
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. Cover-
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
ジャーナル オープンアクセスPDF形式でダウンロード (406K) -
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. Editorial-
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
ジャーナル オープンアクセスPDF形式でダウンロード (704K) -
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. Contents-
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
ジャーナル オープンアクセスPDF形式でダウンロード (316K)
-
Wen Yang, Lifeng Zhang, Ying Ren, Wei Chen, Fenggang Liu原稿種別: Review
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 1-20
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/12/06ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLNozzle clogging is a common phenomenon in the continuous casting of steels, especially for aluminum killed steels, and has detrimental effects on the continuity of casting and the steel cleanliness. The formation and prevention of nozzle clogging during the continuous casting of steels was reviewed in the current study. The characterization of nozzle clogging was firstly summarized, finding that the composition, morphology, and structure of the nozzle clogging significantly depended on the steel grade, casting condition, and clogging degree. Then three factors affecting the formation of nozzle clogging was briefly summarized as the physical adhesion of high-melting-point inclusions, the temperature drop resulted from the insufficient preheating of nozzles and the temperature fluctuation of molten steel, and the chemical reactions occur during the continuous casting. The prevention methods of nozzle clogging could be roughly divided into 5 types, including the cleanliness improvement of steel, the liquid modification of inclusions, the fluid flow control inside the nozzle, the coating treatment on the inner surface of nozzles, and the external field treatment. Moreover, the challenge of the nozzle clogging control in the future was proposed. Multiple methods should be coordinated, especially the external field treatment should be developed to achieve a better inhibitory effect on the nozzle clogging.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2754K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2754K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Raymond James Longbottom, Brian Joseph Monaghan原稿種別: Regular Article
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 21-29
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/11/22ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLThe effects of coke mineralogy and carbon structures on coke dissolution in liquid iron were studied at 1500°C. Coke mineralogy was studied by measuring the dissolution of three cokes, with three different mineralogies, in liquid iron. To allow the change in carbon structures in the coke during dissolution to be determined, samples were quenched and characterised. The dissolution of coke analogue samples were also studied, which contained the ash from the cokes.
The three cokes were found to have distinctly different dissolution rates. The dissolution of the three coke analogue samples was found to closely replicate the dissolution of the three cokes. By using the coke analogue, carbon structure, porosity and particle size were largely eliminated as variables. Therefore, it was likely that the differences in coke minerals between the three cokes were predominantly responsible for the dissolution rates of the samples.
The differences in carbon structure between the cokes likely had little effect on the dissolution of coke in liquid iron. To help understand this, Raman spectroscopy of quenched samples was used to assess the changes in carbon structures in the coke samples during dissolution. The cokes became more graphitic with time at 1500°C. Further, though the coke started off with different carbon structures, the cokes assessed tended to a similar value dominated by the temperature effect on graphitisation.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (999K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (999K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Yifan Duan, Xiaojie Liu, Xin Li, Ran Liu, Hongwei Li, Jun Zhao原稿種別: Regular Article
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 30-43
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/12/06ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLEfficient matching of the preheat-numbers of the molten iron ladle with yield of molten iron in a single iron time is conducive to reducing energy waste, so it is of great economic significance to iron and steel enterprises to accurately predict yield of molten iron according to the characteristics of the per furnace. In this article, considering the variation of yield of molten iron and corresponding synergistic parameters depending on furnace conditions, we use the multi-head attention mechanism to capture the Attention-score of the feature parameters, and the weight matrix of the predictor is dynamically adjusted, so that it can assign more training weights to high-value feature parameters in real time according to the change of furnace conditions, efficiently complete the prediction of yield of molten iron. First, twenty characteristics are selected by mutual information method. Then, the influence degree of selected features on yield of molten iron is calculated in real time. Finally, stacked denoising auto encoder (SDAE) is used to train the deep neural network, and we constructed the predictor after adjusting the parameters to optimal. The test results show that the prediction accuracy of proposed model is 95% under the error range of ±50 t, which is higher than traditional SVM, DAE, and SDAE model without the multi-head attention mechanism. Ultimately, we analyze and quantify the influence process of 20 factors on yield of molten iron, and develop a dynamic prediction system of yield of molten iron based on proposed model, which has good applicability for the prediction of yield of molten iron and effectively guides the transfer scheduling of molten iron ladles.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2364K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2364K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Yoshihiro Kubo原稿種別: Regular Article
