-
編集者のコメント
The pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) parameter of the exposure time that the unbound drug concentration remains above the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for a bacterium (fT ≥ MIC) is used in establishing optimal dosing regimens. The authors revealed that the optimal fT ≥ MIC for the clinical efficacy of de-escalation to cefmetazole (CMZ) for patients with extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli (ESBL-E) bacteremic urinary tract infection (UTI) was clarified as fT ≥ MIC ≥ 57%. These results may lead to optimal dosing regimens when using CMZ for patients with bacteremic UTI caused by ESBL-E.
-
48 巻 (2025) 5 号 p. 545-554Role of Histamine H1 and H3 Receptors in Emotion Regulation in Intermittent Sleep-Deprived Mice もっと読む編集者のコメント
Abnormal behaviors such as low anxiety, impulsivity, hyperactivity, and inattention-like traits have been observed in mice with disrupted sleep patterns, mirroring symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and the central histamine system plays a role in various physiological and neurological functions, including the regulation of the sleep-wake cycle, anxiety-related behaviors (ranging from high to low anxiety), and ADHD. In this study, the authors revealed that the low-anxiety behavior and impulsive-like ADHD symptoms induced by intermittent sleep deprivation may result from the overstimulation of histamine H1 and H3 receptors by elevated histamine together with increased hypothalamic HDC expression. These findings suggest that sufficient sleep may contribute to ameliorating ADHD symptoms.
-
編集者のコメント
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
Detecting low-frequency genetic mutations is crucial in genetic testing, particularly for cancer diagnostics. Wild-type blocking PCR (WTB-PCR) utilizes a blocking oligonucleotide fully complementary to wild-type DNA to suppress its amplification, thereby enabling selective detection of mutant alleles. Incorporating bridged nucleic acids (BNAs) into blocking oligonucleotides can enhance binding affinity, consequently improving inhibitory efficiency. However, the optimal placement of BNAs within blocking oligonucleotides remains uncertain. This study systematically evaluated the effects of BNA positioning and identified significant variations in inhibition efficacy dependent on position, offering essential insights for optimizing WTB-PCR design. -
編集者のコメント
Ergothioneine (ERGO), an amino acid with potent antioxidant activity, is abundantly found in certain mushroom species. The authors demonstrated that dietary ERGO-rich mushrooms significantly alleviated the epidermal thickening, reduction in skin moisture content, and increase in TEWL induced by UVB in mice, at clinically relevant plasma ERGO levels. These protective effects were accompanied by reductions in oxidative stress markers and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Furthermore, ERGO-rich mushroom intake increased epidermal ERGO levels to approx. 100 times the concentration required to inhibit UVB-induced intracellular ROS in keratinocytes. These findings suggest that ERGO-rich mushrooms are promising beneficial foods for the prevention and/or treatment of photoaging.
-
48 巻 (2025) 5 号 p. 706-712Evaluating Signal Peptide Efficiency for Extracellular Protein Secretion for mRNA Vaccine Design もっと読む編集者のコメント
This study systematically compares natural and synthetic signal peptides for boosting extracellular NanoLuc luciferase secretion in HEK293, C2C12, and HepG2 cells. Signal peptides from cystatin S, lactotransferrin, tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), and artificial sequences were tested, with cystatin S driving the highest luciferase secretion in all cell types. Notably, the cystatin S peptide outperformed the commonly used tPA signal peptide. These findings suggest that optimizing signal peptides—such as using cystatin S—could increase antigen expression for mRNA vaccines, potentially enabling robust immune responses at lower mRNA doses.
-
編集者のコメント
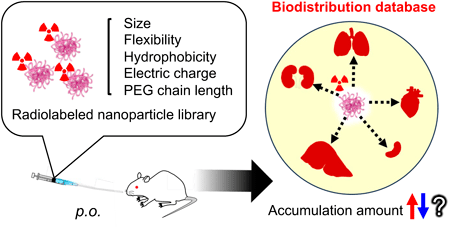
Biodistribution of orally administered nanoparticles (NPs) should be precisely controlled to maximize their function and avoid the side effects. Although several studies have been conducted to understand the influence of NP properties on the biodistribution of NPs after oral administration, these studies have focused on a single element of NPs. In this study, the authors revealed that the size, flexibility, hydrophobicity, surface charge, and surface chemistry of NPs play an important role in controlling the biodistribution of orally administered NPs. Their database contains important information regarding the development of orally administered NP-derived drugs.
