-
編集者のコメント
This retrospective observational cohort study evaluated the chronological order of acute kidney injury (AKI) and hypokalemia with Yokukansan preparation in 258 patients. Among the patients with AKI and hypokalemia, 92% developed hypokalemia associated with Yokukansan preparation after AKI. Excluding one patient with hypokalemia before AKI, the incidence of hypokalemia was higher in patients with AKI than in those without AKI (32% vs. 12%; p = 0.005). Furthermore, the prevalence of hypokalemia differed according to AKI recovery (AKI with recovery, 36%; AKI without recovery, 22%; and no AKI, 12%; p = 0.014).
-
編集者のコメント
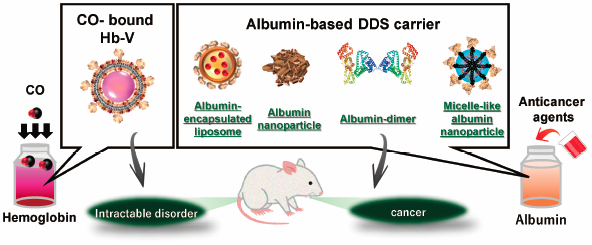
Hemoglobin and albumin are biogenic molecules with unique and interesting inherent characteristics. The utilization of their inherent characteristics makes it possible to develop innovative pharmaceutical and biomedical preparations for the treatment and diagnosis of intractable disorders that can be a groundbreaking strategy to resolve and improve several clinical problems. In this review, author introduces the pharmaceutical technology, strategies, and therapeutic application of drug delivery system carriers that have been designed on the basis of the structure and function of hemoglobin and albumin.
-
編集者のコメント
Bone damage in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) occurs in an early stage after disease onset, and osteoclasts play a pivotal role in its progression and subsequent irreversible structural destruction of joints. Colony stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) is a receptor protein tyrosine kinase specifically expressed in monocytic-lineage cells such as macrophages and osteoclasts. Authors investigated the effect of JTE-952, a novel CSF1R tyrosine kinase inhibitor, on osteoclast formation in vitro and on bone destruction in an animal model of RA. In this article, Uesato et al. suggested that JTE-952 effectively prevents the progression of the structural destruction of joints, a major unmet clinical need for RA.
-
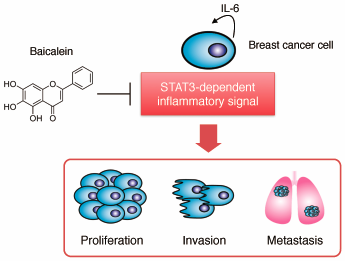
43 巻 (2020) 12 号 p. 1899-1905Anti-metastatic Effects of Baicalein by Targeting STAT3 Activity in Breast Cancer Cells もっと読む編集者のコメント
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) plays an essential role in a pro-carcinogenic inflammatory microenvironment, both at the initiation of malignant transformation and during cancer progression. In this study, Hayakawa and colleagues found that baicalein, a flavone isolated from the roots of Scutelleria baicalensis, inhibited STAT3 transcriptional activity and its phosphorylation, and further exhibited anti-proliferative effects in breast cancer cells. Moreover, baicalein suppressed the production of IL-6 and the metastatic potential of breast cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. This study suggests baicalein as an attractive phytochemical compound for reducing metastatic potential of breast cancer cells by regulating STAT3 activity.
-
43 巻 (2020) 12 号 p. 1911-1916The Carboxyl-Terminal Penta-Peptide Repeats of Major Royal Jelly Protein 3 Enhance Cell Proliferation もっと読む編集者のコメント
Royal jelly (RJ) is a well-known functional foodstuff derived from honey bees and contains various functional substances. In this report, the authors focused on major royal jelly protein 3 (MRJP3), which is one of the major protein components in RJ, and found that MRJP3 possessed cell proliferation activities in cultured cell lines. The activities were identified in the tandem penta-peptide repeats (TPRs) consisting of Q-N-x-N-[K/R] at its C-terminus of MRJP3. As the cell proliferation activities remained even after treatment of TRPs with trypsin, it is plausible that the penta-peptide is the minimal functional unit.
