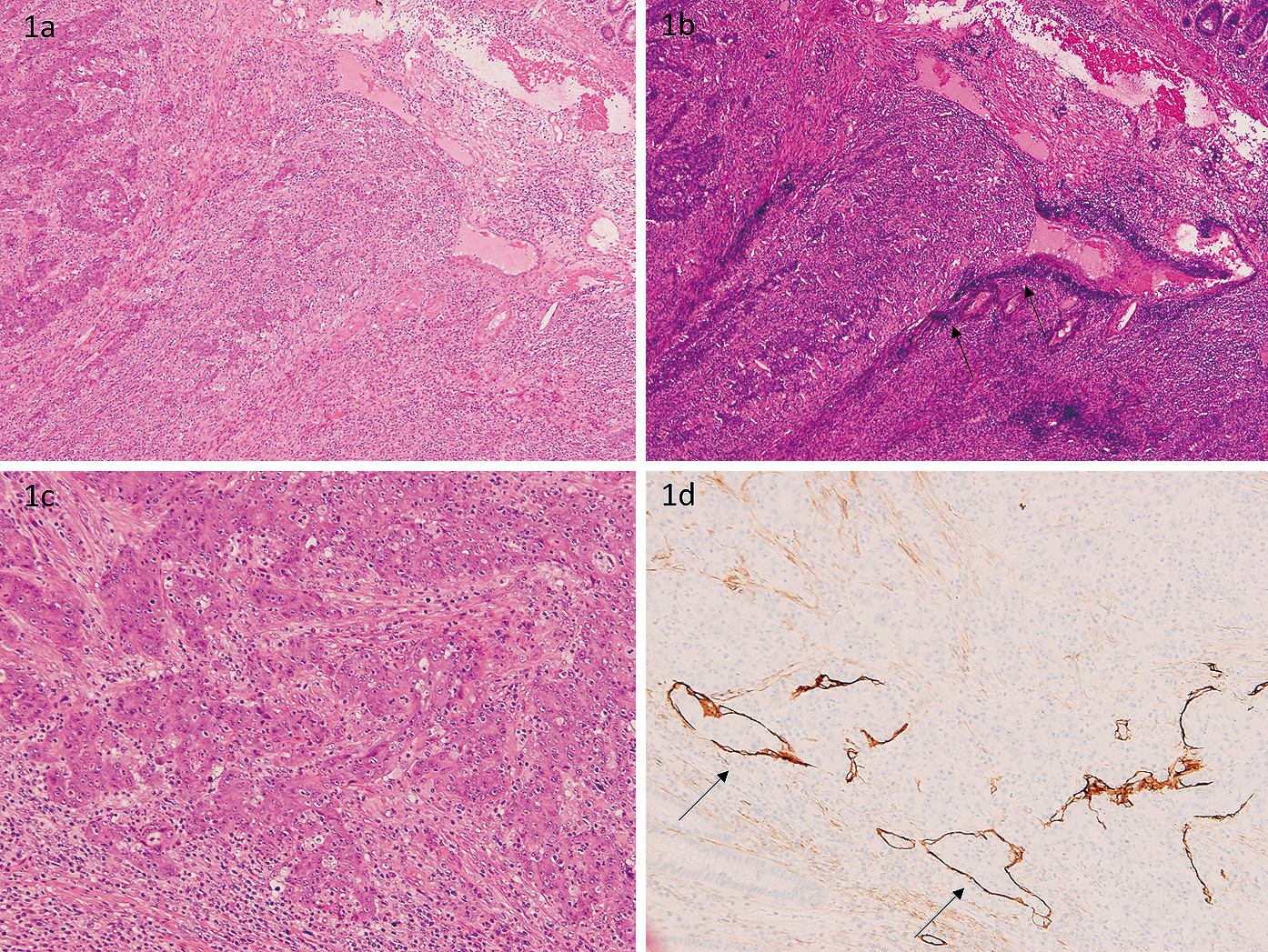
Objectives: There are differences in each country with regards to histopathological managements of colorectal cancer (CRC), such as definition of Tis and lymphatic and venous invasion. In this study, we compared Tis and T1 CRC in Japan and Korea. Methods: We retrospectively compared various clinical characteristics of consecutive patients who had Tis and T1 CRCs and who were newly diagnosed between 2010 and 2014 at the Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine (Japan) and the Konkuk University (Korea). Results: Three hundred and sixty-five cases of T1 cancer and 510 cases of Tis cancer from 726 Japanese and 149 Korean patients were included. The rate of Tis in Japan was higher than in Korea (59.8% vs. 51.0%, P = 0.047), according to the difference of definition of Tis. In the analyses of 365 T1 CRCs, median age was higher in Japan than Korea (67.8 ± 10.6 vs. 62.2 ± 10.1, P < 0.001). Right-sided lesions were more frequent in Japan than they were in Korea (38.7% vs. 22.2%, P < 0.001). The rates of venous and lymphatic invasion were higher in Japan than they were in Korea (venous: 18.6% vs. 1.4%, P < 0.001, lymphatic: 25.3% vs. 13.7%, P = 0.042), according to the different methods of immunohistochemical examinations used (Japan: E-HE and D2-40, Korea: ERG). Conclusions: Our study of T1 CRC showed that there were differences between Japan and Korea in tumor location, elderly incidence, and histopathological lymphatic and venous invasion. Additionally, rates of Tis were different between the two countries. In this international study for CRC, it is considered that we have to pay attention regarding the difference of histopathological definition and method in each country.
抄録全体を表示