All issues

Volume 31, Issue 5
Displaying 1-17 of 17 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Call for Papers
-
Article type: Call for Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 343
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (190K)
Original Papers
-
Ryo MACHIDA, Takashi NAKAZAWA, Naoki FURUTAArticle type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 345-355
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTo elucidate mechanisms of elemental fractionation that are observed in laser ablation–inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, the relative intensities of 34 elements, each normalized by a Ca internal standard, were measured every minute during a 10-min laser ablation of an NIST 610 glass standard. Temporal changes in the fractionation index (FI) were obtained by dividing the relative intensity of every minute by that of the first minute. The particles generated by laser ablation were collected on a filter every minute, and they were observed using scanning electron microscopy to investigate changes in the large size of particles. Large variations among the large size of particles were observed using single-site mode and under 1.0 mm defocus conditions. The 34 measured elements were classified into two groups, depending on their observed FI variation. The FI variation was rationalized by elemental behavior due to changes in the large size of ablated particles introduced into the ICP. View full abstractDownload PDF (2829K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2829K) -
Yuhei YAMAMOTO, Toshihiro SHIRASAKI, Akira YONETANI, Shoji IMAIArticle type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 357-364
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe measurement conditions for determining boron using graphite furnace–atomic absorption spectrometry (GF-AAS) were investigated. Differences in the boron absorbance profiles were found using three different commercially available GF-AAS instruments when the graphite atomizers in them were not tuned. The boron absorbances found with and without adjusting the graphite atomizers suggested that achieving an adequate absorbance for the determination of boron requires a sharp temperature profile that overshoots the target temperature during the atomization process. Chemical modifiers that could improve the boron absorbance without the need for using coating agents were tested. Calcium carbonate improved the boron absorbance but did not suppress variability in the peak height. Improvement of boron absorbance was comparatively less using iron nitrate or copper nitrate than using calcium carbonate, but variability in the peak height was clearly suppressed using iron nitrate or copper nitrate. The limit of detection was 0.0026 mg L−1 when iron nitrate was used. It appears that iron nitrate is a useful new chemical modifier for the quick and simple determination of boron using GF-AAS.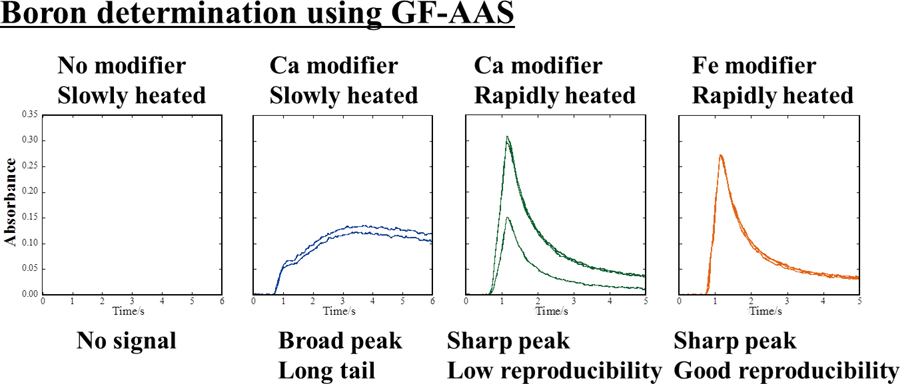 View full abstractDownload PDF (987K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (987K) -
Napaporn YOUNGVISES, Porapichcha THANURAK, Thanatcha CHAIDA, Jaroon JU ...Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 365-370
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMicrofluidics minimize the amounts of reagents and generate less waste. While microdevices are commonly single-sided, producing a substrate with microchannels on multiple surfaces would increase their usefulness. Herein, a polymethymethacrylate substrate incorporating microchannel structures on two sides was sandwiched between two polydimethylsiloxane sheets to create a multi-analysis device, which was used for the spectrophotometric analysis of the ferrous ion (Fe2+) and the ferric ion (Fe3+), by utilizing colorimetric detection. To monitor the signals from both channel networks, dual optical sensors were integrated into the system. The linear ranges for Fe2+ and Fe3+ analyses were 0.1 – 20 mg L−1 (R2 = 0.9988) and 1.0 – 40 mg L−1 (R2 = 0.9974), respectively. The detection limits for Fe2+ and Fe3+ were 0.1 and 0.5 mg L−1, respectively. The percent recoveries of Fe2+ and Fe3+ were 93.5 – 104.3 with an RSD < 8%. The microdevice demonstrated capabilities for simultaneous analysis, low waste generation (7.2 mL h−1), and high sample throughput (180 h−1), making it ideal for greener analytical chemistry applications. View full abstractDownload PDF (2969K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2969K) -
