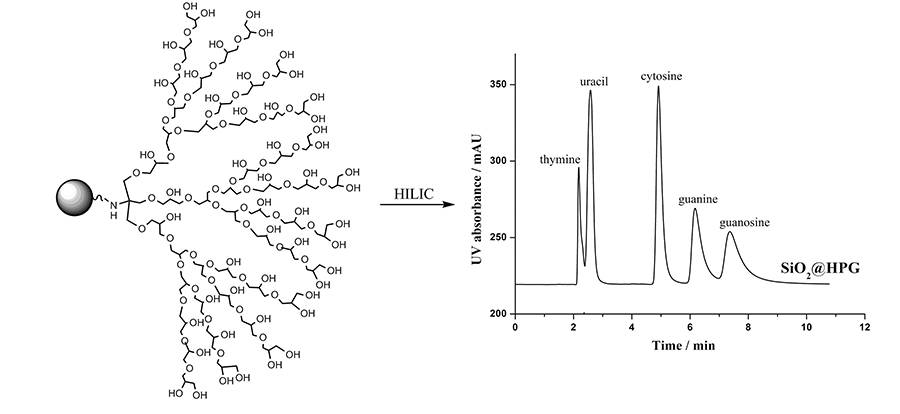
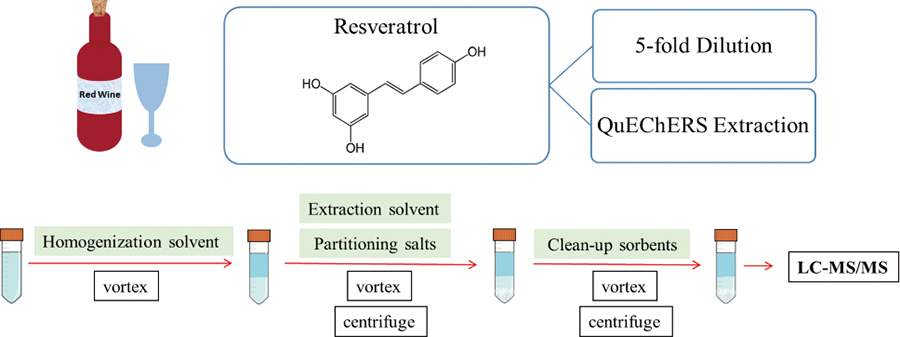
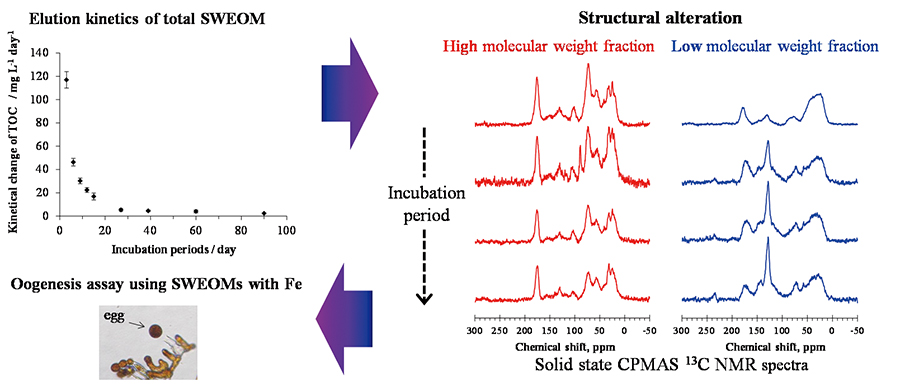
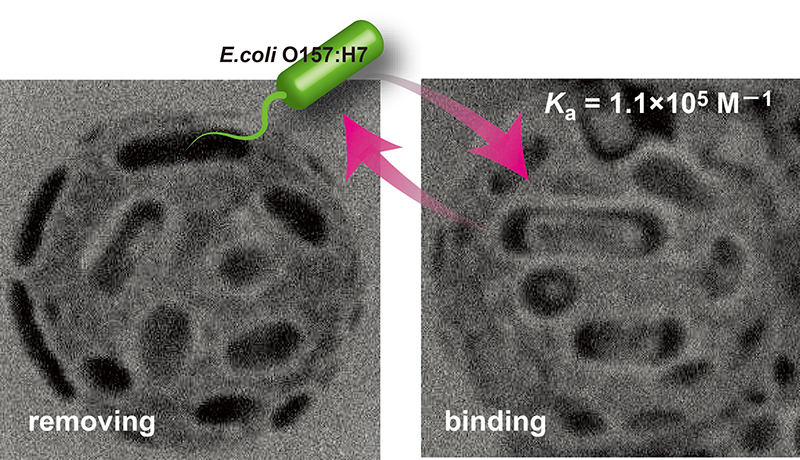
Volume 34, Issue 4
Displaying 1-20 of 20 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 395
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (418K)
Reviews
-
Article type: Reviews
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 397-406
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (17300K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 407-413
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (1113K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 415-419
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (2883K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 421-426
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (1294K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 427-432
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (3055K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 433-438
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (1298K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 439-444
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (475K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 445-451
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (761K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 453-457
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (566K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 459-464
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (782K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 465-470
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (2958K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 471-476
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Advance online publication: March 20, 2018Download PDF (942K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 477-481
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (447K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 483-486
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Advance online publication: March 20, 2018Download PDF (693K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 487-493
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (1427K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 495-500
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (2588K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 501-504
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (660K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 505-508
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (459K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2018Volume 34Issue 4 Pages 509
Published: April 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2018
Download PDF (3276K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|