All issues

Volume 31, Issue 9
Displaying 1-14 of 14 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Article type: Guest Editorial
2015Volume 31Issue 9 Pages 865
Published: September 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (119K)
Reviews
-
Kae SATOArticle type: Reviews
2015Volume 31Issue 9 Pages 867-873
Published: September 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMicrofluidic devices enable the miniaturization, integration, automation, and parallelization of chemical and biochemical processes. This new technology also provides opportunity for expansion in the field of cellular pathology. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is a well-known gene-based method to image genetic abnormalities. Development of a FISH microfluidic platform has offered the possibility of automation with significant time and cost reductions, which overcomes many drawbacks of the current protocols. Microfluidic devices are also powerful tools for single-cell analysis. Capturing the circulating tumor cells (CTCs) from blood samples is one of the most promising approaches to enable the early diagnosis of cancer. The microfluidic devices are also useful to isolate rare CTCs at high efficiency and purity. In this review, I outline recent FISH and CTC analyses using microfluidic devices, and describe their applications for the cellular diagnosis of cancers. View full abstractDownload PDF (5715K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (5715K)
Original Papers
-
Yuko UENO, Kazuaki FURUKAWA, Andrew TIN, Hiroki HIBINOArticle type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 9 Pages 875-879
Published: September 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe propose a molecular design for a biomolecular probe to realize an on-chip graphene oxide (GO) aptasensor with enhanced sensitivity. Here, GO works as an excellent acceptor for fluorescence resonance energy transfer. We inserted a rigid double-stranded DNA as a spacer between the GO surface and the aptamer sequence to extend the distance between a fluorescence dye and the GO surface during molecular recognition. We examined the dependence of the sensitivity on the length of the spacer quantitatively by using a 2×2 linear-array aptasensor. We used the modified aptamer with 10 and 30 base pair (bp) double-stranded DNA spacers. The signal with a 30bp-spacer was about twice as strong that with a 10bp-spacer as regards both thrombin and prostate specific antigen detections. The improvement in the sensitivity was supported by a model calculation that estimated the effect of spacer length on fluorescence recovery efficiency. View full abstractDownload PDF (795K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (795K) -
Michiko AKIMARU, Kohei OKUBO, Yuki HIRUTA, Hideko KANAZAWAArticle type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 9 Pages 881-886
Published: September 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe have developed a novel solid-phase extraction (SPE) system utilizing a temperature-responsive polymer hydrogel-modified stationary phase. Aminopropyl silica beads (average diameter, 40 – 64 μm) were coated with poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm)-based thermo-responsive hydrogels. Butyl methacrylate (BMA) and N,N-dimethylaminopropyl acrylamide (DMAPAAm) were used as the hydrophobic and cationic monomers, respectively, and copolymerized with NIPAAm. To evaluate the use of this SPE cartridge for the analysis of drugs and proteins in biological fluids, we studied the separation of phenytoin and theophylline from human serum albumin (HSA) as a model system. The retention of the analytes in an exclusively aqueous eluent could be modulated by changing the temperature and salt content. These results indicated that this temperature-responsive SPE system can be applied to the pretreatment of biological samples for the measurement of serum drug levels. View full abstractDownload PDF (1901K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1901K) -
Takayo MORIUCHI-KAWAKAMI, Minako OBITA, Toshiki TSUJINAKA, Yasuhiko SH ...Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 9 Pages 887-893
Published: September 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialNickel(II) complexes of [14]tetraazaannulene derivatives incorporating aromatic rings into their azaannulene framework were synthesized, and the anion-selectivity of the [14]tetraazaannulene nickel complexes 1 – 4 was evaluated by potentiometric measurements with solvent polymeric membrane electrodes. All of the [14]Tetraazaannulene nickel complexes, except 3, were found to exhibit high selectivity for the I− ion over the SCN− ion, although considerable interference of the ClO4− ion was observed in all 1 – 4 complexes. Concerning the anion-selectivities of 1 and 4, the incorporation of naphthalene rings into the azaannulene framework decreased not only the interference of the ClO4− ion but also the I− ion-selectivity over the SCN− ion. Comparison studies between the dibenzotetraaza[14]annulene nickel complexes 1 – 3 indicated that differences in the attached substituents of the [14]tetraazaannulene nickel complexes greatly influenced the ion-selectivity as ionophores. According to our computational results, the ionophoric properties of [14]tetraazaannulene nickel complexes 1 – 4 were influenced by their electrostatic properties rather than their topological properties. View full abstractDownload PDF (1344K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1344K) -
