-
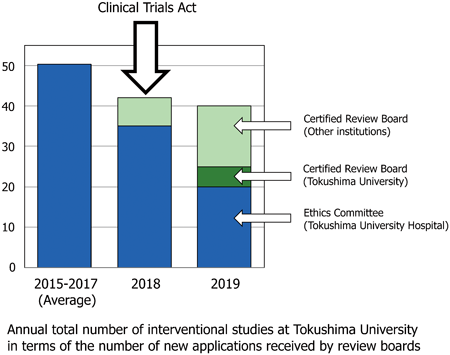
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 3 Pages 374-377Trends in Investigator-Initiated Clinical Studies at a University Hospital after Enforcement of the 2018 Clinical Trials Act in Japan Read moreEditor's pick
The Clinical Trials Act was enforced in 2018 with the aim of ensuring public trust in clinical research. The authors examined the activity of interventional research before and after the enforcement of the law, using the number of applications to the ethics committees as an indicator at a university hospital with a certified review board. It was found that the number of applications tended to decrease with the enforcement of the law. Possible way to promote clinical studies in the new Clinical Trials Act era should be further examined.
-
Editor's pick
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) from tumor cells has multiple roles, including tumor invasion, tumor proliferation, and tumor immunity. In this paper, the author focused on the role of TGF-β against tumor immunity and summarized the potential of anti-tumor immunity by using anti-TGF-β antibody or chemical components with immune checkpoint inhibitors and chimeric antigen receptor cells. Furthermore, the molecular mechanisms by which TGF-β controlled tumor immunity were described in this review.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 2 Pages 162-168RSK-Mediated Non-canonical Activation of EphA2 by Tamoxifen Read moreEditor's pick
The authors have previously demonstrated that non-canonical phosphorylation of EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase is catalyzed by ribosomal S6 kinases (RSKs), downstream kinases of the MEK-ERK pathway, and promotes migratory potentials of cancer cells. The article by Yonehara et al. demonstrated that tamoxifen, a selective estrogen receptor (ER) modulator used to treat breast cancers, induces the rapid phosphorylation of EphA2 by RSK in an ER-independent manner. In addition, tamoxifen significantly enhances the migration of ER-negative breast cancer cells possibly via the activation of RSK-EphA2 axis. These results provide novel insights into the tumor-promoting activity of tamoxifen.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 2 Pages 194-199Effective Anticancer Therapy by Combination of Nanoparticles Encapsulating Chemotherapeutic Agents and Weak Electric Current Read moreEditor's pick
Ameliorating the intratumor delivery of nanoparticles (NPs) is challenging. This study applied weak electric current (WEC) onto the tumor surface to improve the intratumor delivery of I.V. administrated Doxorubicin (DOX) encapsulated NPs. Interestingly, WEC markedly increased NPs accumulation into the tumor. Consequently, WEC/DOX-NPs combination significantly suppressed tumor growth compared to DOX-NPs alone. Mechanistically, WEC-mediated opening of intercellular adhesion in tumor is suggested to employ the increased intratumor accumulation of DOX-NPs utilizing enhanced permeability and retention effect. Therefore, a combined application of WEC and NPs containing chemotherapeutic agents will be useful for effective anticancer therapy.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 2 Pages 207-212Octa-arginine and Octa-lysine Promote Cell Adhesion through Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans and Integrins Read moreEditor's pick
Octa-arginine (R8) has been extensively studied as a cell-penetrating peptide. Meanwhile, R8 is considered a promising cell adhesion molecule owing to its ability to bind to heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) and integrin β1. This study revealed that R8- and octa-lysine (K8)-conjugated agarose matrices mediate cell adhesion via HSPGs and integrin β1, and that the integrin β1 contributes to cell spreading and proliferation on the R8- and K8-matrices. The findings of this study are useful for further understanding of the R8-membrane interactions and demonstrate that R8 and K8 have a potential to be used as a cell adhesion molecule.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 2 Pages 213-219Effect of Corticosteroids on Peptide Transporter 2 Function and Induction of Innate Immune Response by Bacterial Peptides in Alveolar Epithelial Cells Read moreEditor's pick
In the lung alveolar epithelial cells, the innate immune response is induced by bacterial peptides such as Tri-DAP via PEPT2 (a peptide transporter)- and NOD1 (an intracellular pattern recognition receptor)-dependent pathway. In this study, corticosteroids such as budesonide were found to suppress PEPT2 function as well as the increased mRNA expression and secretion of interleukin-8 by Tri-DAP, using NCI-H441 cells having human alveolar type II cell-like phenotype. The results suggest that the innate immune response induced by bacterial peptides in the lung alveolar region may be suppressed during the inhaled corticosteroid therapy.
