All issues

Volume 30, Issue 10
Displaying 1-13 of 13 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Original Papers
-
Jun KAWAKAMI, Arisa SOMA, Kenta KIKUCHI, Yoh KIKUCHI, Shunji ITO, Haru ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 10 Pages 949-954
Published: October 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS1-(2-tryptanthrinylaminoacetoxy)-14-(1-pyrenecarboxy)-3,6,9,12-tetraoxatetradecane (T2NH-P5P) was synthesized as a fluorescent chemosensor for metal ions. We investigated the metal-ion recognition of T2NH-P5P by separately adding Mg2+, Ca2+, Ba2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Ag+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, Al3+, and Pb2+ in an acetonitrile solution. When using excitation at 325 nm, which corresponds to the absorption of the pyrene unit of T2NH-P5P, emission at 600 nm, from the 2-aminotryptanthrin unit, was observed, indicating that intramolecular fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) occurs in T2NH-P5P (FRET-on). However, when Fe2+, Fe3+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, and Al3+ were added to an acetonitrile solution of T2NH-P5P, the behavior changed from FRET-on to FRET-off, which means that the fluorescence of 2-aminotryptanthrin was quenched, whereas that of the pyrene group was revived (FRET-off). Especially, this behavior was remarkable for Fe2+, Fe3+, Cu2+, and Hg2+. T2NH-P5P is suitable for use as a fluorescent chemosensor for Fe2+, Fe3+, Cu2+, and Hg2+. View full abstractDownload PDF (1128K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1128K) -
Ana Cristina M. da COSTA, Ubiratan B. de ARAÚJO, Edgar F. O. de ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 10 Pages 955-960
Published: October 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis paper presents a portable total reflection X-ray fluorescence system composed of a 15 W X-ray tube, with a gold anode, a waveguide constituted by two Perspex® parallel plates, a Si PIN detector and a quartz optical flat. The critical angle of the total reflection system was experimentally determined by measuring a zinc solution (100 mg/L). The accuracy of the system was checked using SRM 1577b Bovine Liver by NIST as standard reference material. We obtained the absolute detection limits of the following elements: P (450 ± 40 ng), S (200 ± 31 ng), K (30 ± 2.5 ng), Ca (19 ± 3.5 ng), Mn (4.1 ± 0.5 ng), Fe (3.6 ± 0.9 ng), Cu (3.3 ± 0.4 ng) and Zn (3.5 ± 0.3 ng). This paper shows that it is possible to produce total reflection X-ray fluorescence with very compact, efficient, low-cost and easy-to-handle instrumentation using a low-power X-ray tube and a Si PIN compact detector.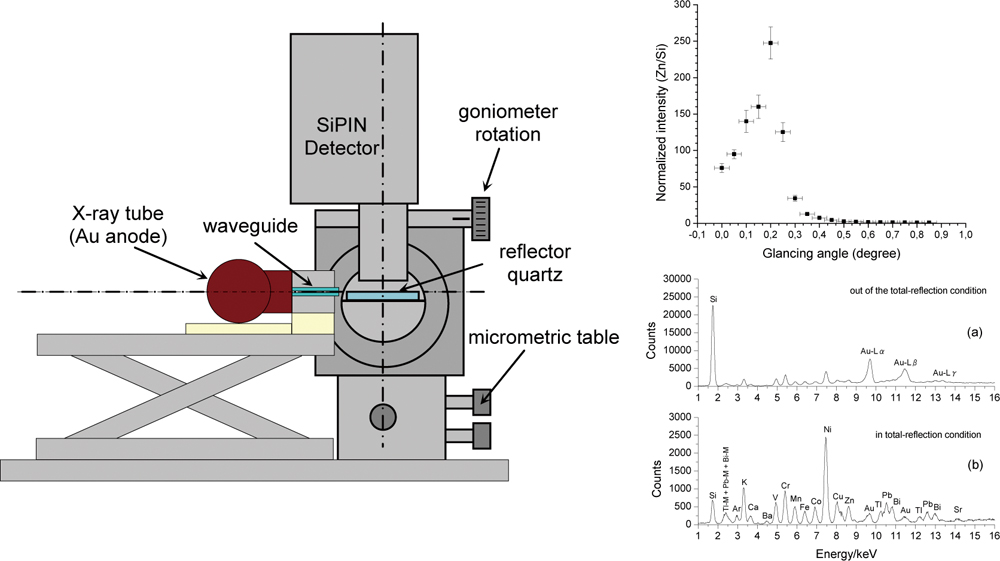 View full abstractDownload PDF (4047K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4047K) -
Toshinori MORISAKU, Sho ARAI, Hiroharu YUIArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 10 Pages 961-969
Published: October 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSConformational changes of hydrated proteins induced by gradual dehydration were monitored by vibrational circular dichroism (VCD) spectroscopy. In myoglobin and casein, representative α-helix-rich and random-coil proteins, respectively, an increase in left-handed optical activity in the amide I band was detected at the initial stage of dehydration, followed by an increase in opposite right-handed activity in both the amide I and II bands with further dehydration. Because the second step was observed with an increase in the turbidity of the proteins, it can be attributed to their aggregation. In contrast, because the increase in left-handed optical activity is induced by the conformational change of the proteins and is followed by the aggregation, it may derive from the increase in the regularity of the local structure in individual myoglobin or casein that triggers the aggregation. View full abstractDownload PDF (1123K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1123K) -
Igor BOTELLO, Francesc BORRULL, Carme AGUILAR, Marta CALULLArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 10 Pages 971-977