-
編集者のコメント
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
Treble methylations are metabolic pathways of selenium (Se) for its excretion into urine, and demethylation is an essential pathway for Se utilization to be incorporated into selenoproteins. Monomethylated and dimethylated Se compounds are known as metabolites of gut microbiota. The authors revealed that monomethylated Se was metabolized into two directions, namely, methylation and demethylation for the Se utilization and excretion, respectively. Whereas, dimethylated Se was metabolized into only methylation to form trimethylated one. The second methylation in the three methylations of gut bacteria could be a crucial step to determine the Se utilization in a host animal. -
編集者のコメント
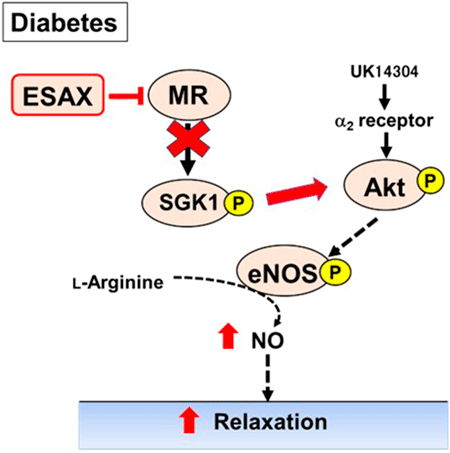
This study highlights the vascular protective effects of esaxerenone, a nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor blocker, in a type 2 diabetic mouse model. Esaxerenone significantly improved endothelial dysfunction by enhancing nitric oxide production via activation of the Akt pathway and suppressing the activity of serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1. Notably, these effects occurred independently of the GRK2 signaling pathway. These findings suggest that esaxerenone may be a promising therapeutic agent for preventing or treating diabetic vascular complications through mechanisms beyond blood pressure control, offering new insight into its role in vascular endothelial health.
-
48 巻 (2025) 4 号 p. 450-456Microfibril-Associated Protein 5 Contributes to the Elastic Fiber Abnormalities in Aged Skin もっと読む編集者のコメント
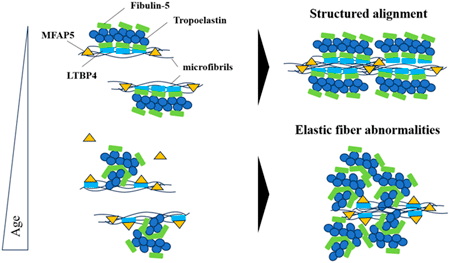
This study highlights the contribution of microfibril-associated protein 5 (MFAP5) to age-related changes in human skin. The authors found that MFAP5 expression increases with age and is associated with disorganized elastic fibers in the dermis. Silencing MFAP5 in dermal fibroblasts partially restored elastic fiber structure, indicating its functional role in dermal aging. These findings provide new insights into the molecular basis of intrinsic skin aging and suggest that MFAP5 could be a promising therapeutic target for maintaining skin elasticity in aging populations.
-
48 巻 (2025) 4 号 p. 457-462Effects of Calcineurin Inhibitors on Intestinal Barrier in Caco-2 Cells もっと読む編集者のコメント
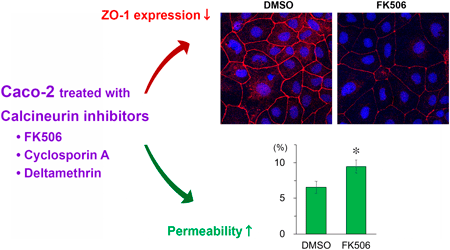
Calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus (FK506) and cyclosporin A (CsA) have various side effects including intestinal mucosal damage. To determine whether intestinal epithelial cells are directly damaged by calcineurin inhibitors, this study examined the effects of calcineurin inhibitors on the intestinal barrier in Caco-2 cells. Treatment of Caco-2 cells with calcineurin inhibitors such as FK506, CsA and deltamethrin inhibited expression of zonula occludens-1, a tight junction protein, and increased permeability of Lucifer Yellow. These findings provide evidence indicating that intestinal epithelial cells can be directly damaged by calcineurin inhibitors.