-
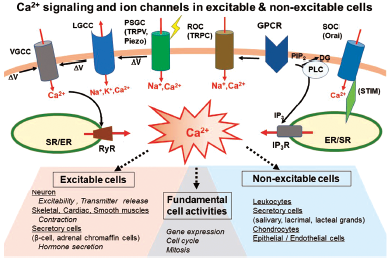
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 1 Pages 1-18Reciprocal Relationship between Ca2+ Signaling and Ca2+-Gated Ion Channels as a Potential Target for Drug Discovery Read moreEditor's pick
About the cover: Cellular Ca2+ signaling functions as one of the most common second messengers of various signal transduction pathways in cells and mediates various physiological roles depending on cell-types and their excitability. Among ion channels, Ca2+-permeable channels in the plasma membrane as well as endo- and sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes play important roles in cellular Ca2+ signaling. Ca2+-gated ion channels indicated by the star (★) often crosstalk reciprocally with Ca2+ signals and are central to the regulation of cellular functions. Ca2+-gated ion channel works as a converter of Ca2+ signals to propagative electrical signals and plays key roles in the opposite feedback regulation of Ca2+ signaling in excitable and non-excitable cells.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 1 Pages 34-41Imatinib Mesylate Exerted Antitumor Effect by Promoting Infiltration of Effector T Cells in Tumor Read moreEditor's pick
Imatinib mesylate is a potent tyrosine kinase inhibitor. It is known that in addition to targeting the oncogenic drivers, the immune system plays an important role in exerting therapeutic effects of imatinib and restraining the emergence of escape mechanisms. However, its influence on the recruitment of effector T cells into the tumors has not been investigated. Authors found that imatinib significantly enhanced the expression of CD8 T cell-recruiting cytokine genes, leading to antitumor effects, which was dependent on the tumor type. This study elucidated a new mechanism of antitumor immunity induced by imatinib.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 1 Pages 104-113Impact of Gut Microbiota on the Pharmacokinetics of Glycyrrhizic Acid in Yokukansan, a Kampo Medicine Read moreEditor's pick
Glycosides are often included as active ingredients in natural medicines. Many glycosides are highly water-soluble, and they are metabolized by intestinal bacteria before being absorbed in the digestive tract. Glycyrrhizic acid (GL), one of the main components of yokukansan, is a glycoside that is metabolized by intestinal bacteria to glycyrrhetinic acid (GA). This study investigated the gut microbiota compositions and pharmacokinetics of GL in yokukansan. The results suggest that oral antibiotics affect the plasma level of GA, and that the blood level of GA changes depending on the gut microbiota composition.
-
Editor's pick
Toxicological profiles of chemicals have been investigated in rodents, but new alternative methods to evaluate compound safety are being developed worldwide using in silico approaches. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling has the potential to play significant roles in estimating internal chemical exposures. The authors generated three major PBPK model input parameters (i.e., absorption rate constants, volumes of the systemic circulation, and hepatic intrinsic clearances) for chemicals using machine learning algorithms. The input parameters for humans of compounds can be reliability estimated using chemical descriptors calculated using in silico tools for illustrating virtual maximum plasma concentrations and areas under the curve.
-
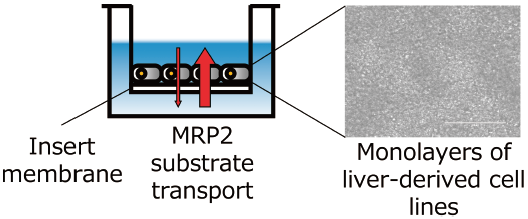
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 1 Pages 150-153Directional Drug Transport through Membrane-Supported Monolayers of Human Liver-Derived Cell Lines Read moreEditor's pick
This report reveals that monolayers of human liver-derived cell lines grown on a membrane exhibit directional transport, i.e. efflux transport of a substrate of multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2). The transport was suppressed by an MRPs inhibitor, supporting the idea that MRP2 is the primary mediator of directional transport. The advantage of this system is its potential to quantitatively evaluate biliary excretion of MRP2 substrates in vitro. The assay system may therefore be utilized for the screening of biliary excretion drugs and for investigating the hepatotoxicity of candidate drugs.
