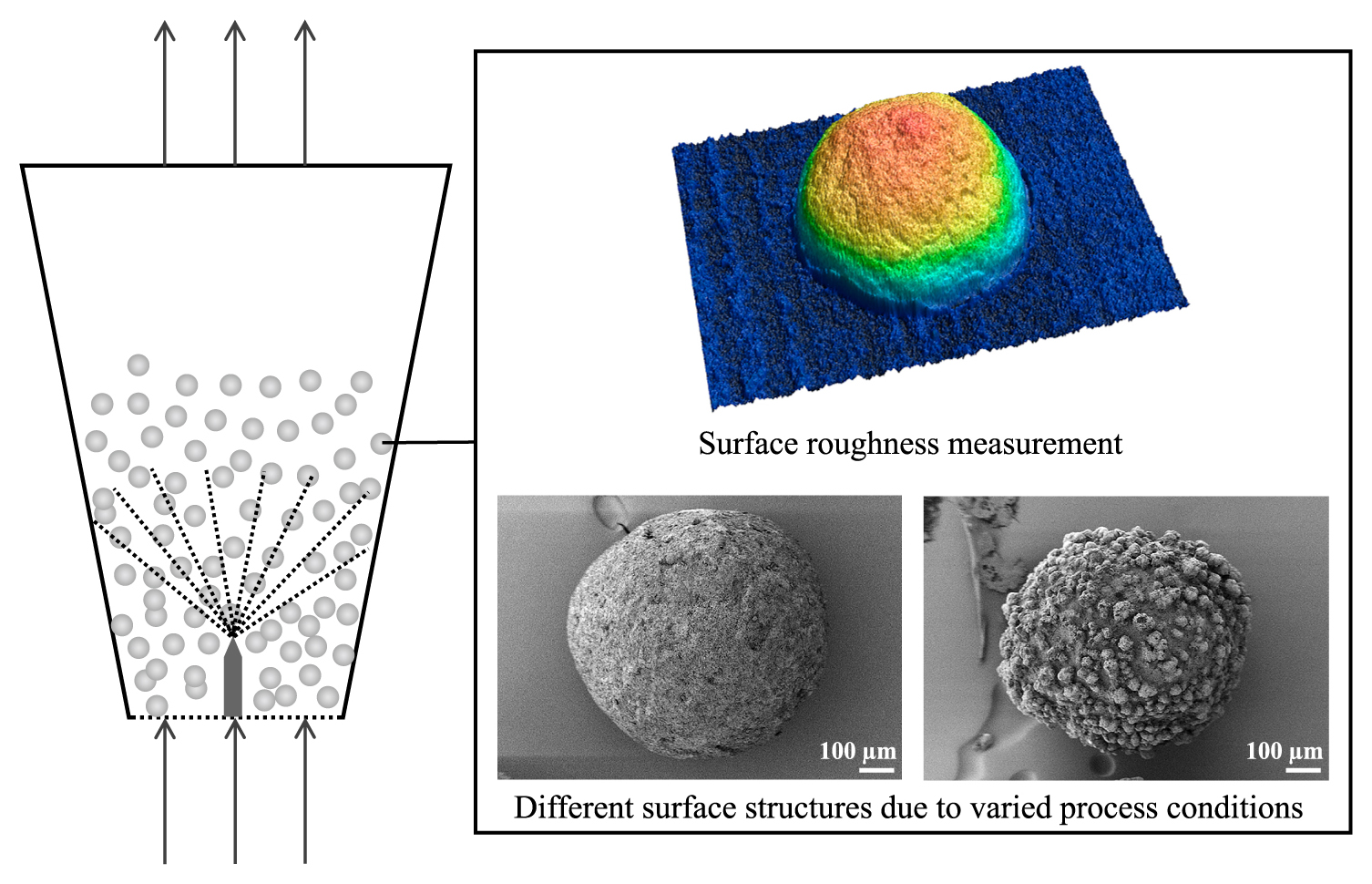
編集者のコメント
Due to their easy handling, transport, and storage compared to liquids and gases, solid products in particulate form are of great interest in both, daily life and industrial applications. Along with the high demand for those products comes the need for a thorough understanding of particle production and modification processes, like fluidized bed spray granulation, to achieve the desired product properties. To contribute to that process understanding and to, in the long term, enable the production of tailor-made particles, this study aims to correlate process parameters and particle surface structure in fluidized bed spray granulation.
