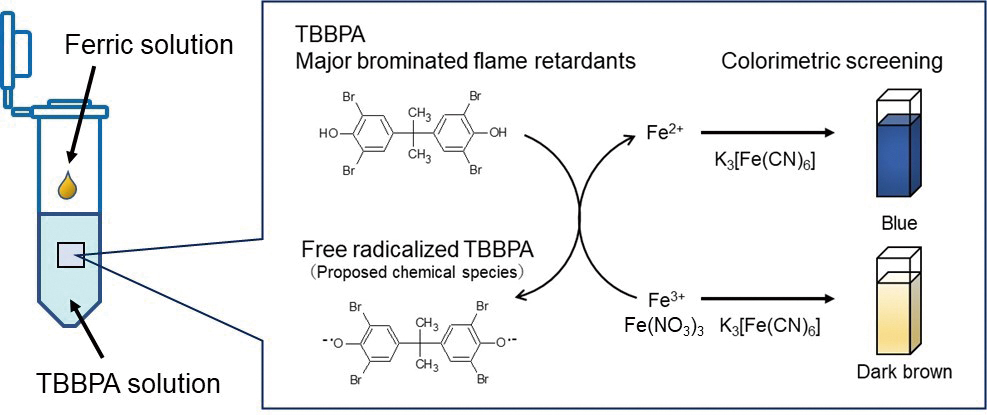
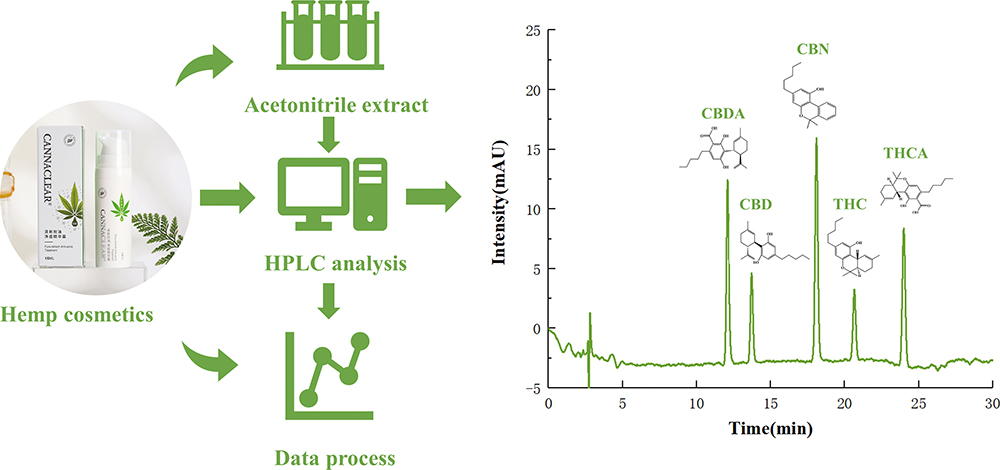
Current issue
Displaying 1-32 of 32 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1653-1654
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Download PDF (163K)
Reviews
-
Article type: Reviews
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1655-1664
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: May 21, 2021Download PDF (320K) -
Article type: Reviews
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1665-1673
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: July 23, 2021Download PDF (888K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1675-1680
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: November 06, 2020Download PDF (625K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1681-1685
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: April 23, 2021Download PDF (320K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1687-1693
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: May 21, 2021Download PDF (1177K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1695-1700
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: May 21, 2021Download PDF (2740K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1701-1706
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: May 28, 2021Download PDF (656K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1707-1712
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: June 04, 2021Download PDF (385K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1713-1718
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: June 11, 2021Download PDF (441K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1719-1725
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: June 18, 2021Download PDF (437K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1727-1733
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: June 18, 2021Download PDF (622K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1735-1740
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: June 18, 2021Download PDF (165K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1741-1748
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: June 25, 2021Download PDF (1017K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1749-1755
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: July 02, 2021Download PDF (1580K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1757-1763
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: July 02, 2021Download PDF (248K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1765-1769
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: July 09, 2021Download PDF (771K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1771-1774
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: July 09, 2021Download PDF (122K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1775-1781
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: July 16, 2021Download PDF (257K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1783-1787
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: July 16, 2021Download PDF (427K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1789-1794
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: July 23, 2021Download PDF (535K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1795-1802
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: August 06, 2021Download PDF (704K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1803-1810
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Download PDF (838K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1811-1814
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Download PDF (235K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1815-1819
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: June 18, 2021Download PDF (305K) -
Article type: Notes
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1821-1824
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: June 18, 2021Download PDF (234K) -
Article type: Notes
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1825-1828
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: July 02, 2021Download PDF (434K) -
Article type: Notes
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1829-1833
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: July 16, 2021Download PDF (490K) -
Article type: Notes
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1835-1837
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: July 16, 2021Download PDF (922K) -
Article type: Notes
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1839-1841
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: July 16, 2021Download PDF (221K) -
Article type: Notes
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1843-1846
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Advance online publication: July 23, 2021Download PDF (236K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2021Volume 37Issue 12 Pages 1847
Published: December 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2021
Download PDF (194K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|