-
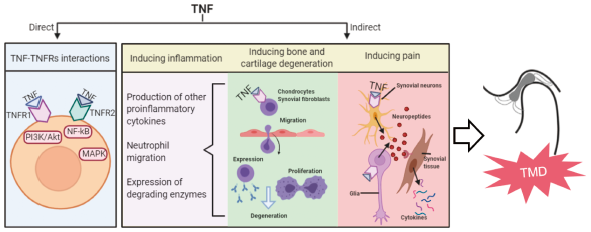
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 12 Pages 1801-1809The Role of TNF-α in the Pathogenesis of Temporomandibular Disorders Read moreEditor's pick
This article concludes the underlying responses of inflammation in temporomandibular disorder(TMD), a complex and common oral dentofacial disease. One of the most involved inflammatory cytokines--TNF-α, has effects on TMD and its inflammation. These effects are summarized comprehensively and explicitly as triggering immune responses, degenerating bone and cartilage and mediating pain of temporomandibular joint. This review gives an insight into this connection between TNF-α and TMD, which may highlight TNF-α as a new therapeutic target for TMD treatment and therefore provide new insight for therapeutic intervention for TMD.
-
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 12 Pages 1810-1818Possible Therapeutic Applications of Targeting STAP Proteins in Cancer Read moreEditor's pick
The signal-transducing adaptor protein (STAP) family, including STAP-1 and STAP-2, contributes to a variety of intracellular signaling pathways. STAP proteins bind to IκB kinase complex, BRK, STAT3, and STAT5, during tumorigenesis and inflammatory/immune responses. STAP proteins positively or negatively regulate critical steps in intracellular signaling pathways through individually unique mechanisms. In this review, the authors describe that STAP proteins are involved in the development and/or progression of some types of malignancies. The authors further describe the possible therapeutic applications of targeting STAP proteins in cancer.
-
Editor's pick
Gamma-glutamylcysteine (g-EC) has antioxidant properties similar to those of glutathione (GSH) and acts as its precursor in mammals. In this paper, the reaction conditions of the phytochelatin synthase-like enzyme derived from Nostoc sp. (NsPCS) which hydrolyzes GSH to g-EC was optimized, resulting that high yield conversion from 100 mM GSH to g -EC was achieved in the absence of ATP and other additives. These results suggest that the NsPCS reaction has great potential for the low-cost industrial-scale production of g-EC from GSH.
-
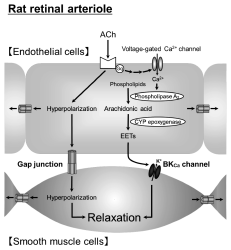
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 12 Pages 1860-1865Involvement of Gap Junctions in Acetylcholine-Induced Endothelium-Derived Hyperpolarization-Type Dilation of Retinal Arterioles in Rats Read moreEditor's pick
Acetylcholine (ACh) stimulates the production of cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenase-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), which activate large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKCa) channels. The article by Mori et al. provides evidence suggesting that ACh-induced hyperpolarization of endothelial cells transmits to adjacent smooth muscle cells via myoendothelial gap junctions. ACh can also facilitate gap junctional communication between endothelial cells and/or between smooth muscle cells. These pathways contribute to the hyperpolarization and relaxation of vascular smooth muscle cells in rat retinal arterioles.
-
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 12 Pages 1894-1897Positive Lusitropic Effect of Quercetin on Isolated Ventricular Myocardia from Normal and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice Read moreEditor's pick
Diastolic dysfunction is a major cardiac deficit underlying heart failure accompanying hypertension, coronary artery disease, and diabetes mellitus and is partly mediated by impaired myocardial relaxation and Ca2+ handling. Therapeutic agents targeting diastolic dysfunction are not yet clinically available. Quercetin is one of the major flavonoid compounds contained in fruits and vegetables. The authors examined the lusitropic effect of quercetin on isolated ventricular myocardial tissue preparations from normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice and showed that quercetin accelerated myocardial relaxation through activation of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. This finding may lead to the development of novel therapeutic agents of natural origin.
