2022 Volume 86 Issue 4 Pages 722-
2022 Volume 86 Issue 4 Pages 722-
A 72-year-old man with an implantable cardioverter defibrillator for hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy was admitted for Staphylococcus aureus infective endocarditis about 3 weeks after symptom onset. Echocardiography and computed tomography both showed vegetations on the tricuspid valve and the ventricular lead (Figure A,B). Ceftriaxone was started on admission, and then appropriately changed to vancomycin and then to cefazolin in 2 days. Inflammatory markers quickly improved in 1 week, and the whole device was percutaneously removed according to the guideline.1
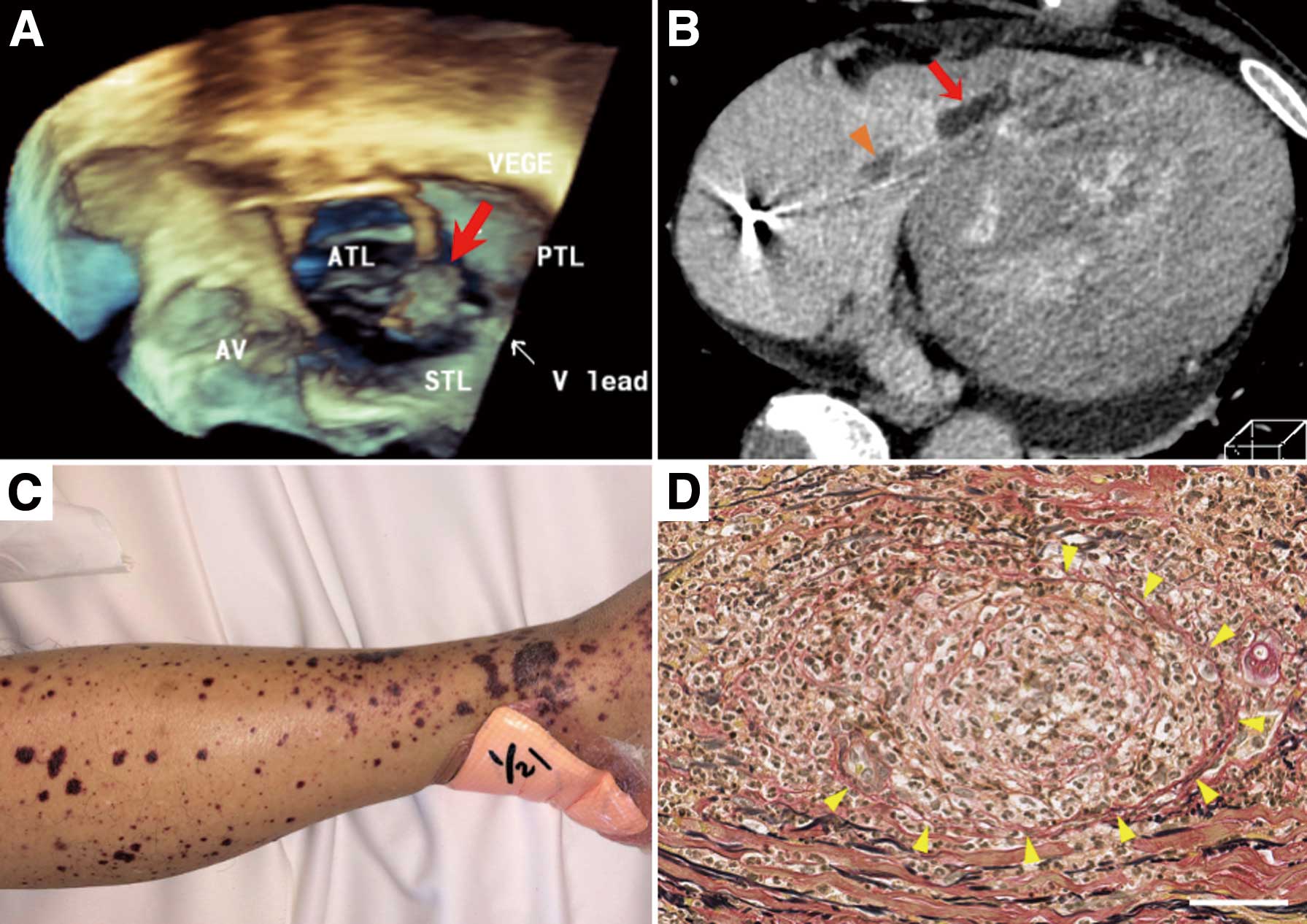
(A) 3D transesophageal echocardiographic image showing a vegetation (red arrow). (B) Vegetations in the right ventricle (red arrow) and at the tricuspid valve (arrowhead). (C) Purpuric skin lesions with petechiae and ecchymosis. (D) Neutrophilic infiltration around the disrupted small vessels in the dermis (arrowheads). Scale bar=50 μm, elastica van Gieson staining. A, anterior; AV, atrioventricular node; P, posterior; S, septal; TL, tricuspid leaflet; V, ventricle; VEGE, vegetation.
However, 2 days after, he experienced epigastralgia, tarry stool and anuria. Furthermore, diffuse purpura developed on the extremities (Figure C). Gastroscopy revealed necrotic esophagitis and ischemic duodenal ulcer, and skin biopsy demonstrated leukocytoclastic small vessel vasculitis (Figure D). These findings fulfilled the diagnostic criteria of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura (HSP), but severe infection limited the use of systemic steroids against devastating renal injury.2 Protracted inflammation gradually deteriorated his hemodynamic status and eventually lead to hemodialysis intolerance. Percutaneous transluminal septal myocardial ablation, performed after controversial discussion, alleviated outflow obstruction but failed to recover hemodynamic instability. He finally died of non-occlusive mesenteric ischemia.
HSP, or IgA vasculitis, is an immune complex vasculitis caused by IgA deposits. It is pathologically characterized by leukocytoclastic vasculitis, and clinically by cutaneous purpura, arthritis, acute enteritis and glomerulonephritis. Various pathogens and drugs have been reported to induce HSP, although the precise mechanism is unknown.3 This report highlights that whole device removal against infection is reasonable but could cause life-threatening HSP, especially with S. aureus infection.
Y. Kobayashi is a member of the Circulation Journal’s Editorial Team.