論文ID: J2016064
論文ID: J2016064
Argon ion sputter etching was applied to commercially pure titanium at a radio frequency power of 100, 200 or 250 W for 1.8 to 9 ks. Cone-shaped protrusions with base diameters of 2-5 μm were formed when the specimens were put on a stainless steel disk as well as on a copper disk. On the other hand, no protrusion was formed on a 3N-purity titanium specimen put on the copper disk. These facts mean that the origin of protrusions formed on the commercially pure titanium is not Fe, Ni, Cr and Cu particles arrived from these disks. The origin is considered to be fine titanium oxides precipitated near the surface area, i.e., the collision of argon ions with titanium atoms of specimen surface have brought about high temperature, high temperature-gradient and high vacancy-density gradient, and have promoted quick formation of oxides due to a large amount of oxygen diffusion from interior to surface of the specimen. It is probable that the oxide grow to a pillar perpendicular to the surface under the high temperature and vacancy-density gradient. The pillar acts as a mask and the protrusion begins to form at the root of the pillar. According to an EBSD analysis, the protrusions were densely formed preferentially on the grains with 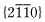 crystal plane but not with closed-packed {0001} plane and
crystal plane but not with closed-packed {0001} plane and  plane. This corresponds that the oxide pillar can grow stably perpendicular to the
plane. This corresponds that the oxide pillar can grow stably perpendicular to the 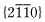 plane without being sputtered out.
plane without being sputtered out.