Published: October 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe abuse of barbiturate drugs is widespread, and the development of methods for their efficient separation and quantification is needed. Three barbiturate drugs were preconcentrated and determined by in-line solid-phase extraction (SPE) capillary electrophoresis (CE) in urine samples. Different parameters affecting preconcentration were evaluated, such as the sample pH, the volume of the elution plug and the sample injection time. This strategy enhanced the detection sensitivity in the range of 170- to 1840-fold, compared with normal hydrodynamic injection. The method provides limits of detection (LODs) for standard samples in the range of 0.5 to 5 ng/mL with good repeatability and reproducibility values. The LODs obtained for urine samples were in the range of 5 to 60 ng/mL. The validation with human urine samples spiked with the studied compounds demonstrated the applicability of the optimized method. This method provides a reproducible and sensitive analysis of urine samples in the determination of barbiturates drugs. View full abstractDownload PDF (674K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (674K) -
Ikuo UETA, Tomoki MITSUMORI, Susumu KAWAKUBO, Yoshihiro SAITOArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 10 Pages 979-983
Published: October 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe musty-odor compounds (MOCs) 2-methylisoborneol (2-MIB) and geosmin in water samples were determined by a purge-and-trap method using a needle-type extraction device followed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. For the extraction of these compounds, a triple-layer-type extraction needle containing divinylbenzene and activated carbon particles as the particulate extraction media was introduced. Several experimental parameters, including the sample temperature during extraction, the addition of sodium chloride, and desorption conditions, were thoroughly optimized in this study. The detection limits for 2-MIB and geosmin were 1.0 and 0.5 ng L−1, respectively. The method was successfully applied to the simultaneous determination of MOCs and other volatile organic compounds in tap-water samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (512K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (512K) -
Ji-Eun EOM, Eunyoung LEE, Kyung-Hwa JEON, Jeongeun SIM, Minah SUH, Gil ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 10 Pages 985-990
Published: October 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialMyocardial ischemia (MI) induces many changes in the body, including pH decrease and electrolyte imbalance. No obvious symptoms of MI appear until irreversible cellular injuries occur. Since early treatment is critical for recovery from ischemia, the development of reliable diagnostic tool is demanded to detect the early ischemic status. Ischemia modified albumin (IMA), formed by cleavage of the last two amino acids of the human serum albumin (HSA) N-terminus, has been considered so far as the most trustworthy and accurate marker for the investigation of ischemia. IMA levels are elevated in plasma within a few minutes of ischemic onset, and may last for up to 6 h. In the present study, we developed a novel assay for the examination of IMA levels to ameliorate the known albumin cobalt binding (ACB) test established previously. We observed a stronger copper ion bound to the HSA N-terminal peptide than cobalt ion by HPLC and ESI-TOF mass spectrometric analyses. The copper ion was employed with lucifer yellow (LY), a copper-specific reagent to develop a new albumin copper binding (ACuB) assay. The parameters capable of affecting the assay results were optimized, and the finally-optimized ACuB assay was validated. The result of the IMA level measurement in normal versus stroke rat serum suggests that the ACuB assay is likely to be a reliable and sensitive method for the detection of ischemic states. View full abstractDownload PDF (1292K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1292K) -
Jinseok HEOArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 10 Pages 991-997