-
編集者のコメント
High-precision AuNPs can provide more focused optical absorption, better-targeted drug delivery, higher yield and efficiency in chemical reactions, and more reliable performance. However, the precision control of the nanoparticles has presented a major challenge. This work investigated and discussed the major process parameters of AuNPs synthesis using the Turkevich method. The authors provided detailed characterization and explanations to the correlations between the processing parameters and the nanoparticle properties. The additional knowledge would facilitate larger-scale synthesis of precision gold nanoparticles, encourage broader applications and provide insight into the synthesis and study of other engineered nanomaterials.
-
編集者のコメント
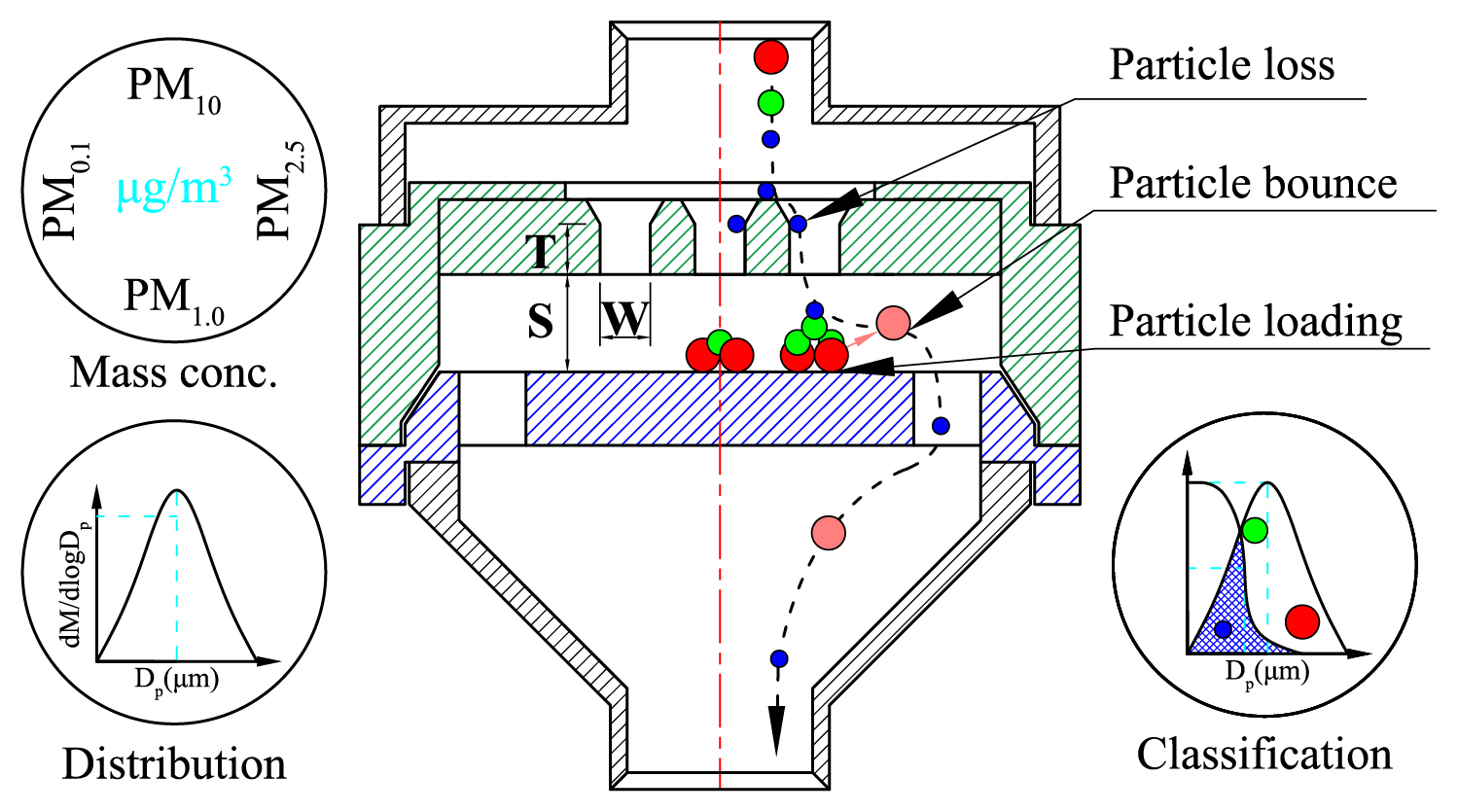
The inertial impaction technique is applied extensively for particulate matter classification and understanding the characteristics of inertial impactors is important for designing a good classifier. This article reviewed and synthesized the knowledge of the design and improvement of inertial impactors for long-term use without frequent maintenance needs. The applications of the inertial impactors for personal exposure measurement, particulate matter control and potential power classification at very high concentrations with the cutoff diameter down to submicron even nanometer sizes were addressed.