Yukio YOKOYAMA, Takeru FUJISHIMA, Kazuki KUROTAArticle type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 371-376
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis paper presents a new HPLC technique for the determination of biogenic cations such as amino acids and nucleobases, using a weak-acid cation-exchange column. Fourteen analytes, five amino acids and seven bases in addition to creatinine and creatine, were separated in 12 min by means of a two-liquid gradient elution with UV detection. The newly released column packed with a carboxy-functionalized polymethacrylate resin could give excellent selectivity to the organic cations of interest, although such a column is in general suitable for the separation of inorganic common cations. The chromatographic intra-day repeatability was very good with RSDs less than 0.4%, and the quantitation precision based on peak area intensities was also good with RSDs less than 5% for all analytes. The linear calibration lines for quantitation ranged between 5 and 500 μM on 20-μL injections with R2 more than 0.9990. Since the method could provide concentration data of urinary creatinine and some metabolites simultaneously, for example, the urinary phenylalanine/creatinine ratios for phenylketonuria of inborn errors of metabolism were simply determined through one chromatographic run. The ratios for patients were significantly higher than those for controls. We found that the new weak-acid cation-exchange column was suitable for the separation of organic cations as well as inorganic cations. View full abstractDownload PDF (622K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (622K) -
Yong MENG, Jin-Feng LIU, Shi-Zhong YANG, Ru-Qiang YE, Bo-Zhong MUArticle type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 377-382
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA highly sensitive and selective high-performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) method has been developed for the determination of microbial lipopeptides of fluorescent derivatization with 1-bromoacetylpyrene to overcome the limitations of trace detection of lipopeptides in aqueous solutions. The derivatization of lipopeptides with 1-bromoacetylpyrene was conducted at 60°C for 20 min under catalysis of triethylamine. The resulting derivative products were separated by HPLC and determined by a fluorescence detector. Each homolog of lipopeptides in samples was identified by HPLC-MS and the detection limit after derivatization in an aqueous solution was 2.5 μg/mL (S/N = 3). The calibration curve for lipopeptides was linear in the concentration range of 0.250 – 4.00 mg/mL. This method has adequate sensitivity and selectivity for microdetection of lipopeptides in aqueous solutions in mild reaction conditions, which allows this method to be used in the determination of trace lipopeptides in environmental samples and complex samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (961K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (961K) -
Georgia GIAKISIKLI, Alejandro AYALA QUEZADA, Junpei TANAKA, Aristidis ...Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 383-389
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA fully automated sequential injection column preconcentration method for the on-line determination of trace vanadium, cadmium and lead in urine samples was successfully developed, utilizing electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry (ETAAS). Polyamino-polycarboxylic acid chelating resin (Nobias chelate PA-1) packed into a handmade minicolumn was used as a sorbent material. Effective on-line retention of chelate complexes of analytes was achieved at pH 6.0, while the highest elution effectiveness was observed with 1.0 mol L−1 HNO3 in the reverse