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 44-51
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/10/31ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLThe aim of this project was to learn roles of titanium oxide (TiO2), an impurity contained in iron sand, in the products resulting from traditional iron making processes, tatara operations. For this purpose, iron sand was collected using two different mineral processing methods from four different locations in the Chugoku area of Japan, and these samples were used to run small-scale tatara experiments. Iron sand collected with traditional gravity separation method contained 8 to 12% TiO2, while iron sand collected with modern magnetic separation method contained less than 5% TiO2. When gravity-separated iron sand was used in a tatara under strong reducing conditions, zuku (cast iron) flowed out of the tatara. In contrast, magnetically collected iron sand failed to produce zuku, but did produce raw steel at the bottom of the furnace. Further, even magnetically isolated iron sand could produce zuku when it was supplemented with ilmenite, a titanium-iron oxide containing mineral. The results show that TiO2 plays a key role in producing cast iron in tatara operations, and the fact that Akome iron sand is known to produce cast iron as it contains higher levels of TiO2. In contrast, Masa iron sand which is known to produce steel (tamahagane) contains much less TiO2 and hence is not suitable to produce cast iron. These observations agree with historical descriptions stating that pre-modern tatara operators knew to add iron sand from a specific locality (which is rich in TiO2) to Masa-type iron sand to produce cast iron.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (676K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (676K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Sha Ji, Kaijun Niu, Alberto N. Conejo原稿種別: Regular Article
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 52-58
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/12/06ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTML
電子付録A three-dimensional computational fluid-dynamics (CFD) model containing three phases: water, oil, and air was developed to study the mass transfer process at the slag-steel interface in the ladle. The transient mass transfer between slag and metal phases occurred only at the interface and the transient irregular distorted interface was considered. A more realistic concentration distribution and transient variation process of mass transfer in the bottom-blown ladle was obtained.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1024K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1024K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Guangye Xu, Kazuhiko Iwai原稿種別: Regular Article
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 59-66
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/11/29ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLThe mass transfer in the concentration boundary layer is often the rate-determining step for solid-liquid chemical reactions. Decreasing the concentration boundary layer thickness is essential to intensify the solid-liquid chemical reaction. Because convection contributes to decreasing the concentration boundary layer thickness, traditional methods excite a macro-scale flow in the bulk region. Since the concentration boundary layer exists in the velocity boundary layer near the solid-liquid interface, the traditional methods have limitation in enhancing the mass transfer. Based on this reason, the direct flow excitation near the solid-liquid interface by imposing an electromagnetic force was proposed. The aim of this research is to evaluate the effect of the time-varying electromagnetic force and its frequency on the mass transfer near the solid-liquid interface by evaluating the effective diffusion coefficient. The effective diffusion coefficient was evaluated under the imposition of a static electromagnetic force or a time-varying electromagnetic force with a frequency of 2 Hz or 6 Hz. The results found that by imposing the time-varying electromagnetic force, the mass transfer was enhanced compared to that under the imposition of the static electromagnetic force. The mass transfer was further enhanced by decreasing the time-varying electromagnetic force frequency.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1219K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1219K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Kun Lu, Wenyan Wang, Xuejuan Pan, Yuming Zhou, Zhaoquan Chen, Yuan Zha ...原稿種別: Regular Article
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 67-75
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/11/04ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLIdentifying surface defects is an essential task in the hot-rolled process. Currently, various computer vision-based classification and detection methods have achieved superior results in recognizing surface defects. However, defects typically exhibit irregular shapes caused by intra-class differences. Therefore, these two methods are unable to accurately identify the specific locations of the defects. To address this issue, this work proposes a U-shaped Encoder-Decoder framework called Resformer-Unet, which can effectively detect surface defects of hot-rolled strip at the pixel-level. In this framework, the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Transformer work in parallel to extract multi-scale features from the image, which enhances the ability of network to capture both global and local information. Additionally, feature coupling modules are employed to fuse multi-scale features, thereby compensating for the information loss that occurs during down-sampling. On the SD-saliency-900 dataset for strip steel surface defect segmentation, Resformer-Unet achieves a mean Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) of 89.96% and an average Hausdorff Distance of 12.03%. These results outperform those of several advanced methods.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1589K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1589K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Zi-xuan Xiao, Zheng-hai Zhu, Guang-xu Wei, Shang-Dong Liang, Cheng-che ...原稿種別: Regular Article