-
43 巻 (2020) 12 号 p. 1924-1930Silver Nanoparticles Induce DNA Hypomethylation through Proteasome-Mediated Degradation of DNA Methyltransferase 1 もっと読む編集者のコメント
In this study, Maki et al., evaluated changes in DNA methylation induced by silver nanoparticles and attempted to elucidate the induction mechanism. The results showed that silver nanoparticles with diameter of 10 nm (nAg10) induces DNA hypomethylation accompanied with a decrease in the level of Dnmt1 in A549 alveolar epithelial cells. We The authors also revealed that nAg10 promotes the degradation of Dnmt1 by the proteasome system. Collectively, these results suggest that nAg10 induced DNA hypomethylation through a proteasome-mediated degradation of Dnmt1. This paper provides basic evidence for the effect of silver nanoparticles on DNA methylation.
-
43 巻 (2020) 11 号 p. 1617-1625Development of an SS-Cleavable pH-Activated Lipid-Like Material (ssPalm) as a Nucleic Acid Delivery Device もっと読む編集者のコメント
DNA/RNA-based medication is an ultimate strategy in the field of personalized medicine. The authors summarized the recent progress in the development of their original lipid-like material: SS-cleavable pH-Activated Lipid-like Material (ssPalm) as a platform of the DNA/RNA delivery system. The material forms a DNA/RNA-encapsulating nanoparticle with neutral charge, and it confer the endosomal escape, and subsequent release of their encapsulating cargos to the cytoplasm. Also, the trafficking and physiological functions of the particles can be controlled by the changing of the hydrophobic structure. Furthermore, the transfection activity was highly improved by the insertion of self-degradable linker. The authors summarized the concept and application of a series of ssPalm.
-
43 巻 (2020) 11 号 p. 1643-1652Sinomenine Inhibited Interleukin-1β-Induced Matrix Metalloproteinases Levels via SOCS3 Up-Regulation in SW1353 Cells もっと読む編集者のコメント
Sinomenine (SN), an alkaloid isolated from Sinomenium acutum, has been used therapeutically for arthritis in China over many years. Herein, it was found that SN dose-dependently increased SOCS3 expression levels and inhibited matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) levels in human chondrocyte cells. SOCS3 expression was increased by SN blocked IL-1β-induced interaction between TRAF6 and TAK1, thereby culminating in the inhibition of MMPs levels. In addition, SN also inhibited IL-6-induced JAK2 and STAT3 phosphorylation. These findings provided a molecular basis for the potential application of SN and suggested that SN exhibited a cartilage protective property for the treatment of arthritis.
-
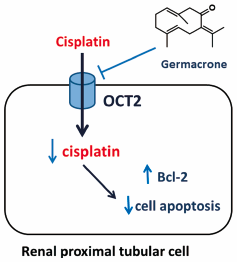
編集者のコメント
Nephrotoxicity induced by chemotherapy is common and limits the use of anticancer drug especially cisplatin. To improve the therapeutic efficiency of cisplatin, minimizing nephrotoxicity is very important. The present study investigated whether germacrone, a bioactive compound found in Curcuma species, has a protective effect on renal proximal tubular cells toxicity induced by cisplatin. The authors found that germacrone reduces cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in renal proximal tubular cells by inhibition of OCT2-mediated cisplatin uptake into renal proximal tubular cells. This result suggests that germacrone may be a candidate agent for reducing nephrotoxicity during cisplatin chemotherapy.
-
編集者のコメント
Lubiprostone is an effective drug for various types of constipation in patients without cancer; however, efficacy and safety in patients with cancer have not been clarified. In the present study, Sada et al. retrospectively compared the efficacy and safety of lubiprostone on constipation in patients with and without cancer. It is shown that while lubiprostone was as effective in cancer patients as in non-cancer patients, in cancer patients it was associated with a high incidence of diarrhea and nausea side effects, especially in patients with a low body-mass index.
