Abstract
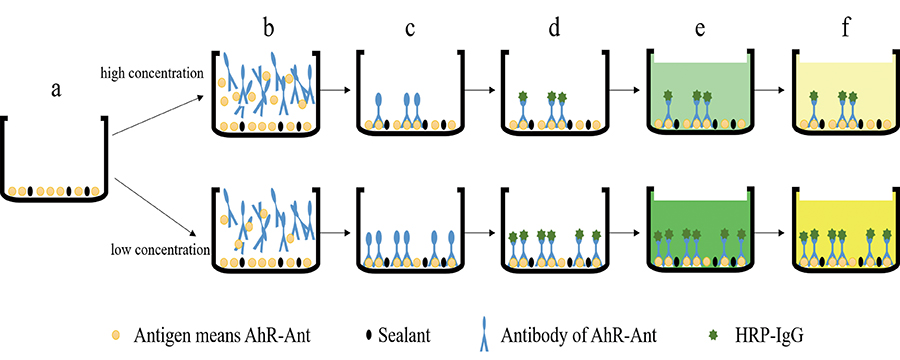
The degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) can generate AhR-binding compounds, exhibiting genotoxicity and carcinogenicity. In this investigation, aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) from carp and anthracene (Ant) were coupled as antigen to establish an indirect competition ELISA (ic-ELISA) with an AhR-Ant antibody. A standard curve was determined for the ic-ELISA concerning detection range and limit. Also, the specificity, stability and the recovery of the ic-ELISA were checked. Results indicate that the ratio of antibody to antigen titer is 1:64000. The resulting standard curve is Y = 21.326 × X + 1.8213. The detection range lies within 10 – 1000 ng mL−1 and the limiting concentration is 2.43 ng mL−1. The cross reaction ratio (CR) between Ant and naphthalene (Nap), Ant and phenanthrene (Phe) or Ant and fluoranthene (Flu) were 5.7, 19.1 and less than 0.1%, respectively. The range of the coefficient of variance (C.V) amounts was from 4.2 up to 9.5% and the recovery range was from 90 to 115%. These results show that the AhR-Ant ic-ELISA is sensitive, and can be used as a technical support to quantify Ant in the environment.