All issues

Volume 30, Issue 4
Displaying 1-15 of 15 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Rapid Communications
-
Shogo OSHIMA, Tomonori NOMOTO, Taro TOYOTA, Masanori FUJINAMIArticle type: Rapid Communications
2014 Volume 30 Issue 4 Pages 441-444
Published: April 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe surface tension gradients in the front and rear sides of a 1-hexanol droplet exhibiting self-propelled motion were compared by a time-resolved quasi-elastic laser scattering method. The velocity of the alcohol droplet strongly correlated to the difference of the inverse of the recovery distances of the surface tensions between the front and rear sides. This result indicates that the spontaneous alcohol droplet motion is governed by an imbalance in the Marangoni convection flow, induced by an asymmetric surface tension distribution. View full abstractDownload PDF (3703K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3703K)
Original Papers
-
Taiki MATSUI, Totaro IMASAKAArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 4 Pages 445-449
Published: April 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTo enhance sensitivity in multiphoton ionization/time-of-flight mass spectrometry, the sample, in the form of an effusive molecular flow, was introduced at a small angle relative to the laser beam. This approach enlarged the volume of interaction between the sample and the laser beam, thus increasing the number of ions formed by multiphoton ionization. The sensitivity obtained using this technique was compared with that obtained using a previous method based on the off-axis sample introduction technique with detection limits for organic hydrocarbons at the subfemtogram level. The detection limit was examined for dioxins and an improvement of 2.5 ± 0.4 fold was found. The technique developed herein is applicable for practical ultratrace analysis of persistent organic pollutants. View full abstractDownload PDF (1975K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1975K) -
Mi-Sun HA, Hyunjung SEO, Dong-Ho BAE, Woon-Seok YEOArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 4 Pages 451-455
Published: April 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis paper describes a new, simple, and sensitive method for detecting two fluoroquinolones: enrofloxacin and its metabolite ciprofloxacin, which are widely used as drugs for humans and animals. We utilized gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (LDI-TOF) mass spectrometry (MS) with a matrix-free format. An antibody for the drug was immobilized on a chip based on self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) on gold, and AuNPs were decorated with the drug along with a large excess of small molecules, called amplification tags (Am-tags). In this strategy, target drugs in solution bound to the antibody on the chip compete with the AuNP-immobilized drugs. The presence of targets was verified by the amplified LDI-TOF MS signals of Am-tags on AuNPs.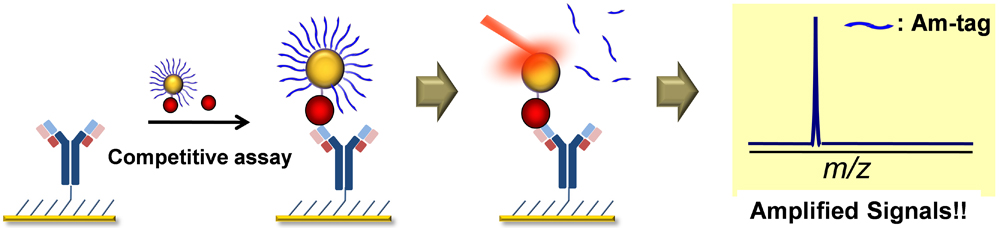 View full abstractDownload PDF (671K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (671K) -
Jun FAN, Ruiping LI, Pingping XU, Junwei DI, Yifeng TU, Jilin YANArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 4 Pages 457-462
Published: April 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this work, we synthesized a trypsin-stabilized fluorescent gold nanocluster. It was found that sulfide interacted with the nanocluster, which could result in significant fluorescence quenching. With this quenching effect, a fluorescence sulfide sensor was developed. This sensor responded linearly to sulfide in the range of 50 nM to 8 μM, and was capable of detecting sulfide as low as 5.5 nM. This provided a facile and sensitive scheme for sulfide analysis; the mechanism of the sensor was also provided. The sensor was then tested for real sample analysis, and good recoveries were obtained. Furthermore, persulfate was found to be effective to remove the quenching of sulfide, and this interaction was adopted for an indirect analysis of persulfate. View full abstractDownload PDF (3988K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3988K) -
Tomonori NOMOTO, Kazuma GOTO, Koyo UCHIYAMA, Taro TOYOTA, Masanori FUJ ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 4 Pages 463-469