-
43 巻 (2020) 11 号 p. 1792-1798Renal Reabsorptive Transport of Uric Acid Precursor Xanthine by URAT1 and GLUT9 もっと読む編集者のコメント
Xanthine and hypoxanthine are intermediate metabolites of uric acid formation and a source of reactive oxidative species (ROS) by xanthine oxidoreductase (XOR). They are reabsorbed in renal proximal tubules, but the mechanism has not been clarified yet. This study showed that xanthine is reabsorbed in the same manner as uric acid through uric acid transporters URAT1 and GLUT9, while hypoxanthine is not. Accordingly, it is expected that treatment with URAT1 inhibitor along with XOR inhibitor will effectively decrease purine pools in the body by suppressing reabsorption of xanthine increased by XOR inhibitor, thereby preventing cell injury due to ROS generated during XOR-mediated reactions.
-
編集者のコメント
The usefulness of the urine protein:creatine ratio (UPCR) in management of molecular targeted therapy has not been studied, although urine protein dipstick testing (uPr) is widely used. The authors investigated the usefulness of UPCR as compared to uPr in patients undergoing molecular targeted therapy for advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). They found that uPr-based grade tends to be higher than UPCR-based grade, which may lead to overestimate of proteinuria and unnecessary interruption of treatment. UPCR may be a better tool for evaluation of proteinuria in RCC patients receiving molecular targeted therapy.
-
編集者のコメント
Introduction: The present study was designed to explore the impacts of sinomenine on cell proliferation and invasion ability of RB cells and the related mechanism. WERI-RB-1 and Y79 cells were cultured and treated by different concentration of sinomenine. The authors found that sinomenine was able to decrease the proliferation and promote the apoptosis of RB cells in a dose-dependent manner; and also significantly suppressed the migration as well as invasion ability of WERI-RB-1 and Y79 cells in vitro via regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, suggesting that sinomenine has the potential to become an alternative medication for the treatment of RB.
-
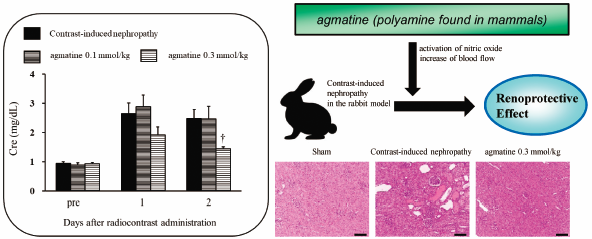
43 巻 (2020) 10 号 p. 1556-1561Effects of Agmatine on Contrast-Induced Nephropathy in Rats and Rabbits もっと読む編集者のコメント
The rapid degradation in kidney function caused by contrast media usually is temporary, but it can result in chronic kidney disease or even end-stage renal disease. Contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) is a common clinical problem for which there is no effective medical treatment. The aim of this study was to examine the protective effects of agmatine, which is a polyamine found in mammals, in a rat and a rabbit model of CIN. The results indicate that agmatine prevents the development of CIN-induced renal insufficiency in rabbits, and the effect is accompanied by activation of nitric oxide synthase and subsequent increase of blood flow.
-
43 巻 (2020) 10 号 p. 1562-1569Elaidic Acid Potentiates Extracellular ATP-Induced Apoptosis via the P2X7-ROS-ASK1-p38 Axis in Microglial Cell Lines もっと読む編集者のコメント
Elaidic acid (EA) is the most abundant food-derived trans-fatty acid (TFA), whose intake is associated with neurodegenerative diseases (NDs) including Alzheimer’s disease. Hirata et al. provide evidence implicating a novel microglial apoptosis signaling pathway in TFA-related NDs. In microglial cell lines such as MG6 and BV2, extracellular ATP, a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) leaked from injured cells, triggered reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent activation of the apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1)-p38 MAP kinase pathway, and ultimately apoptosis. EA strongly enhanced activation of the microglial apoptosis pathway, which may account for the underlying pathological mechanisms of TFA-related NDs that are closely associated with neuronal cell death and inflammation.
