Abstract
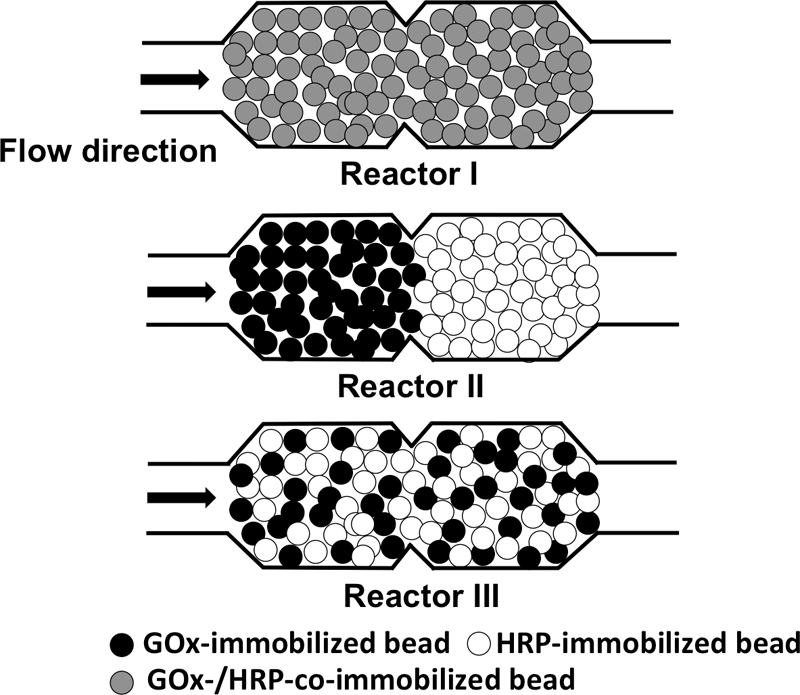
Three different configurations of microfluidic reactors packed with enzyme-bearing microbeads were examined to show that the overall efficiency of coupled enzyme-catalyzed reactions depends on the spatial relationship of two enzymes immobilized on the bead surfaces. The spatial distances of glucose oxidase (GOx) and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) enzymes were controlled by using microbeads as a supporting matrix for immobilizing the two enzymes and packing them in two microfluidic chambers. A microreactor packed with microbeads coimmobilized with the two enzymes showed a better overall reaction efficiency than the other two reactors, where the two enzymes were spatially distant, under a flow condition. These results are ascribed to the reduced diffusional loss of an intermediate product in the bienzyme-coimmobilized microreactor. Furthermore, the inhibition of the GOx enzyme by H2O2, an intermediate product, can be eliminated by quickly converting H2O2 to a final non-inhibiting product in the bienzyme-coimmobilized microreactor.