Published: October 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThree different configurations of microfluidic reactors packed with enzyme-bearing microbeads were examined to show that the overall efficiency of coupled enzyme-catalyzed reactions depends on the spatial relationship of two enzymes immobilized on the bead surfaces. The spatial distances of glucose oxidase (GOx) and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) enzymes were controlled by using microbeads as a supporting matrix for immobilizing the two enzymes and packing them in two microfluidic chambers. A microreactor packed with microbeads coimmobilized with the two enzymes showed a better overall reaction efficiency than the other two reactors, where the two enzymes were spatially distant, under a flow condition. These results are ascribed to the reduced diffusional loss of an intermediate product in the bienzyme-coimmobilized microreactor. Furthermore, the inhibition of the GOx enzyme by H2O2, an intermediate product, can be eliminated by quickly converting H2O2 to a final non-inhibiting product in the bienzyme-coimmobilized microreactor.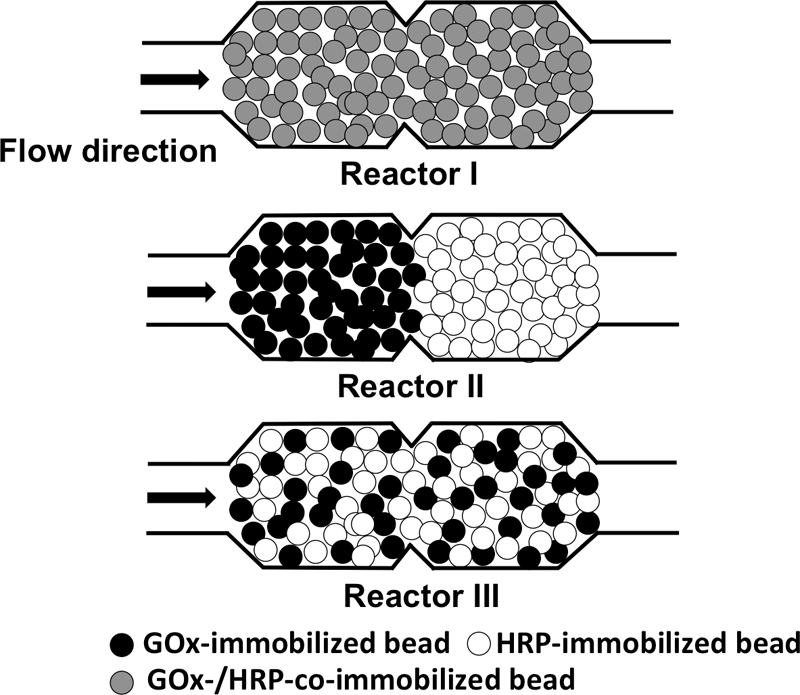 View full abstractDownload PDF (1403K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1403K) -
Xilin XIAO, Jinhua XUE, Lifu LIAO, Xiangcheng CHEN, Yanhua ZENG, Yimou ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 10 Pages 999-1004
Published: October 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA direct fluorescence spectra method was applied for the determination of metallothioneins at nanomolar levels. In Britton–Robison (B-R) buffer (pH 7.0), the interaction of bis(1,10-phenanthroline)copper(II) complex cation [Cu(phen)2]2+ and metallothioneins enhanced the fluorescence intensity of system. The fluorescence enhancement at 365 nm was proportional to the concentration of metallothioneins. The mechanism was studied and discussed in terms of the fluorescence and UV-absorption spectra. Under the optimal experimental conditions, at 365 nm, there was a linear relationship between the fluorescence intensity and the concentration of the metallothioneins in the range of 8.30 × 10−9 – 7.70 × 10−7 mol L−1. The linear regression equation was ΔF = 8.96 + 38.01c (mol L−1), with a correlation coefficient of r = 0.998 and detection limit 2.50 × 10−9 mol L−1. The relative standard deviation was 0.47% (n = 11), and the average recovery 97.2%. The proposed method was successfully reliable, selective and sensitive in determining trace metallothioneins in fish visceral organ samples with the results in good agreement with those obtained by HPLC. View full abstractDownload PDF (1134K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1134K) -
Satoshi FUJINAGA, Katsuya UNESAKI, Yuki KAWAI, Koichi KITAGUCHI, Kosuk ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 10 Pages 1005-1011
Published: October 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWhen mixed solvent solutions, such as ternary water–hydrophilic/hydrophobic organic solvents, water–surfactant, water–ionic liquid, and fluorous–organic solvents are delivered into a microspace under laminar flow conditions, the solvent molecules are radially distributed in the microspace, generating inner and outer phases. This specific fluidic behavior is termed “tube radial distribution phenomenon” (TRDP). In this study, the factors influencing the formation of inner and outer phases in the TRDP using the above-mentioned mixed solvent solutions were investigated. We examined phase diagrams, viscosities of the two phases (upper and lower phases in a batch vessel), volume ratios of the phases, and bright-light or fluorescence photographs of the TRDP. When the difference in viscosities between the two phases was large (> approximately 0.73 mPa·s), the phase with the larger viscosity formed an inner phase regardless of the volume ratios, whereas when the difference was small (< approximately 0.42 mPa·s), the phase with the larger volume formed an inner phase. The TRDP using a water–surfactant mixed solution was also investigated in capillary chromatography based on TRDP. View full abstractDownload PDF (1985K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1985K)