-
43 巻 (2020) 10 号 p. 1583-1590Effect of Cinacalcet on the Redox Status of Albumin in Secondary Hyperparathyroidism Patients Receiving Hemodialysis もっと読む編集者のコメント
Cinacalcet is a calcimimetic that permits impaired endothelial functions to be recovered via inhibiting parathyroid hormone (PTH) production in SHPT patients receiving hemodialysis. However, the underlying mechanism for its action remains unknown. The article by Imafuku et al. reported cinacalcet improves the redox status of human serum albumin (HSA) by inhibiting PTH production and partially by its radical scavenging action and increaed the anti-oxidant defense system in the blood circulation of SHPT patients. Such an anti-oxidative action of cinacalcet may, in part, explain the reduced risk for cardiovascular and all-cause mortality during cinacalcet treatment.
-
43 巻 (2020) 9 号 p. 1293-1300Current Understanding of the Intestinal Absorption of Nucleobases and Analogs もっと読む編集者のコメント
Knowledge of the intestinal absorption of nucleobases and analogs has accumulated, as is generally the case, mainly from studies using non-primate experimental animals. However, the recent identification of sodium-dependent nucleobase transporter 1, which plays a major role in their absorption in such animals, has led to exposing the fact that this important transporter is genetically missing in humans. To help to embark on efforts now needed to elucidate the mechanism of intestinal absorption of nucleobases and analogs in humans, which could be totally different from that in non-primate experimental animals, this article presents a comprehensive review on relevant knowledge and issues.
-
編集者のコメント
Vascular dementia (VD) is a common neurodegenerative disease, in the progress of which neuroinflammation and beta-amyloid (Aβ) deposition act as vital elements. In this study, lots of Aβ and nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome were found in VD rats’ brains induced by bilateral common carotid artery occlusion. A traditional Chinese medicine-Shechuangzi (osthole) extracted from the fruit of Cnidium monnieri (L.) possesses multiple pharmacological characteristics. This study has been proved the effect of osthole on VD rat evidenced by improving the behavior function, inhibiting the activation of microglia and reducing NLRP3 content, as well as decreasing the Aβ formation.
-
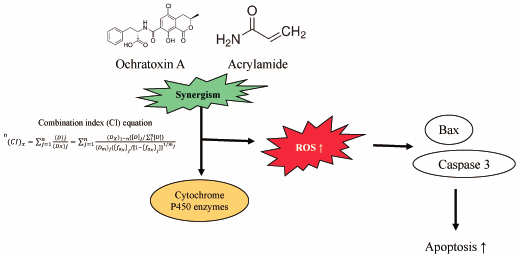
43 巻 (2020) 9 号 p. 1346-1355Synergistic Interaction of Ochratoxin A and Acrylamide Toxins in Human Kidney and Liver Cells もっと読む編集者のコメント
The toxicity of each ochratoxin A and acrylamide is known but there is uncertainty about the cumulative toxicity of two compounds. In this research, Pyo et al. demonstrated that there is a synergistic relationship between ochratoxin A and acrylamide that raises oxidative stress, reduces antioxidant enzymes and causes apoptosis, exacerbating liver and kidney toxicity. These findings indicate that the risk could be increased further by the food-borne toxicant 's interaction with the toxicant produced during processing.
-
編集者のコメント
Crocetin is a major bioactive component in saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and it has favorable cardiovascular protective effects. This study investigated the regulative effects of crocetin on L-type Ca2+ current (ICa-L), contractility, and the Ca2+ transients in rat ventricular cardiomyocytes using patch-clamp technique and Ion Optix system. The results indicated that crocetin inhibited ICa-L, intracellular Ca2+ concentration and contractility of cardiomyocytes. Crocetin (600 μg/ml) reduced cell shortening and the crest value of the ephemeral Ca2+ by 28.6 ± 2.31%, 31.87 ± 2.57%, respectively. These findings reveal that crocetin could be a potential calcium blocker for the treatment of cardiovascular disease.