Tomoko FUKUUCHI, Noriko YAMAOKA, Kiyoko KANEKOArticle type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 9 Pages 895-901
Published: September 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTo evaluate cellular uptake and purine transport, we developed a high-performance liquid chromatography method for intra- and extracellular purine quantification. Our aim was to develop an effective method for simultaneously quantifying the substrate and metabolites with high sensitivity. C18 columns from different manufacturers were tested for simultaneous quantification of 22 different purine bases, nucleosides, and nucleotides. We used a YMC-Triart C18 column. The analysis conditions, including extraction solutions for the cells and cell culture medium, were optimized to achieve good quantification. Linearity, accuracy, determination limits, and recovery were assessed and showed good performance. The developed HPLC method was successfully applied to the qualitative analysis of 22 different intra- and extracellular purines, demonstrating that it is useful for studying the overall pattern of purine metabolism. This method could also be useful for evaluating metabolic dynamics of purines under a variety of stimulatory conditions of culture cells. View full abstractDownload PDF (931K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (931K) -
Liangmian CHEN, Akira KOTANI, Hideki HAKAMATA, Risa TSUTSUMI, Yuzuru H ...Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 9 Pages 903-909
Published: September 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe have proposed an assessment methods to estimate the measurement relative standard deviation (RSD) of chromatographic peaks in quantitative HPLC for herbal medicines by the methodology of ISO 11843 Part 7 (ISO 11843-7:2012), which provides detection limits stochastically. In quantitative HPLC with UV detection (HPLC-UV) of Scutellaria Radix for the determination of baicalin, the measurement RSD of baicalin by ISO 11843-7:2012 stochastically was within a 95% confidence interval of the statistically obtained RSD by repetitive measurements (n = 6). Thus, our findings show that it is applicable for estimating of the repeatability of HPLC-UV for determining baicalin without repeated measurements. In addition, the allowable limit of the “System repeatability” in “Liquid Chromatography” regulated in a pharmacopoeia can be obtained by the present assessment method. Moreover, the present assessment method was also successfully applied to estimate the measurement RSDs of quantitative three-channel liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection (LC-3ECD) of Chrysanthemi Flos for determining caffeoylquinic acids and flavonoids. By the present repeatability assessment method, reliable measurement RSD was obtained stochastically, and the experimental time was remarkably reduced.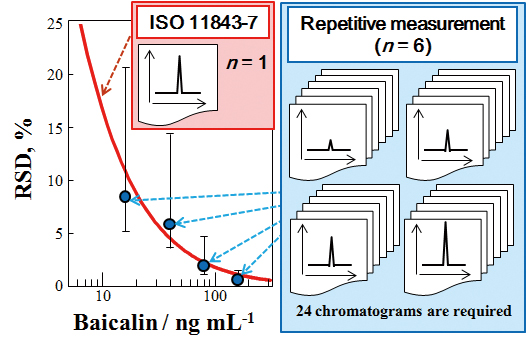 View full abstractDownload PDF (751K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (751K) -
Mika TADA, Yoshimi NIWANO, Masahiro KOHNOArticle type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 9 Pages 911-916
Published: September 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialNitroxide radical formations of deferoxamine mesylate (DFX) that is used clinically to treat iron-overload patients was examined by a tyrosine-tyrosinase reaction system as models of the H-atom transfer or proton-coupled electron transfer. When DFX was exposed to the tyrosine-tyrosinase reaction, nine-line ESR spectrum (g = 2.0063, hfcc; aN = 0.78 mT, aH(2) = 0.63 mT) was detected, indicating that the oxidation of DFX leads to a nitroxide radical. The signal intensity of the DFX radical increased dependently on the concentrations of tyrosine and tyrosinase. The amounts of DMPO-OH spin adducts via the tyrosine-tyrosinase reaction declined with DFX. Furthermore, mass spectra of an extra removed from the tyrosine-tyrosinase reaction mixture showed that the enzyme reactions might not be degradations of DFX. Therefore, there might be two types of DFX reaction passways, which could be through an internal electron transfer from tyrosine and hydrogen absorptions by ·OH directly. View full abstractDownload PDF (857K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (857K) -
Maria ATANASSOVA, Vanya KURTEVA, Isabelle BILLARDArticle type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 9 Pages 917-922
Published: September 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialTwo Eu(III) complexes were synthesized using 4-acylpyrazolone ligands: 3-methyl-4-(4-methylbenzoyl)-1-phenyl-pyrazol-5-one (HPMMBP) and 3-methyl-1-phenyl-4-(4-phenylbenzoyl)-pyrazol-5-one (HPPMBP). The composition of the obtained solid complexes was determined as Eu(PMMBP)3·C2H5OH and Eu(PPMBP)3·3H2O based on elemental analysis and was further studied by IR, NMR and TG-TSC data. The lanthanoid complexation in solid state and in solution during liquid-liquid extraction (molecular diluent and ionic liquid) is discussed. View full abstractDownload PDF (820K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (820K) -