phase. Several analytical parameters, like the sample acidity, concentration and volume of the eluent as well as the loading/elution flow rates, have been studied, regarding the efficiency of the method, providing appropriate conditions for the analysis of real samples. For a 4.5 mL sample volume, the sampling frequency was 27 h−1. The detection limits were found to be 3.0, 0.06 and 2.0 ng L−1 for V(V), Cd(II) and Pb(II), respectively, with the relative standard deviations ranging between 1.9 – 3.7%. The accuracy of the proposed method was evaluated by analyzing a certified reference material (SeronormTM trace elements urine) and spiked urine samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (767K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (767K) -
Sami M. Abdel AZEEM, Hassan A. HANAFI, M. F. EL-SHAHATArticle type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 391-397
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA fast and sensitive on-line procedure for the determination of zinc in water and biological samples was developed. Zinc was preconcentrated in a mini-column packed with polyurethane foam (PUF) chemically modified with zincon via –N=N– bonding. The optimal conditions for preconcentration were pH 8.5 and sample flow rate of 4.0 mL min−1. Quantitative desorption of Zn(II) was obtained by 0.1 mol L−1 hydrochloric acid and subsequent spectrophotmetric determination using 4-(2-pyridylazo)-resorcinol at 498 nm. The obtained detection limit was found to be 3.0 ng mL−1, precision (RSD) was 4.8 and 6.7% at 20 and 110 ng mL−1, respectively, for 60 s preconcentration time and enrichment factor was 31. The linearity range was from 10 to 120 ng mL−1 and maximum sample throughput was 20 h−1. Finally, the method was successfully applied to the determination of zinc in tap water, Nile River water and human urine samples with RSD in the range of 1.1 – 8.3%. View full abstractDownload PDF (648K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (648K) -
Zufei FENG, Yuehong XU, Shuguang WEI, Bao ZHANG, Fanglin GUAN, Shengbi ...Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 399-406
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA magnetic carbon nanomaterial for Fe3O4-modified hydroxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes (Fe3O4-MWCNTs-OH) was prepared by the aggregating effect of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on MWCNTs-OH, and this material was combined with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)/photodiode array detector (PAD) to determine strychnine in human serum samples. Some important parameters that could influence the extraction efficiency of strychnine were optimized, including the extraction time, amounts of Fe3O4-MWCNTs-OH, pH of sample solution, desorption solvent and desorption time. Under optimal conditions, the recoveries of spiked serum samples were between 98.3 and 102.7%, and the relative standard deviations (RSDs) ranged from 0.9 to 5.3%. The correlation coefficient was 0.9997. The LODs and LOQs of strychnine were 6.2 and 20.5 ng mL−1, at signal-to-noise ratios of 3 and 10, respectively. These experimental results showed that the proposed method is feasible for the analysis of strychnine in serum samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (1608K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1608K) -
Elham GHASEMI, Massoud KAYKHAIIArticle type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 407-411
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA fast, simple, and economical method was developed for simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of uranium(VI) and vanadium(V) in water samples based on micro cloud point extraction (MCPE) at room temperature. This is the first report on the simultaneous extraction and determination of U(VI) and V(V). In this method, Triton X114 was employed as a non-ionic surfactant for the cloud point procedure and 4-(2-pyridylazo) resorcinol (PAR) was used as the chelating agent for both analytes. To reach the cloud point at room temperature, the MCPE procedure was carried out in brine. The factors influencing the extraction efficiency were investigated and optimized. Under the optimized condition, the linear calibration curve was found to be in the concentration range between100 – 750 and 50 – 600 μg L−1 for U(VI) and V(V), respectively, with a limit of detection of 17.03 μg L−1 (U) and 5.51 μg L−1 (V). Total analysis time including microextraction was less than 5 min.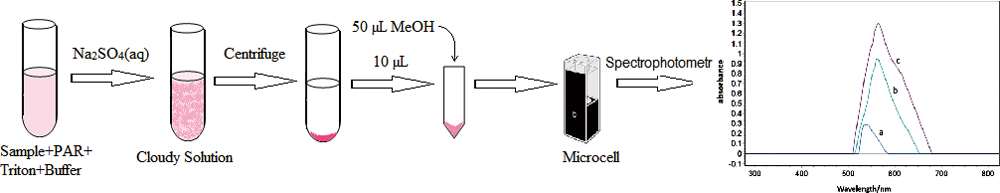 View full abstractDownload PDF (994K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (994K) -