Published: April 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe time courses of the interfacial tension of two interfaces and the electric potential between the donor/membrane/acceptor phases were simultaneously examined using a quasi-elastic laser scattering method, which monitors capillary wave frequencies. An aqueous solution of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), a nitrobenzene solution of tetrabutylammonium tetraphenylborate (TPATPB), and an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (NaCl) were used as the surfactant in the aqueous donor phase, the hydrophobic electrolyte in the organic membrane phase, and the electrolyte in the aqueous acceptor phase, respectively. It has been found that the oscillatory behavior of the potential is synchronized with that of the interface tension at the membrane/acceptor interface, which is caused by the feeding and the following rapid adsorption of CTA+ surfactants to it due to the Marangoni effect. The dependence of the interfacial tension on a co-surfactant, 1-butanol, and the electrolyte, NaCl, was also examined in order to clarify the relationship among the interval and the amplitude in the oscillatory electric potential behavior.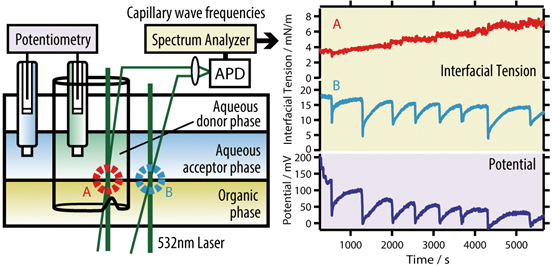 View full abstractDownload PDF (707K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (707K) -
Nobuyasu ITOH, Taichi YAMAZAKI, Ayako SATO, Masahiko NUMATA, Akiko TAK ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 4 Pages 471-476
Published: April 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe examined the reliability of a certified reference material (CRM) for urea (NMIJ CRM 6006-a) as a calibrant for N, C, and H in elemental analyzers. Only the N content for this CRM is provided as an indicative value. To estimate the C and H contents of the urea CRM, we took into account the purity of the urea and the presence of other identified impurities. When we examined the use of various masses of the calibrant (0.2 to 2 mg), we unexpectedly observed low signal intensities for small masses of H and N, but these plateaued at about 2 mg. We therefore analyzed four amino acid CRMs and four food CRMs on a 2-mg scale with the urea CRM as the calibrant. For the amino acid CRMs, the differences in the analytical and theoretical contents (≤0.0026 kg/kg) were acceptable with good repeatability (≤0.0013 kg/kg in standard deviation; n = 4). For food CRMs, comparable repeatabilities to those obtained with amino acid CRMs (≤0.0025 kg/kg in standard deviation; n = 4) were obtained. The urea CRM can therefore be used as a reliable calibrant for C, H, and N in an elemental analyzer. View full abstractDownload PDF (1061K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1061K) -
Hiroto MASUNAGA, Yuji HIGO, Mizuo ISHII, Noboru MARUYAMA, Shigeo YAMAZ ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 4 Pages 477-482
Published: April 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis paper reports on a new suppressor that can be used in the ion chromatography (IC) of inorganic cations. The space in which the electrode is set on both sides of the device is separated into three cells using anion- and cation-exchange membranes. Each of the cells is packed with either an anion- or cation-exchange resin. Anions in the eluent and injected sample are removed by electrical regeneration, based on the electrokinetic phenomenon on both the surface of the ion-exchange resins and the membranes. The electrical conductivity of the suppressed eluent reaches a level similar to that of ultrapure water; therefore, a cation detection limit of sub-ppb order is achieved in IC using the device as a suppressor. View full abstractDownload PDF (1127K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1127K) -
Yuki YAGI, Kazuaki KAKEHI, Takao HAYAKAWA, Shigeo SUZUKIArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 4 Pages 483-488
