Abstract
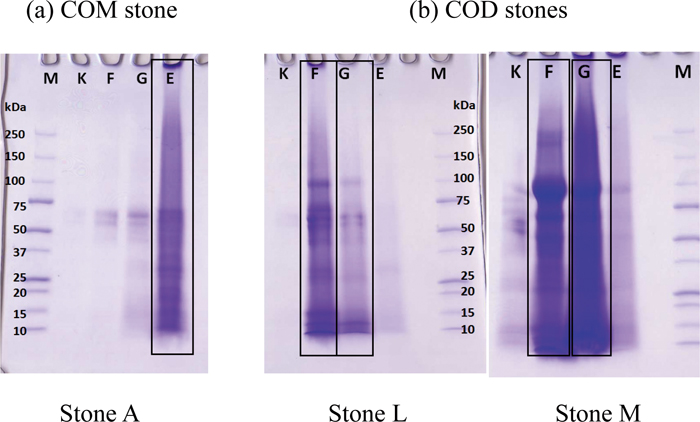
In this study, we performed proteomic analysis following sequential protein extraction on calcium oxalate monohydrate (COM) and calcium oxalate dihydrate (COD) urinary stones to determine the specific matrix proteins according to the crystal components of the stones. After X-ray and IR analysis of 13 urinary stones, matrix proteins were sequentially extracted with KCl, formic acid, guanidine-HCl, and EDTA, before SDS-electrophoresis followed by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). The electrophoretic patterns of the extracted proteins differed from that of COM and COD stones. LC-MS/MS identified 65 proteins, of which many were cellular plasma proteins, and were frequently detected regardless of the crystal components. However, 6 proteins (protein Z, protein S, prothrombin, osteopontin, fatty acid binding protein 5, and ubiquitin) were detected in the final EDTA fractions of COM stones. These proteins are involved in the coagulation process or osteometabolism, and thus the roles they play are of particular interest.