Qiao-Jing LI, Yong-Sheng LI, Xiu-Feng GAOArticle type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 413-419
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialBased on fluorescence capillary analysis technology, a method for quantitating lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity in a micro-volume sample was developed. Sample and reagent consumptions were merely 2 and 16 μL per time, respectively. The optimized test conditions were as follows. The reaction reagent consisted of 0.10 M phosphate buffer (pH 6.5), 0.30 mM NADH and 1.20 mM pyruvate. NADH standard was prepared with a phosphate buffer of pH 8.0, and its linear response was controlled in 0.05 – 0.30 mM. LDH standards containing 2.0 mM PEG could exhibit long-term stability. Under the optimized conditions, a linear response for LDH from 50 to 1200 U L−1 and a detection limit of 31 U L−1 were obtained with good precision (RSD: 2.1 – 2.2%, n = 10) and better recovery of 96 – 105%. The method’s characteristics was high sensitivity, low consumptions, simple operations, good precision and reliability, lending itself to the miniaturization of fluorophotometer which transformed into a bedside instrument in the hospital. View full abstractDownload PDF (2289K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2289K) -
Hongbo LIU, Mei YUAN, Xiaolan YANG, Xiaolei HU, Juan LIAO, Jizheng DAN ...Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 421-427
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialSpectrophotometric-dual-enzyme-simultaneous-assay (SDESA) for enzyme-linked-immunosorbent-assay (ELISA) of two components in one well is a patented platform when a special pair of labels is accessible. With microplate readers, alkaline phosphatase on 4-nitro-1-naphthylphosphate (4NNPP) served as label A; Pseudomonas aeruginosa arylsulfatase (PAAS) and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) on their substrates derived from 4-nitrophenol/analogue served as candidate label B, and were compared for SDESA with an engineered alkaline phosphatase of Eschrichia coli (ECAP). For SDESA, the interference from overlapped absorbance was corrected based on linear additivity of absorbance to derive initial rates reflected by absorbance change at 450 nm for ECAP and at 405 nm for PAAS or AChE, after the correction of spontaneous hydrolysis. For SDESA with ECAP, AChE already had sufficient activity in an optimized buffer; PAAS was more favorable for substrate stability and product absorbance except for lower activity. Therefore, PAAS engineered for sufficient activity plus alkaline phosphatase is absorbing for ELISA via SDESA.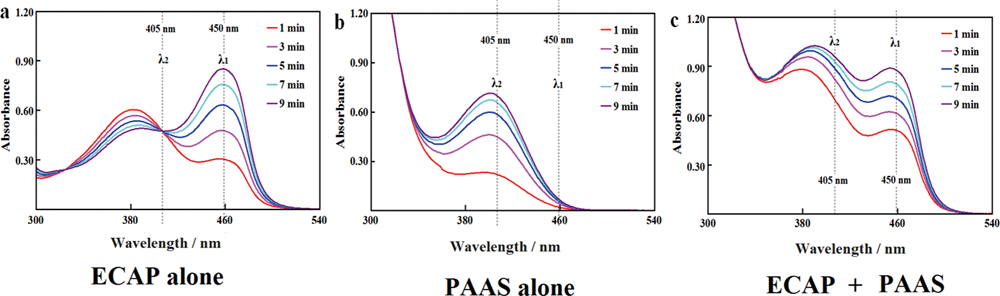 View full abstractDownload PDF (1170K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1170K) -
Xinfei ZHOU, Kunyun HE, Yu WANG, Haitao ZHENG, Shin-ichiro SUYEArticle type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 429-436
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA new composite film-modified electrode was prepared by the electropolymerisation of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) and superconductive carbon black (SCB) on a gold electrode. The PEDOT-SCB/Au electrode exhibited excellent ability towards the electrocatalytic oxidation of ascorbic acid, in terms of a 480 mV shift of the oxidation potential in the negative direction, and a dramatically enhanced oxidation current. Under the optimum conditions, the amperometric detection of ascorbic acid provided a wide linear detection range from 1.0 × 10−7 to 8.0 × 10−4 M, and a detection limit of 5.0 × 10−8 M (S/N = 2) as well as good reproducibility and stability.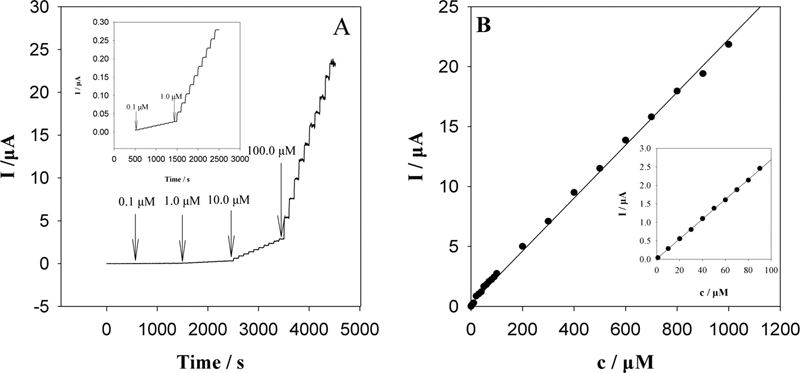 View full abstractDownload PDF (1599K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1599K) -