Etsuko NAKAMURA, Yuki HIRUTA, Takafumi WATANABE, Naoko IWASAWA, Daniel ...Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 9 Pages 923-928
Published: September 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe properties of a fluorous solvent extraction system for trivalent lanthanide metal ions are reported. A fluorinated extractant, 4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8,9,9,9-tridecafluoro-1-(2-thienyl)-1,3-nonanedione, and HFE-7200 (C4F9OC2H5) as the extraction solvent were chosen. With this fluorous extractant/solvent combination, higher extraction ratios and separation factors compared to a conventional organic solvent system (thenoyltrifluoroacetone in CHCl3) were achieved for 5 heavy lanthanide ions (Lu, Yb, Tm, Er and Ho). On the other hand, light lanthanide ions (Nd, Pr, Ce and La) are hardly extracted, therefore enabling the mutual separation of light lanthanides from middle or heavy lanthanide ions. View full abstractDownload PDF (2837K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2837K) -
Yuko NISHIMOTO, Hiroki EGUCHI, Eita SHIMODA, Toshiyuki SUZUKIArticle type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 9 Pages 929-934
Published: September 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe gelation of aqueous methylcellulose (MC) solutions containing polyethylene glycol (PEG) was studied by the combination of differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and Raman spectrometry. The gelation of MC hydrogels containing PEG occurred in two-steps. First, the gel network was formed by the hydrophobic interaction between MC and PEG at 310 – 313 K, and then, the gel network was formed between MC chains at 323 K. On the other hand, in the MC hydrogels containing PEG and NaCl, sodium ion assumed to be enclosed by PEG, forming a helix with the hydrophobic groups outward. The sodium ion in the gel was expected to be surrounded by the ether oxygen of PEG as crown ether. View full abstractDownload PDF (5306K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (5306K) -
Kiyoko KANEKO, Shin-ichiro NISHII, Yoko IZUMI, Makoto YASUDA, Tomoyo Y ...Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 9 Pages 935-942
Published: September 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this study, we performed proteomic analysis following sequential protein extraction on calcium oxalate monohydrate (COM) and calcium oxalate dihydrate (COD) urinary stones to determine the specific matrix proteins according to the crystal components of the stones. After X-ray and IR analysis of 13 urinary stones, matrix proteins were sequentially extracted with KCl, formic acid, guanidine-HCl, and EDTA, before SDS-electrophoresis followed by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). The electrophoretic patterns of the extracted proteins differed from that of COM and COD stones. LC-MS/MS identified 65 proteins, of which many were cellular plasma proteins, and were frequently detected regardless of the crystal components. However, 6 proteins (protein Z, protein S, prothrombin, osteopontin, fatty acid binding protein 5, and ubiquitin) were detected in the final EDTA fractions of COM stones. These proteins are involved in the coagulation process or osteometabolism, and thus the roles they play are of particular interest.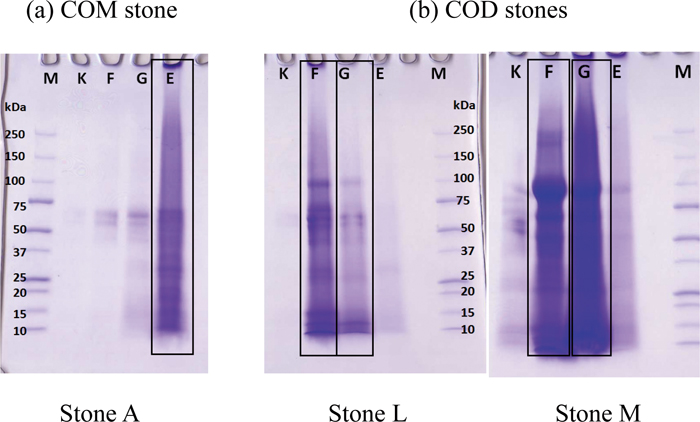 View full abstractDownload PDF (952K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (952K)
Notes
-
Fawzia IBRAHIM, Nahed EL-ENANY, Rania N. EL-SHAHENY, Ibraam E. MIKHAILArticle type: Notes
2015Volume 31Issue 9 Pages 943-947
Published: September 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe first HPLC method was developed for the simultaneous determination of paracetamol (PC), ascorbic acid (AA), and pseudoephedrine HCl (PE) in their co-formulated tablets. Separation was achieved on a C18 column in 5 min using a mobile phase composed of methanol-0.05 M phosphate buffer (35:65, v/v) at pH 2.5 with UV detection at 220 nm. Linear calibration curves were constructed over concentration ranges of 1.0 – 50.0, 3.0 – 60.0 and 3.0 – 80.0 μg mL−1 for PC, AA, and PE, respectively. The method was validated and applied for the simultaneous determination of these drugs in their tablets with average % recoveries of 101.17 ± 0.67, 98.34 ± 0.77, and 98.95 ± 1.11%, for PC, AA, and PE, respectively. The proposed method was also used to construct in vitro dissolution profiles of the co-formulated tablets containing the three drugs. View full abstractDownload PDF (541K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (541K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2015Volume 31Issue 9 Pages 949
Published: September 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2724K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|