Abstract
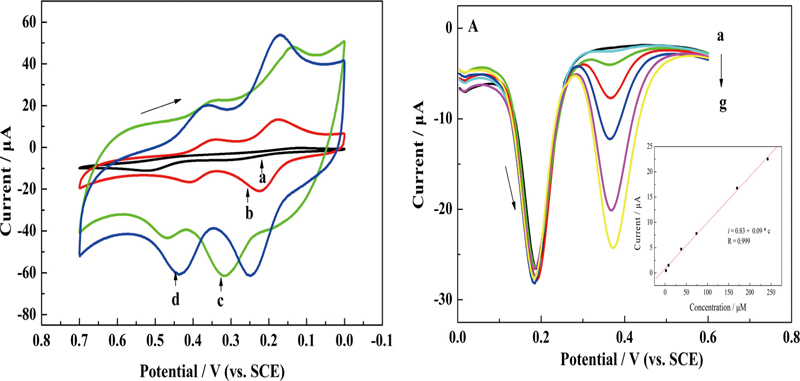
Graphite nanosheets prepared by thermal expansion and successive sonication were utilized for the construction of a multi-walled carbon nanotubes/graphite nanosheets based amperometric sensing platform to simultaneously determine acetaminophen and dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid in physiological conditions. The synergistic effect of multi-walled carbon nanotubes and graphite nanosheets catalyzed the electrooxidation of acetaminophen and dopamine, leading to a remarkable potential difference up to 200 mV. The as-prepared modified electrode exhibited linear responses to acetaminophen and dopamine in the concentration ranges of 2.0 × 10−6 – 2.4 × 10−4 M (R = 0.999) and 2.0 × 10−6 – 2.0 × 10−4 M (R = 0.998), respectively. The detection limits were down to 2.3 × 10−7 M for acetaminophen and 3.5 × 10−7 M for dopamine (S/N = 3). Based on the simple preparation and prominent electrochemical properties, the obtained multi-walled carbon nanotubes/graphite nanosheets modified electrode would be a good candidate for the determination of acetaminophen and dopamine without the interference of ascorbic acid.