-
38 巻 (2021) p. 189-208Scaling-up the Calcium-Looping Process for CO2 Capture and Energy Storage もっと読む編集者のコメント
Increasing renewable energy storage and boosting CO2 capture systems are considered two key routes within the near-future energy scenario. The calcium looping (CaL) process, based on limestone as (cheap) raw material, is a flexible technology that can operate under both routes simply by modifying its operation conditions, namely, reactor gas composition, temperature, pressure, and particle size. As a post-combustion CO2 capture system, the CaL process (TRL7) could capture CO2 on a large scale with an energy consumption lower than 3MJ/kg CO2. As a thermochemical energy storage system (TRL 5), thermal-to-electric efficiencies above 45% could be reached in fully dispatchable renewable plants.
-
編集者のコメント
The current trend in nano- and microparticle technology towards ever increasing complexity requires methods for the multidimensional characterization of the underlying particle property space in terms size, shape, structure, surface and composition. In this review the mathematical description and handling of multidimensional property distributions is outlined. In particular, the authors present and discuss state-of-the-art measurement techniques which are able to extract multidimensional information.
-
編集者のコメント
The role of modeling and simulation becomes more important in the era of digital transformation. As designated in Industry 4.0 and Society 5.0, a smart factory will appear, where cyber and physical spaces will be highly integrated. A physics simulation-based digital twin is one of the promising technologies. This paper presents the latest numerical models for powder systems, which will contribute to the realization of the digital twin in the future.
-
37 巻 (2020) p. 3-18Cohesive Powder Flow: Trends and Challenges in Characterisation and Analysis もっと読む編集者のコメント
Cohesive powders are troublesome in terms of flow reliability, consistency and accuracy, posing great challenges in manufacturing. In this article the current understanding of rheological behaviour of powders, considering bulk friction and apparent shear viscosity, is reviewed. Flow rules accounting for particle properties, process dynamics, and their interactions have been proposed in literature, but require rigorous experimental validation. The suitability of state-of-the-art instruments for this purpose is critically reviewed. The current understanding of the influence of particle properties, fluid drag and shear strain rate on the dynamics of powder flow is summarised, including the topical subject of powder spreadability for additive manufacturing.
-
編集者のコメント
The recent pandemic of COVID-19 brings the topic of vaccines and the urgency with which they are required into the popular literature. This article focuses on the merits of using nanovaccines to establish mucosal immunity in the respiratory tract the primary site of infection and transmission for a variety of infectious diseases. Targeting the innate immune response which is mediated by airway macrophages, the host cell for some pathogens, can be achieved with a variety of nanoparticle technologies conferring protection from the disease.
-
編集者のコメント
The article reviewed the solid collection performance and scale-up methodology of gas-solid cyclones at high solid density conditions based on experimental and numerical studies mainly published after 2007. The models to predict pressure drop of cyclone, the non-uniform distribution of gas-solids flow, and scale-up methodology, the phase graph of the stability of uniform distribution/maldistribution of solids in parallel cyclones, and recent progress in high-solid loading cyclones are summarized.
-
37 巻 (2020) p. 114-131Fluidised Bed Reactors for the Thermochemical Conversion of Biomass and Waste もっと読む編集者のコメント
With increasing quantity of waste generated and fast growing concerns about climate change, there has been renewed impetus recently to develop advanced thermochemical processes using waste biomass as a feedstock. This is because these processes have the potential to add value to cheap and abundant materials by converting them into advanced biofuels and chemicals. This reviews paper is concerned principally with newest applications of fluidised bed reactors for waste treatment, with particular attention given to those processes aimed at the production of clean syngas for the subsequent synthesis of high-value products, including bio-hydrogen, synthetic natural gas, and liquid fuels.
-
編集者のコメント
Understanding particle properties and powder behavior during handling and processing requires the characterization of the inner-core and surface properties. Most routine characterization methods involve the former. However, the dynamic behavior of large collections of particles, even if they are much larger than the nanoparticle scale, are dominated by their surface energy at the bulk (square meter, not microscopic) level. Bulk-surface energy of powder blends can differentiate between uniform mixing and the system’s inability to reach mixing equilibrium. Single-particle microscopic characterization techniques, while excellent complement to bulk-level methods, are not ideal for assessing surface energy in connection to properties like powder flow. However, microscopic techniques are invaluable in predicting some bulk-level properties of powders, such as the specific type of surface exposed when powders are subjected to processes such as milling.