Abstract
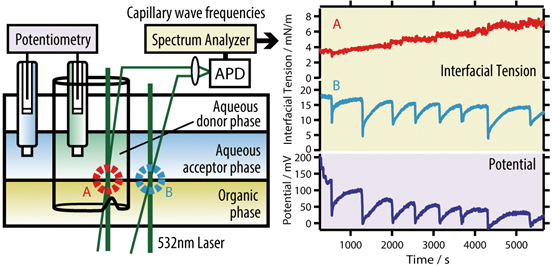
The time courses of the interfacial tension of two interfaces and the electric potential between the donor/membrane/acceptor phases were simultaneously examined using a quasi-elastic laser scattering method, which monitors capillary wave frequencies. An aqueous solution of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), a nitrobenzene solution of tetrabutylammonium tetraphenylborate (TPATPB), and an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (NaCl) were used as the surfactant in the aqueous donor phase, the hydrophobic electrolyte in the organic membrane phase, and the electrolyte in the aqueous acceptor phase, respectively. It has been found that the oscillatory behavior of the potential is synchronized with that of the interface tension at the membrane/acceptor interface, which is caused by the feeding and the following rapid adsorption of CTA+ surfactants to it due to the Marangoni effect. The dependence of the interfacial tension on a co-surfactant, 1-butanol, and the electrolyte, NaCl, was also examined in order to clarify the relationship among the interval and the amplitude in the oscillatory electric potential behavior.