Published: April 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe evaluated the performance of a commercial microchip electrophoresis instrument (LabChip® GXII) for the evaluation of change of degradation species of therapeutic antibodies in stability testing. This system requires a sample volume of only 5 μg, and indicates fine resolution of size variant species such as light chain, heavy chain, non-glycosylated heavy chain and various degradation species. Precision and accuracy were high; the intermediate precision of 18 determinations was only 2.1% or less as RSD and recoveries ranged from 97.8 to 103.0% for major species as heavy chain, light chain and intact molecule of a therapeutic antibody. The applicability of this method was demonstrated by applying the method for the analysis of heat-degraded products of three pharmaceutical antibodies. Though some fragment peaks commonly appeared and increased according to temperature regardless of the source of preparations, one of them indicated specific peaks implying the cleavage of the peptide chain of the heavy chain. We also compared the performance of the method with those using conventional capillary-based SDS electrophoresis. Although the absolute purity values expressed as peak area % were different for the two methods, probably due to the difference in the detection methods, similar quality profiles were obtained within 40 s by microchip-based SDS electrophoresis. In addition, the degradation manner of three marketed antibodies depending on temperature was almost the same for the two methods. At the first stage in the development of manufacturing antibody pharmaceuticals, various factors including cell selection, cell cultivation, and formulation development should be evaluated using limited sample amounts. The stability testing using microchip-based electrophoresis seems suitable for these purposes.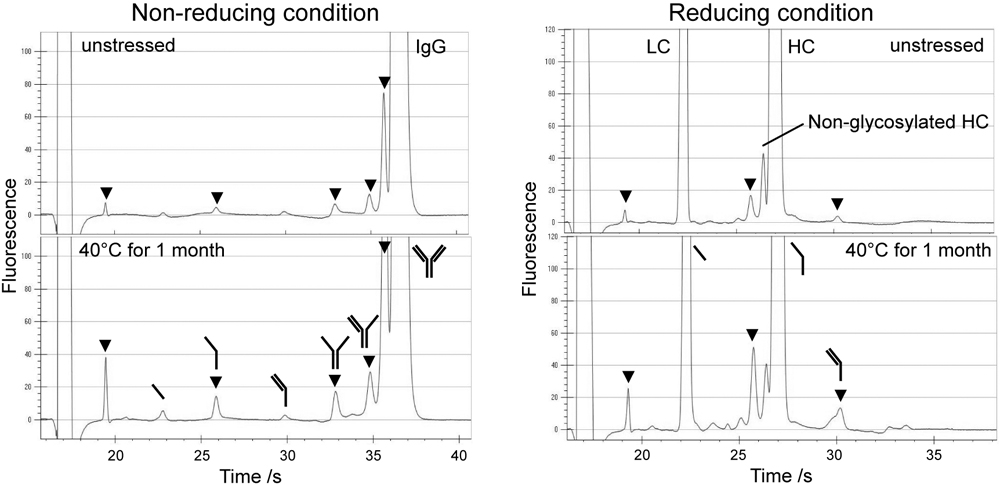 View full abstractDownload PDF (3764K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3764K) -
Xiu-Fang YAN, Hai-Long WU, Xiang-Dong QING, Yan-Mei SUN, Ru-Qin YUArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 4 Pages 489-494
Published: April 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this work, a simple and practicable method that combines excitation-emission matrix (EEMs) fluorescence with a second-order calibration method based on parallel factor analysis-alternative least-squares (PARAFAC-ALS) algorithm was developed for the direct interference-free determination of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) in two real systems, coconut water (CW) and coconut milk (CM). Although the excitation and emission profiles of IAA heavily overlapped with that of unknown interferents in the complex real systems, the actual contents and satisfactory recoveries were still obtained successfully. The contents of IAA in CW and CM were 10.8 ± 0.3 and 4.9 ± 0.2 μg mL−1, respectively, which were consistent with those reported by LC-MS/MS assays in the reference material. The average spike recoveries of IAA in the validation set based on CW and CM were 102.1 ± 3.2 and 98.0 ± 1.9%, respectively. In addition, routine experiments were performed for establishing the validity of the assay to internationally accepted criteria.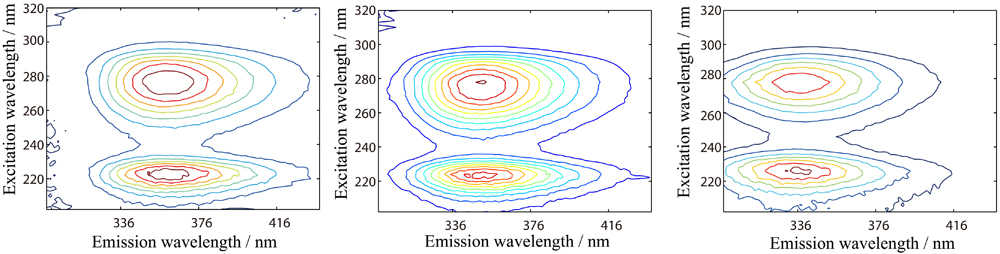 View full abstractDownload PDF (3173K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3173K) -
Suqin HAN, Xia LI, Bei WEIArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 4 Pages 495-500
Published: April 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe report on a simple and sensitive chemiluminescence (CL) method to determine nitrazepam. This method is based on the fact that rhodamine 6G (Rh6G) enhanced the weak CL emission of the reaction of hexacyanoferrate with nitrazepam, and that it was further enhanced by silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). The effects of the concentrations of K3Fe(CN)6, Rh6G, AgNPs and NaOH on the CL reaction were investigated. Under the optimum conditions, the CL intensity was proportional to the concentration of nitrazepam in the range from 1.0 nM to 10.0 μM. The detection limit (3σ) was at 0.1 nM. The relative standard deviation was 2.1% (at a 0.1 μM concentration and for n = 11). The method was successfully applied to the determination of nitrazepam in Coca-Cola beverage, urine and plasma, and the recovery was 98 – 103%. We also considered the possible CL reaction mechanism.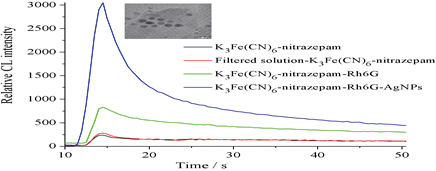 View full abstractDownload PDF (767K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (767K) -
Nidhi CHAUHAN, PREETI, PINKY, C. S. PUNDIRArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 4 Pages 501-506
