- J-STAGE home
- /
- Interventional Radiology
- /
- Volume 10 (2025)
- /
- Article overview
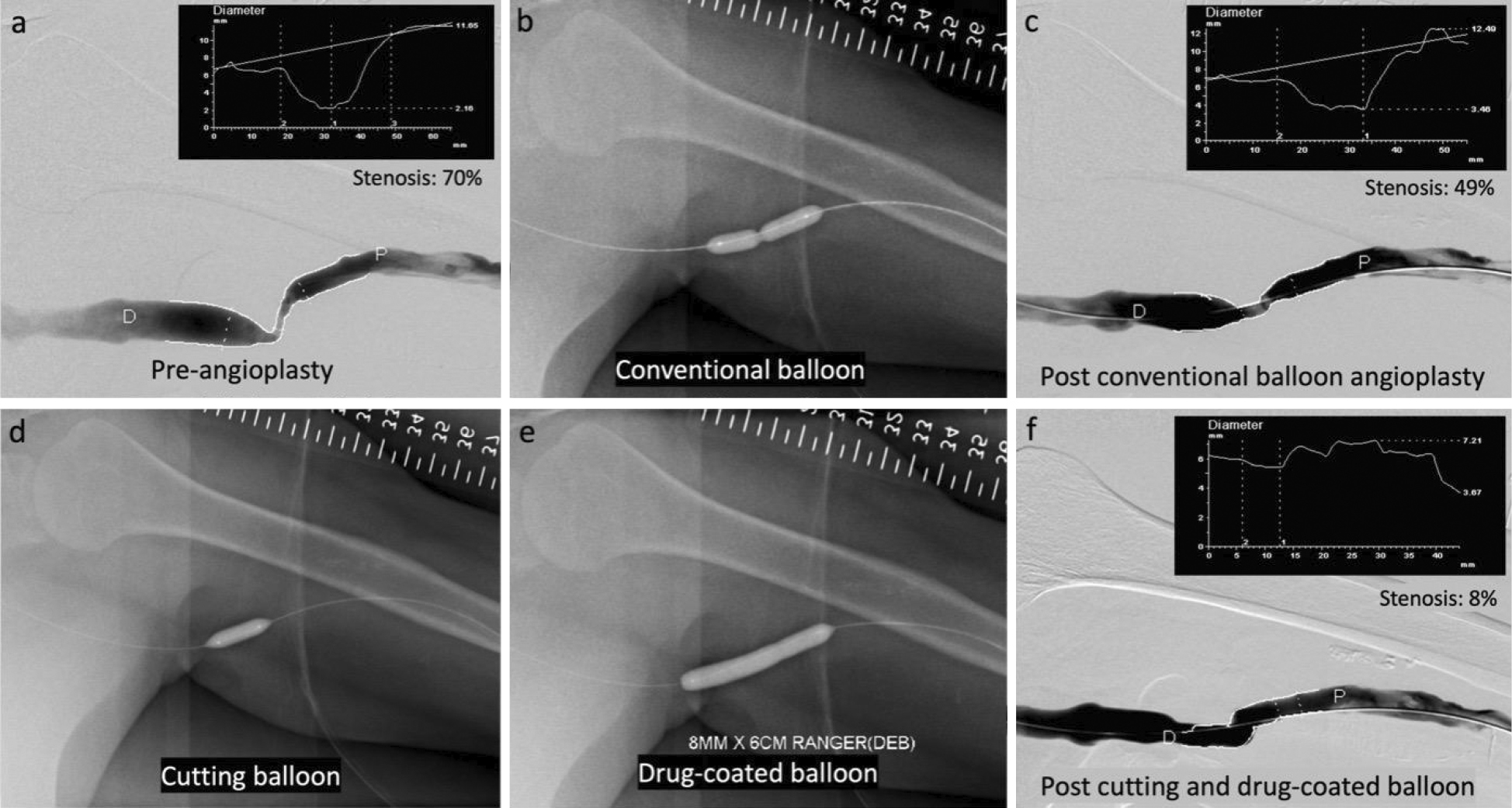
-
Kun Da Zhuang
Department of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
-
Mark Wang Qi Wei
Department of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
-
Shaun Xavier Chan Ju Min
Department of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
-
Apoorva Gogna
Department of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
-
Nanda Venkatanarasimha
Department of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
-
Ankur Patel
Department of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
-
Jasmine Chua Ming Er
Department of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
-
Farah Gillan Irani
Department of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
-
Sum Leong
Department of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
-
Chow Wei Too
Department of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
-
Sivanathan Chandramohan
Department of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
-
Kiang Hiong Tay
Department of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
-
Bien Soo Tan
Department of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
2025 Volume 10 Pages e2024-0030
- Published: March 28, 2025 Received: June 26, 2024 Available on J-STAGE: March 28, 2025 Accepted: October 08, 2024 Advance online publication: December 13, 2024 Revised: -
(compatible with EndNote, Reference Manager, ProCite, RefWorks)
(compatible with BibDesk, LaTeX)