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 76-83
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/12/06ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLTo address the problem that speed and accuracy cannot be taken into account in intelligent detection models of center porosity in round bloom, an improved model for it based on YOLO v5s (the fifth version of You only look once) was determined by establishing a data set of about 10000 images, setting up a contrast experiment and an ablation experiment embedded with Coordinate Attention and Slim-neck modules. The results show that the improved YOLO v5s has good detection performance: mAP@0.5 of the verification set reaches 99.17%, which is respectively 0.2%, 0.1%, 2.9% and 1.7% higher than Faster RCNN, SSD, YOLO v3-Tiny and YOLO v5s; the detection speed is 86 fps, which is respectively 514.2%, 168.8% higher than Faster RCNN, SSD and maintains the speed of the original YOLO v5s while its accuracy is improved. The operation time of a single picture in the testing set is only 0.015 s, which could be implemented the achieve real-time and accurate location of center porosity in round bloom. This study provides a new method for the research of detecting center porosity, which is helpful to the development of intelligent detection of defects in continuous casting billet.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1036K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1036K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Cancan Yi, Kun Liu, Tao Huang, Han Xiao原稿種別: Regular Article
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 84-95
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/11/22ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLIn steel production, the recognition of hot-cast billet numbers suffers from low efficiency and susceptibility to misjudgment. This paper proposes a novel method for identifying hot-cast billet numbers on the basis of improved Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network (ICRNN). Although the existing CRNN has achieved acceptable results in text recognition and music symbol recognition, it is not effective in recognizing industrial characters that are blurred or low-contrast. Based on the theoretical framework of CRNN, the Grayscale Spatial Transformation Network (GSTN) is added before character recognition to rectify the skew caused by shooting angles. The backbone network for feature extraction is changed to ResNet50. Moreover, the Efficient Channel Attention (ECA) module is added to construct the Res-ECA network, which extracts more features of the billet number characters. In the sequence modeling stage, the Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Unit (BiGRU) is used to reduce the risk of overfitting and accelerate convergence. After experimental comparison on a self-made billet number dataset, the put forward ICRNN has faster recognition speed and higher accuracy, with a recognition accuracy of 99.49%, which is 4.8% higher than that of the CRNN. The result fully demonstrates that ICRNN meets the requirements of accuracy and speed for billet number recognition.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1424K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1424K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Fumin Li, Lingru Meng, Xiaojie Liu, Xin Li, Hongyang Li, Jianjun Mi原稿種別: Regular Article
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 96-104
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/12/06ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLBlast furnace hanging is an abnormal furnace condition with the highest frequency. The judgment of hanging mainly relies on manual analysis, but this approach has strong subjectivity and time lag. In order to solve the above problems, this paper proposes a ReliefF - Decision Tree based anomaly diagnosis model to identify the hanging. Firstly, 10 relevant parameters are extracted based on expert experience, and each characteristic parameter is weighted using ReliefF algorithm after preprocessing. Secondly, the calculated weights of the characteristic parameters are sorted from the largest to the smallest, and the seven most effective characteristic parameter sets are selected as the decision nodes of the decision tree, which is constructed according to the expert rules of hanging diagnosis to complete the training and testing of the classifier. Simulation results show that the accuracy of the ReliefF - Decision Tree model reaches 96.5%, and the recognition rate of the two anomalies of “burden stop” and “sudden rise of differential pressure” exceeds 80%, which is 83.1% and 87.5%, respectively, indicating that the performance of the model is good. Finally, the expert diagnosis system is built, which effectively improves the diagnosis efficiency of hanging.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1035K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1035K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Linghui Meng, Kai Dong, Chao Feng原稿種別: Regular Article
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 105-115