-
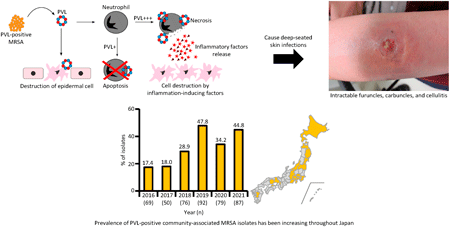
48 巻 (2025) 3 号 p. 196-204Molecular Epidemiological Features of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Japan もっと読む編集者のコメント
This review shows how the prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Japan has changed significantly in just a decade. In particular, the prevalence of the USA300 clone, a highly virulent community-associated MRSA, has become a serious problem in the community, and the number of patients with severe skin infections has increased. If such highly virulent strains of MRSA spread to hospitals, where there are many compromised patients, there is a risk of serious outbreaks. This review highlights the importance of staying abreast of the latest MRSA prevalence and implementing appropriate infection control.
-
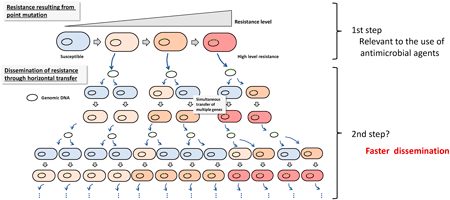
48 巻 (2025) 3 号 p. 205-212Unique and Ingenious Mechanisms Underlying Antimicrobial Resistance and Spread of Haemophilus influenzae もっと読む編集者のコメント
Haemophilus influenzae is one of the most common pathogens causing community infections. Historically, H. influenzae has been known for its rapid emergence of antimicrobial-resistant isolates in response to antimicrobial usage. In this paper, the authors summarised the mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance to therapeutic agents based on recently published studies. Furthermore, they highlighted the transformation ability of H. influenzae, which allows it to adapt to its environment by acquiring extracellular DNA. This unique and ingenious feature could serve as an efficient system for the spread of antimicrobial resistance.
-
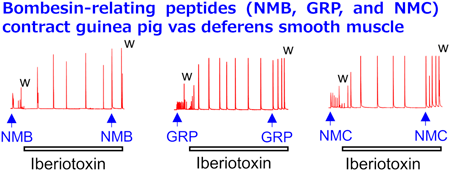
48 巻 (2025) 3 号 p. 298-307Evidence Showing Bombesin-Like Peptides Contract Guinea Pig Vas Deferens Smooth Muscle もっと読む編集者のコメント
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
This study is the first to demonstrate that bombesin-like peptides—neuromedin B, gastrin-releasing peptide, and neuromedin C—induce contraction in guinea pig vas deferens smooth muscle (VDSM), likely through activation of bombesin BB2 receptors, highlighting a novel physiological role for these peptides. It further reveals that large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels act as key negative regulators of VDSM contractility by suppressing voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels. These findings provide new insights into the regulation of the reproductive system and suggest potential therapeutic targets in urogenital physiology. -
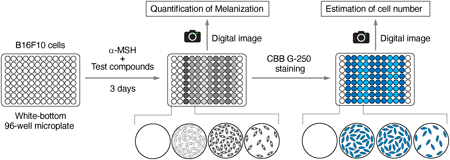
48 巻 (2025) 3 号 p. 308-313Development of a Digital Image-Based Method to Screen Molecules That Regulate Melanization もっと読む編集者のコメント
The authors established a simple method to quantify melanization by analyzing the digital images of the entire microplates. Compared to the conventional method measuring the absorbance of cell lysates at UV-A wavelengths, their digital image-based method was found to have higher sensitivity and be applicable to high-throughput screening assays to identify molecules that affect melanization.
-
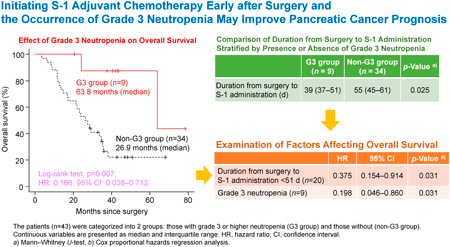
48 巻 (2025) 2 号 p. 132-136Effect of Severe Neutropenia Caused by S-1 Adjuvant Chemotherapy on Pancreatic Cancer Prognosis もっと読む編集者のコメント
This study is the first to reveal that severe neutropenia during S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy may affect pancreatic cancer prognosis. Cox proportional hazards regression analysis showed that the presence of grade 3 neutropenia and a duration from surgery to S-1 administration <51 d were significantly associated with prolonged OS in patients with pancreatic cancer after curative resection. Patients who developed grade 3 neutropenia have no other adverse events and are in good general condition, continuation of S-1 treatment may contribute to improving the prognosis. This information may prove valuable for the treatment of pancreatic cancer, a highly lethal disease with limited effective therapies.