Masoom R. SIDDIQUI, M. Z. A. RAFIQUEE, Saikh M. WABAIDUR, Zeid A. ALOT ...Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 437-443
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSilver nanoparticle (AgNP) has been synthesized using adrenaline. Adrenaline readily undergoes an autoxidation reaction in an alkaline medium with the dissolved oxygen to form adrenochrome, thus behaving as a mild reducing agent for the dissolved oxygen. This reducing behavior of adrenaline when employed to reduce Ag+ ions yielded a large enhancement in the intensity of absorbance in the visible region. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies have been performed to confirm the surface morphology of AgNPs. Further, the metallic nanoparticles with size greater than 2 nm caused a strong and broad absorption band in the UV-visible spectrum called surface plasmon band or Mie resonance. The formation of AgNPs caused the large enhancement in the absorbance values with λmax at 436 nm through the excitation of the surface plasmon band. The formation of AgNPs was adopted to for the quantitative assessment of adrenaline using spectrophotometry with lower detection limit and higher precision values. View full abstractDownload PDF (771K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (771K)
Notes
-
Shin-ichi KAWANO, Yoshihiro HAYAKAWA, Yuki HASHI, Jin-Ming LINArticle type: Notes
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 445-450
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn on-line pretreatment liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) system was developed for the analysis of chloramphenicol (CAP) in royal jelly. A novel methylcellulose-immobilized restricted access media column with a higher-pressure capability of 60 MPa (MC-ODS HP) was developed for the effective removal of proteins and other compounds in the sample matrix. CAP in a sample solution was extracted in 2 min by the column-switching LC-MS/MS system. The system provides a minimum sample pretreatment along with highly sensitive and reproducible analysis. As a result, the limit of quantitation of CAP was 10 pg/mL (= 0.1 μg/kg royal jelly) and the linear dynamic range was between 10 and 10000 pg/mL (correlation coefficient greater than 0.999). The proposed method meets the requirements of regulations in EU (0.3 μg/kg). The inter-day precision and accuracy of CAP at 100 pg/mL over 3 days were 4.5 and 95.4%, respectively. Compared with the conventional method with a pressure of below 25 MPa, the peak separation in the MRM chromatogram was improved by using smaller particles (1.6 μm) for the analytical ODS column. The LC-MS/MS system with an MC-ODS HP expanded the applicability of the automated pretreatment.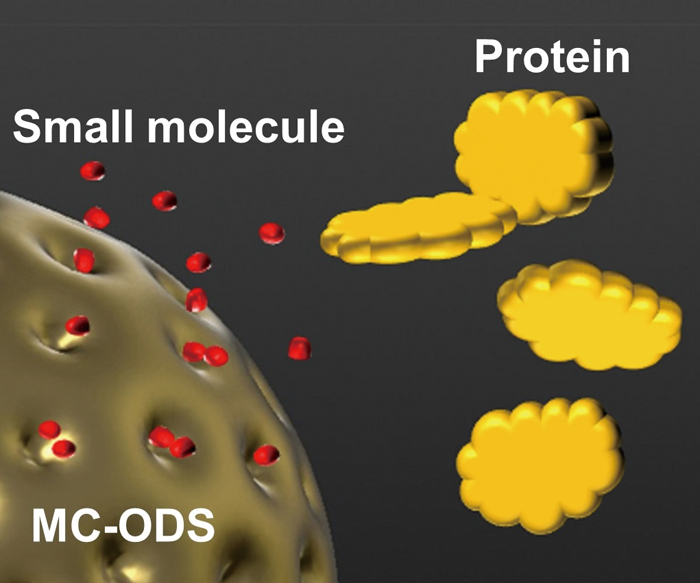 View full abstractDownload PDF (814K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (814K) -
Hikaru YOSHINO, Yuika SAITO, Yasuaki KUMAMOTO, Atushi TAGUCHI, Prabhat ...Article type: Notes
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 451-454
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialTemperature-dependent photodegradation during UV-resonance Raman spectroscopy was investigated. Photodegradation was quantitatively probed by monitoring the temporal evolution of UV-resonance Raman spectra obtained from bacteriochlorophyll (BChl) showing, resonance effect at a 355-nm excitation wavelength. At 80 K, the molecular photodecomposition rate was 5-times lower than that at room temperature. The decomposition rates of BChl were analyzed by the Arrhenius formula, indicating that the mechanism of photodegradation includes a thermal process having an activation energy of 1.4 kJ/mol. View full abstractDownload PDF (1192K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1192K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2015Volume 31Issue 5 Pages 455
Published: May 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2684K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|