Notes
-
SARENQIQIGE, Akihiro MAEDA, Kazuhisa YOSHIMURAArticle type: Notes
2014Volume 30Issue 10 Pages 1013-1017
Published: October 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA sensitive, simple and low-cost determination method for the total iron concentration in boiler water systems of power generation plants was developed by solid phase spectrometry (SPS) using 2,4,6-tris(2-pyridyl)-1,3,5-triazine (TPTZ) as a coloring agent. The reagents and 0.08 cm3 of a cation exchanger were added to a 50-cm3 boiler water sample, then mixed for 30 min to adsorb/concentrate the produced Fe(TPTZ)22+ colored complex on the solid beads, resulting in a 625 times concentration of the target analyte without any other procedure. The detection limit of 0.1 μg dm−3 was obtained, and the optimum conditions for the digestion procedure and color developing reaction was investigated and reported. According to the application of this method to real samples, the present SPS method is the best one because of the shorter analysis time, simpler operation and use of very low-cost equipment compared to the conventional methods, such as TPTZ solution spectrophotometric method after a 16 times concentration, ICP-MS and AAS. View full abstractDownload PDF (1066K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1066K) -
Kamila KOLACINSKA, Robert KONCKIArticle type: Notes
2014Volume 30Issue 10 Pages 1019-1022
Published: October 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis paper presents a simple, rapid and effective method for ammonia determination in a flow analysis regime using Nessler’s reagent. The proposed modification of the common flow procedure results in the total elimination of the problem of precipitate deposition inside the flow manifold. The improved procedure has been adapted to a flow analysis system based on microsolenoid pumps combined with a dedicated optoelectronic detector fabricated specifically for this purpose. This photometric device has been constructed in the form of a compact flow-through cell (70 μL total volume and 1 cm optical pathlength) integrated with 395 nm LED emitter and 405 nm LED-based detector. The presented analytical system is capable of ammonia determination in the submillimolar concentration range with a detection limit below 0.1 mM and high throughput (over 20 injections per hour). View full abstractDownload PDF (3585K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3585K) -
Xing-Zheng WU, Tomohisa KATO, Satoshi TERADAArticle type: Notes
2014Volume 30Issue 10 Pages 1023-1025
Published: October 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCell death and its deregulation characterize numerous human diseases. Here, we report on real-time noninvasive monitoring of UV light-induced cell death by the deflection of a probe beam. UV light of 330 – 370 nm from a high-pressure Hg lamp illuminated cultured HepG2 cells, and at the same time a probe beam from a diode laser was passed through a vicinity of the HepG2 cell. The deflection signal of the probe beam, which was induced by changes of the concentration gradients in processes of the active materials movements across the cell membrane, was monitored. It was found that the deflection signals changed greatly after UV illumination, suggesting that the materials movements across the cell membrane were greatly affected by the UV illumination. After UV illumination of about 5400 – 7400 s at a light power of 0.028 W/cm2, the deflection signals became little changed with time, suggesting that the living cells had been killed by the UV illumination. This conclusion agreed well with cell viability determinations of the traditional trypan blue method.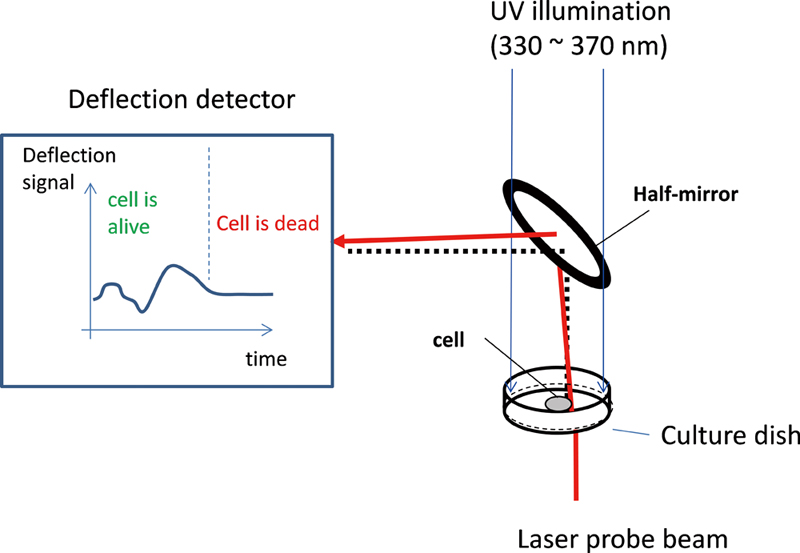 View full abstractDownload PDF (2579K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2579K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2014Volume 30Issue 10 Pages 1027
Published: October 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2578K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|