-
編集者のコメント
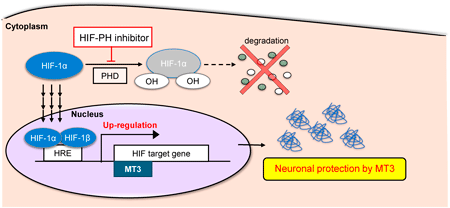
Metallothionein (MT) is a small-molecule protein that functions in essential trace element homeostasis. Among MT isoforms, MT3 is involved in neuronal activity, and its expression is reported to be decreased in patients with neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD); however, only a few effective drugs have been reported to induce MT3 expression. In this study, authors evaluated existing drugs for the induction of MT3 expression in the neuronal cell line of ReNcell CX cells. Authors treated ReNcell CX cells with several HIF-PH inhibitors and evaluated MT3 expression. Authors found that FG4592 significantly enhanced MT3 expression at both RNA and protein levels. FG4592 treatment increased the amount of HIF1α binding to the MT3 promoter. These findings indicate that FG4592 induces MT3 expression via increased HIF1α. In conclusion, authors found FG4592 to be an endogenous MT3 inducer in the cells of the nervous system in this study. The findings of this study are expected to lead to the development of new MT3-inducing drugs for neurodegenerative diseases based on FG4592.
-
編集者のコメント
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
The role of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX) was evaluated in the automaticity of the sinus node, the orthotopic pacemaker, and the pulmonary vein, a potential ectopic pacemaker that may cause atrial fibrillation. The authors demonstrated that in guinea pigs, forward mode NCX was involved in spontaneous activity in the pulmonary vein cardiomyocytes but not in the sinus node; this was probably because the Ca2+ supply and the driving force for the forward mode NCX were both larger in the pulmonary vein cardiomyocytes. Considering the ionic environment is critically important for studying the contribution of NCX to the phenomenon of interest. -
編集者のコメント
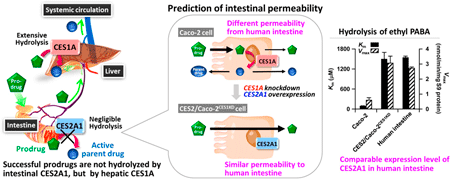
An oral prodrug with an ester is desirable to be resistant to the major human intestinal esterase, carboxylesterase 2A1 (CES2A1). The authors recently obtained CES2/Caco-2CES1KD cells with reduced human CES1A and highly expressed CES2A1. In this study, the authors demonstrated that CES2/Caco-2CES1KD cells essentially maintained their Caco-2 cell background with respect to transport and metabolic profiles, with the exception of CES. The expression level of CES2A1 in CES2/Caco-2CES1KD cells was comparable to that in human intestine. The present data indicated the potential of CES2/Caco-2CES1KD cells for the estimation of membrane transport of prodrugs.
-
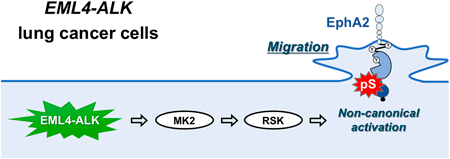
48 巻 (2025) 2 号 p. 172-176Stress Response Kinase MK2 Induces Non-canonical Activation of EphA2 in EML4-ALK Lung Cancer Cells もっと読む編集者のコメント
The non-canonical activation of EphA2 mediated by its Ser-897 phosphorylation plays a crucial role in cancer malignant transformation, including cell migration. The authors have previously reported that Ser-897 phosphorylation of EphA2 is catalyzed by RSK through the oncogenic ERK signaling pathway or the p38-MK2 cellular stress response pathway. In the present study, the authors found that MK2 regulates the RSK-EphA2 axis in a p38-independent manner in ERK-activated EML4-ALK lung adenocarcinoma cells, resulting in enhanced cell motility. These results reveal an important crosstalk between MK2 and ERK in the non-canonical activation of EphA2.