Abstract
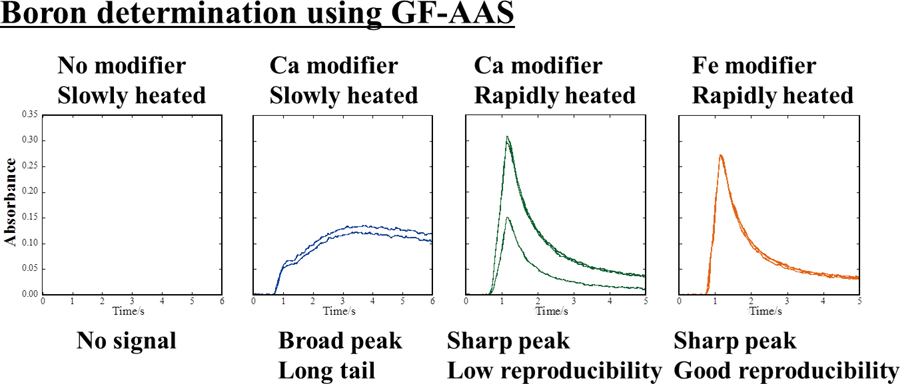
The measurement conditions for determining boron using graphite furnace–atomic absorption spectrometry (GF-AAS) were investigated. Differences in the boron absorbance profiles were found using three different commercially available GF-AAS instruments when the graphite atomizers in them were not tuned. The boron absorbances found with and without adjusting the graphite atomizers suggested that achieving an adequate absorbance for the determination of boron requires a sharp temperature profile that overshoots the target temperature during the atomization process. Chemical modifiers that could improve the boron absorbance without the need for using coating agents were tested. Calcium carbonate improved the boron absorbance but did not suppress variability in the peak height. Improvement of boron absorbance was comparatively less using iron nitrate or copper nitrate than using calcium carbonate, but variability in the peak height was clearly suppressed using iron nitrate or copper nitrate. The limit of detection was 0.0026 mg L−1 when iron nitrate was used. It appears that iron nitrate is a useful new chemical modifier for the quick and simple determination of boron using GF-AAS.