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/11/01ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLUsing high-temperature pure iron (DT8) as the research object, the spectral irradiation intensity properties of DT8 at temperatures ranging from 1510 to 1620°C were analysed. The luminescence spectrum of DT8 exhibited four characteristic peaks within the measured wavelength range. The corresponding wavelength ranges were 588–590, 765–770, 940–950, and 960–970 nm. The peaks in each wavelength range decreased significantly with decreasing temperature. The luminescence spectrum of DT8 was further investigated using a multiple-peak fit, and a mathematical model of the spectrum was created using the link between the fitted peak parameters and the temperature. Error analysis was performed on the model-calculated and original spectra after supplementation, and the error evaluation index, R, of the actual measured and model-calculated spectra was defined. Through calculations, it was determined that the degree of coincidence, R, between the calculated results of the model and the actual measured results was >99.1%, whereas R increased slightly with an increase in temperature.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1358K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1358K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Yuto Watanabe, Takashi Matsuno, Takayuki Hama, Tomoko Matsuda, Yoshita ...原稿種別: Regular Article
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 116-125
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/12/06ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLMartensite-matrix dual-phase (DP) steel is increasingly used for high-strength automobile parts owing to its excellent compatibility, ductility, and tensile strength. However, its higher fracture strain, reflected by the hole expansion ratio, hinders further adoption of this material. Therefore, in this study, we conducted a microscale investigation of the ductile fracture behavior of 1180-MPa class martensite-matrix DP steel to obtain a guideline for microstructural design and improve fracture strain. In situ tensile test was conducted simultaneously with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and crystal plasticity finite element analysis (CP-FEA). The in situ tensile test results indicated that microcracks initiated at certain martensite packets, not propagating into other packets. The CP-FEA results revealed that the martensite crystal orientation caused this behavior to induce remarkable stress and strain localization at interfaces within the vicinity of ferrite islands, relaxing the stress and strain localization at distant martensite packets. Although the cracks observed around the ferrite–martensite interfaces were similar to those observed in conventional ferrite-matrix DP steels, such matrix-phase cracks have rarely been reported, except for those immediately before final fracture. Thus, the optimization of the ferrite island distribution to suppress the formation of stress and strain localization sites was identified as the key aspect of martensite-matrix DP steel microstructural design. This design can be achieved using a combination of data science and CP-FEA.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4103K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4103K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Daiki Nakanishi, Tetsuya Uchiyama, Hiroyuki Shirahata, Manabu Takahash ...原稿種別: Regular Article
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 126-133
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/11/29ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLThe microstructures of intra-granular bainite nucleated on Ti-oxide particles (IGB) and grain boundary upper bainite (GBB) in Ti-deoxidized steel (Fe-0.1mass%C-1.5mass%Mn-2mass%Ni-1mass%Cu) were investigated by EBSD analysis and 3-dimentional observation. The steel was austenitized at 1673 K for 23 s, held at 803 K for 7 s-20 ks and then quenched to room temperature. 803 K is just below the bainite transformation start temperature. IGB and GBB were observed at 5% bainite transformation. Despite the formation of IGB, part of GBB grew to a size of 100 µm at 17% bainite transformation, and coarsened to 130–200 µm at 85% bainite transformation. Mechanism of the GBB coarsening is discussed in terms of differences in (1) the microstructures and (2) the nucleation site of IGB and GBB. A single packet with many blocks was observed in GBB nucleated at whole surface of austenite grain boundaries with a size of 400–500 µm, while multiple packets with two blocks were observed in IGB nucleated on Ti-oxide particles with a size of 1–2 µm. IGB suppressed the growth of GBB by impingement. However, as the GBB was much larger than IGB, part of the GBB was not impinged by the IGB and continued to grow. GBB grew until all blocks of GBB were impinged by IGB and/or transformation was finished, resulted in GBB coarsening.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1908K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1908K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Junji Miyamoto, Masashi Yoshida原稿種別: Regular Article
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 134-141
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/11/29ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLSamples treated using conventional plasma nitriding have good surface hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and fatigue strength, but their friction coefficients are not low enough. This study presents a novel method of reducing the friction coefficient of AISI H13 tool steel through a hybrid treatment consisting of atmospheric-pressure plasma nitriding and superheated steam treatment. The surface structures and tribological and mechanical properties of a hybrid-treated sample were investigated. Results showed that atmospheric-pressure plasma nitriding had no effect on the formation of Fe3O4, which improves the corrosion and tribological properties of tool steel. The surface of the hybrid-treated sample had an oxide layer separated into two layers. The nitrided and non-nitrided samples had nearly the same thickness of the oxide layer. The outermost layer of the hybrid-treated sample contained almost no Cr, a large amount of nitrogen, and small amounts of Fe and O. From its outermost surface to its base material, this sample had a three-layer structure consisting of a nitride layer, a Fe3O4 layer, and a Cr-rich oxide layer. The depth of the diffusion layer of the hybrid-treated sample was greater than that of a sample treated using atmospheric-pressure plasma nitriding only. The outermost surface of the hybrid-treated sample was softer than its inner part, and the hybrid-treated sample had the lowest friction coefficient among all samples. Overall, the hybrid treatment reduced the friction coefficient and improved the wear resistance of AISI H13 tool steel.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2098K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2098K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Satoshi Noguchi, Syuji Aihara, Junya Inoue原稿種別: Regular Article
