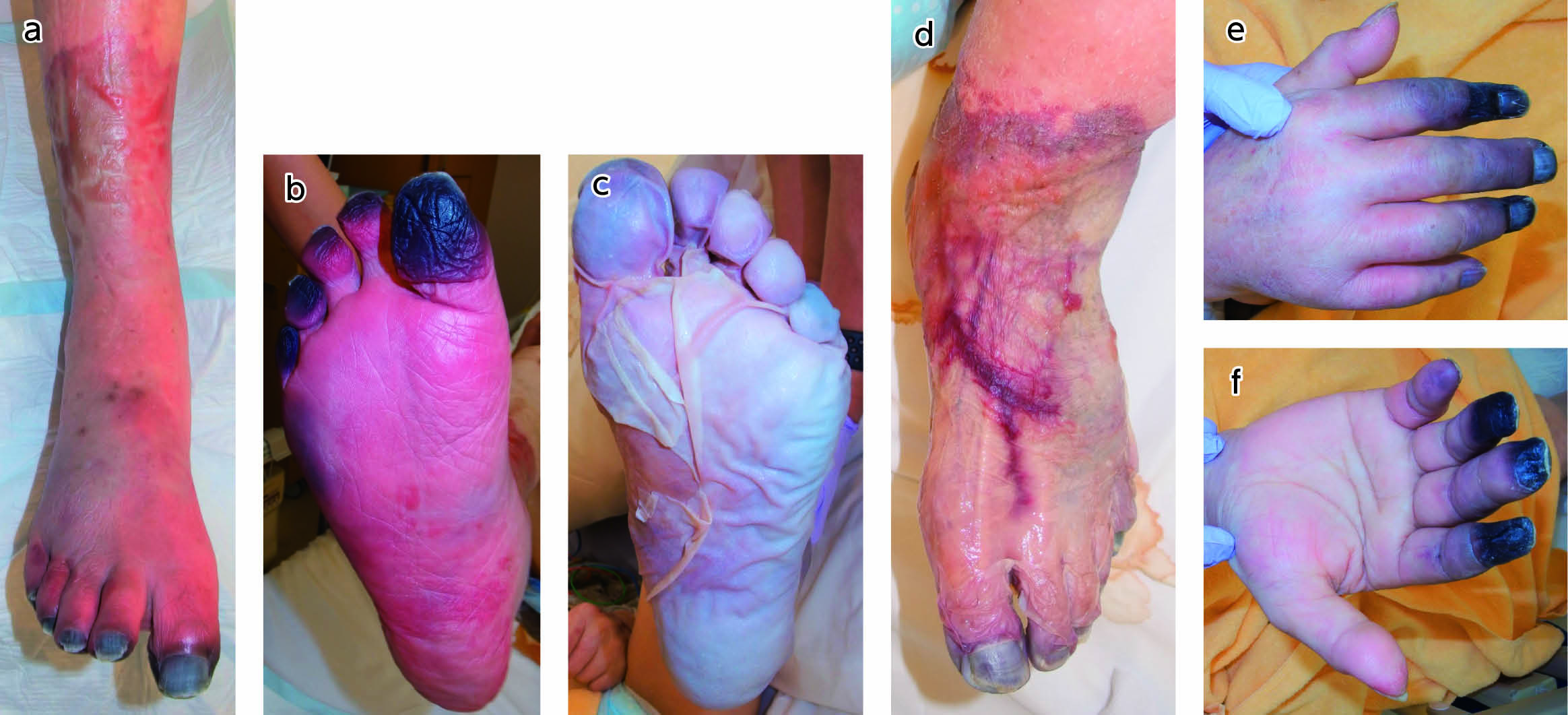
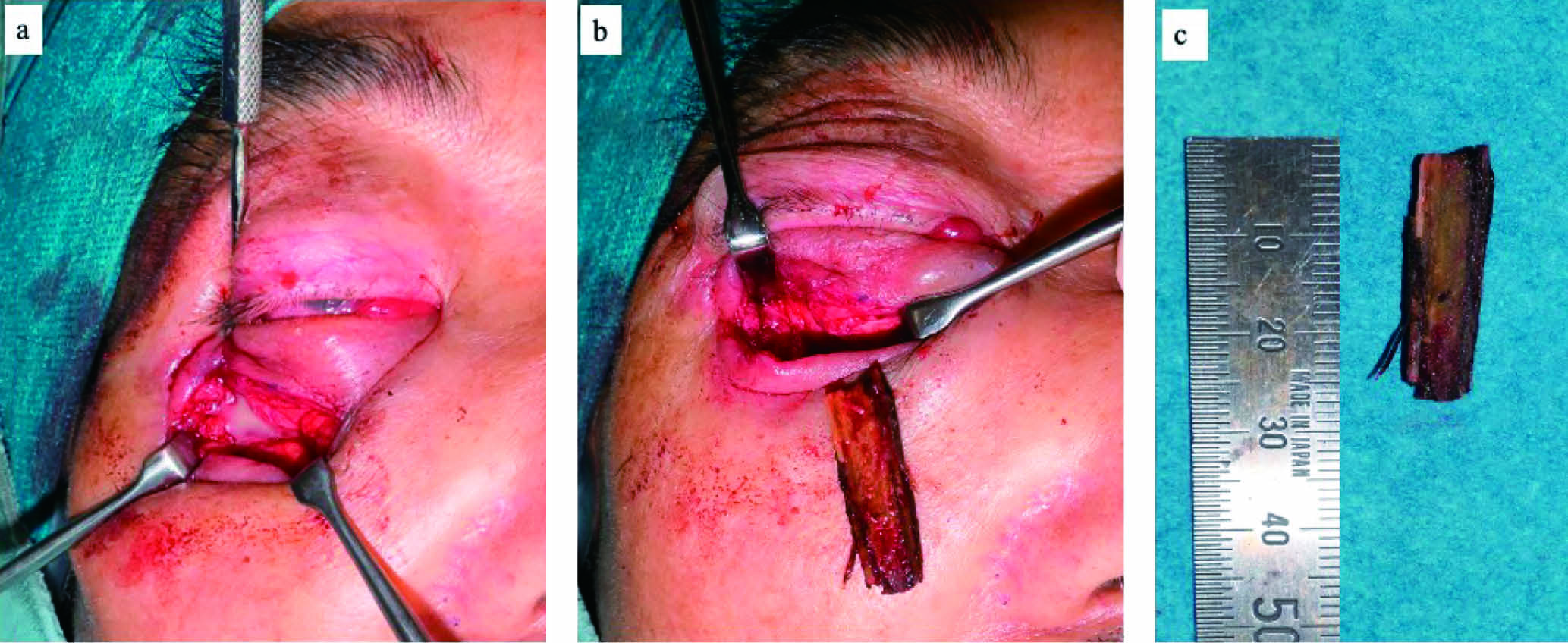
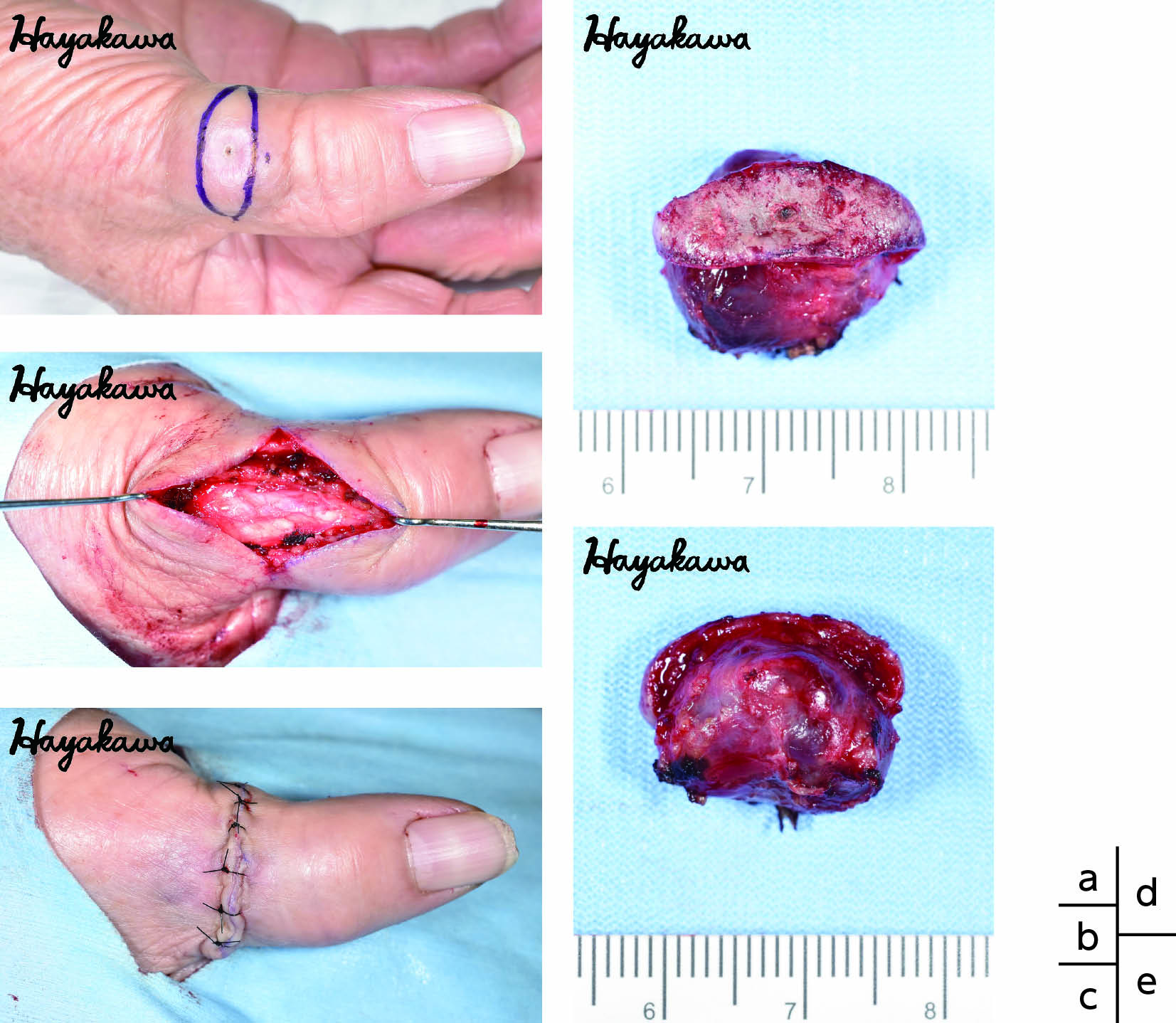
4 巻, 3 号
選択された号の論文の7件中1~7を表示しています
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Original Article
-
2023 年 4 巻 3 号 p. 81-91
発行日: 2023年
公開日: 2023/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1533K)
Case Reports
-
2023 年 4 巻 3 号 p. 92-98
発行日: 2023年
公開日: 2023/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1176K) -
2023 年 4 巻 3 号 p. 99-103
発行日: 2023年
公開日: 2023/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1043K) -
2023 年 4 巻 3 号 p. 104-108
発行日: 2023年
公開日: 2023/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (986K) -
2023 年 4 巻 3 号 p. 109-113
発行日: 2023年
公開日: 2023/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (824K) -
2023 年 4 巻 3 号 p. 114-120
発行日: 2023年
公開日: 2023/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1023K) -
2023 年 4 巻 3 号 p. 121-127
発行日: 2023年
公開日: 2023/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1238K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|