-
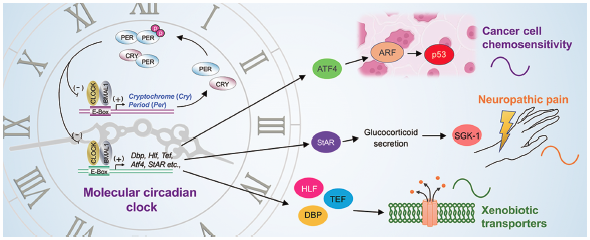
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 11 Pages 1577-1584Chrono-Pharmaceutical Approaches to Optimize Dosing Regimens Based on the Circadian Clock Machinery Read moreEditor's pick
The sensitivity to drugs and their disposition are changed depending on the circadian time. Hence, choosing appropriate times of day to administer drugs enables to enhance the therapeutic index of pharmacotherapy. On the other hand, various disease conditions also exhibit circadian changes in symptom intensity. Several therapeutic approaches are facilitated by the identification of chemical compound targeted to key molecules that cause circadian exacerbation of disease events. The author describes the current understanding of the role of the circadian biological clock in regulating drug efficacy and disease condition, and also presents ‘chrono-pharmaceutical’ strategy for treatment of diseases and drug development.
-
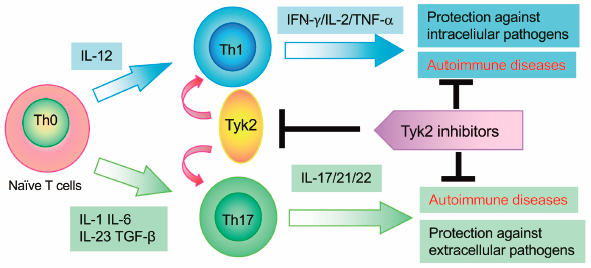
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 11 Pages 1585-1592Therapeutic Advantage of Tyk2 Inhibition for Treating Autoimmune and Chronic Inflammatory Diseases Read moreEditor's pick
Tyrosine kinase 2 (Tyk2) is a member of the Janus family of protein tyrosine kinases (JAKs). Tyk2 associates with interferon (IFN)-α, IFN-β, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, IL-12, and IL-23 receptors and mediates their downstream signaling pathways. The authors summarize that Tyk2 plays crucial roles in the differentiation, maintenance, and function of T helper 1 (Th1) and Th17 cells and that its dysregulation in autoimmune and/or inflammatory diseases using Tyk2-deficient mice and cells. The authors further describe that Tyk2 inhibition has great potential for clinical application in the management of a variety of immune-relating diseases.
-
Editor's pick
This Current Topics includes 5 reviews, and the authors for individual reviews were invited to contribute papers updating/improving readers’ understanding of the nuclear receptors- and drug-metabolizing enzymes-mediated inter-individual differences. Nuclear receptors (e.g., ERα/β, PPARβ/δ, and RORα) are basically ligand-inducible and are known to be involved in the regulation of numerous physiological processes. At the post-transcriptional level, some microRNAs are involved in the regulation of CYP3A protein expression. In addition, at the post-translational levels, there are functional protein-protein interactions between different kinds of drug-metabolizing enzymes i.e., P450 and UGT, which results in modulation of the enzyme(s) activities.
-
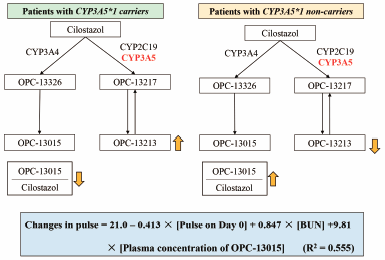
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 11 Pages 1767-1774Impact of Cilostazol Pharmacokinetics on the Development of Cardiovascular Side Effects in Patients with Cerebral Infarction Read moreEditor's pick
Cilostazol is metabolized to two active metabolites in humans. This study investigated the influence of the plasma concentrations of cilostazol and the metabolites on pulse rate in patients with cerebral infarction. Polymorphisms of metabolic enzymes significantly influenced plasma disposition of OPC-13015, a metabolite by CYP3A4, and OPC-13213, another metabolite by CYP3A5 and CYP2C19. A multiple regression model, consisting of factors of the plasma concentration of OPC-13015, levels of blood urea nitrogen, and pulse rate at the start of cilostazol therapy explained 55.5% of the interindividual variability of the changes in pulse rate before and after the treatment.