Published: April 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialUricase from Candida species was immobilized covalently onto the inner wall of a plasticized polyvinyl chloride (PVC/plastic) vial through glutraldehyde coupling with a 65.23% retention of its initial activity and a conjugation yield of 0.37 mg/cm2. The vial-bound enzyme showed the optimum activity at pH 7.2, when incubated at 45°C for 5 min. There was a linear relationship between the immobilized uricase activity and the uric acid concentration in the range of 0.01 to 1.2 mM with an apparent Km for uric acid of 0.17 mM. The vial-bound enzyme was employed for an enzymic colorimetric determination of uric acid in serum and urine. The minimum detection limit of the method was 0.01 mM. The analytical recoveries of added uric acid in serum (10 and 20 mM) were 98.0 and 96.5%, respectively. Within and between assays, the coefficients of variation (CVs) for urate in sera determinations were 5.6 and 4.7%, respectively. A good correlation (r = 0.997) was obtained between the serum uric acid values by the standard enzymic colorimetric method using free enzyme and the present method. The vial was reused 200-times over a period of 4 months, when stored at 4°C. View full abstractDownload PDF (585K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (585K) -
Benjaporn TOSSANAITADA, Takashi MASADOME, Toshihiko IMATOArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 4 Pages 507-511
Published: April 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA sequential injection analysis (SIA) system for the determination of SCN− ion using a microfluidic polymer chip with an embedded SCN− ion-selective electrode (SCN−-ISE) as a detector was developed. Under the optimal flow conditions of the SIA system, the SCN−-ISE showed a good linear relationship between peak heights and logarithmic concentrations of SCN− ion with a Nernstian slope of 59.4 ± 3.8 mV decade−1 in a concentration range from 1.0 × 10−5 to 1.0 × 10−1 mol dm−3. Sample throughput of the present system for the determination of SCN− ion was approximately 12 samples h−1. The proposed SIA system was applied to the determination of the level of SCN− ion in human saliva samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (485K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (485K)
Notes
-
Kojiro SHIMOJO, Ayaka NAKAI, Hiroyuki OKAMURA, Takumi SAITO, Akira OHA ...Article type: Notes
2014 Volume 30 Issue 4 Pages 513-517
Published: April 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe report on the acid dissociation constants (Ka) of diglycolamic acid-type ligands together with comprehensive data on the extraction performance of N,N-dioctyldiglycolamic acid (DODGAA) for 54 metal ions. The pKa of the diglycolamic acid framework was determined to be 3.54 ± 0.03 in water (0.1 M LiCl, 25°C) by potentiometric titration, indicating that DODGAA is strongly acidic compared with acetic acid. DODGAA can quantitatively transfer various metal ions among the 54 metal ions through a proton-exchange reaction, and provides excellent extraction performance and separation ability for rare-earth metal ions, In(III), Fe(III), Hg(II), and Pb(II) among the 54 metal ions. View full abstractDownload PDF (444K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (444K) -
Hiroya MURAKAMI, Rieko KAWAMURA, Takayoshi SAKAKIBARA, Yukihiro ESAKA, ...Article type: Notes
2014 Volume 30 Issue 4 Pages 519-522
Published: April 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe preparation and application of a stop and go extraction tip (StageTip) used for pre-purification of sample solutions for LC-MS/MS analysis of DNA adducts was simplified and improved to increase throughput while maintaining high adduct selectivity. It was demonstrated that the StageTip composed of two sheets of a poly(styrene-divinylbenzene) copolymer disk could be easily prepared and proved useful for selective extraction of trace amounts of DNA adducts from a sample solution containing a great quantity of normal deoxynucleosides. View full abstractDownload PDF (620K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (620K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2014 Volume 30 Issue 4 Pages 523
Published: April 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2490K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|