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 142-153
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/11/04ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLIn material design, the establishment of process–structure–property relationship is crucial for analyzing and controlling material microstructures. For the establishment of process–structure–property relationship, a central problem is the analysis, characterization, and control of microstructures, since microstructures are highly sensitive to material processing and critically affect material’s properties. Therefore, accurately estimating the morphology of material microstructures plays a significant role in understanding the process–structure–property relationship. In this paper, we propose a deep-learning framework for estimating material microstructures under specific process conditions. The framework utilizes two deep learning networks: vector quantized variational autoencoder (VQVAE) and pixel convolutional neural network (PixelCNN). The framework can predict material microstructures from the transformation behavior given by some physical models. In this sense, the framework is consistent with the physical knowledge accumulated in the field of material science. Importantly, our study demonstrates qualitative and quantitative evidence that incorporating physical models enhances the accuracy of microstructure prediction by deep learning models. These results highlight the importance of appropriately integrating field-specific knowledge when applying data-driven frameworks to materials design. Consequently, our results provide a basis for integrating data-driven methods with the accumulated knowledge in the field. This integration holds great potential for advancing material design through deep learning.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4263K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4263K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Kuo-Tsung Huang, Shih-Hsien Chang, Che-Wei Chang原稿種別: Regular Article
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 154-164
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/11/22ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLThis research added different ratios of Ta50Nb50C and B4C powders to Vanadis 60 high-speed steel powders, and then, sintered the Vanadis 60 composite from 1205 to 1225°C by vacuum sintering for 1 hour. Subsequently, a series of heat treatments were conducted, including quenching, sub-zero, and tempering processes. The study results show that the optimal sintering temperature and the additive ratio for Vanadis 60 composites were 1205°C and 0.975 mass% Ta50Nb50C-0.025 mass% B4C powders, respectively. Simultaneously, the transverse rupture strength (TRS) value was 2328.2±0.90.7 MPa and the hardness value was 81.3±0.1 HRA, respectively. In particular, when the optimally sintered Vanadis 60 composite underwent sub-zero plus heat treatments, the TRS and hardness values obviously increased to 2456.6±76.3 MPa and 85.7±0.3 HRA, respectively. Finally, the TEM and EBSD study results also revealed that various MC and M6C-type carbides significantly appeared in the Vanadis 60 composite after vacuum sintering and sub-zero plus heat treatments.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3631K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3631K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Ganna Stovpchenko, Lev Medovar, Danylo Stepanenko, Zhouhua Jiang, Yanw ...原稿種別: Regular Article
2024 年 64 巻 1 号 p. 165-173
発行日: 2024/01/15
公開日: 2024/01/15
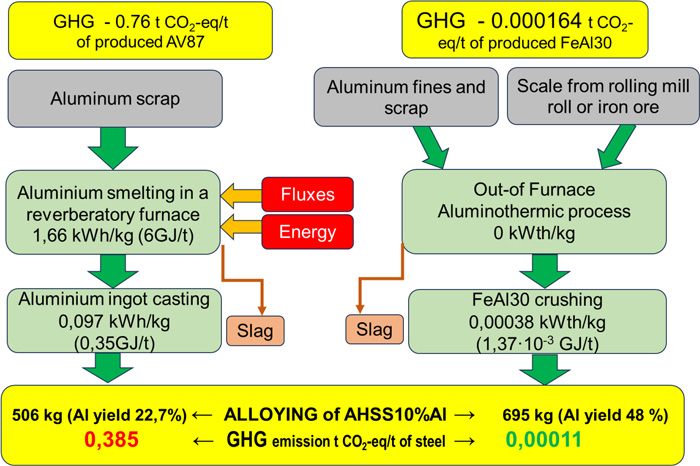
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/11/04ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLThe ironmaking and steelmaking industry is one of the heavy polluters responsible for nearly 7% of global carbon dioxide and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Creating new technologies and equipment and renewing the assortment of metallurgy products is compulsory to achieve the goal of climate change prevention. Lightweight and advanced higher-strength steels (AHSS) to replace old mild grades and simultaneously decrease the mass of ready products is one of the efficient ways. Three generations of AHSS of different chemical compositions and properties have already been developed, including lightweight grades alloyed with a high aluminium content. A review of the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) results proves the energy and environmental efficiency of Advanced High Strength Steels (AHSS) compared with aluminium and HSS for the same purpose structures in vehicles. Using aluminothermic ferroaluminium from secondary materials helps to reduce the cost of lightweight steels with high aluminium content due to the 2–3 times higher assimilation of aluminium by liquid steel at both deoxidation and alloying, which was experimentally proved for HSS grades. Due to less energy consumption at ferroaluminium than secondary aluminium ingots manufacturing, alloying of AHSS (10% wt of Al) by FeAl30 reduces GHG emission for more than 0.384 t CO2-eq per ton of steel.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (795K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (795K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|