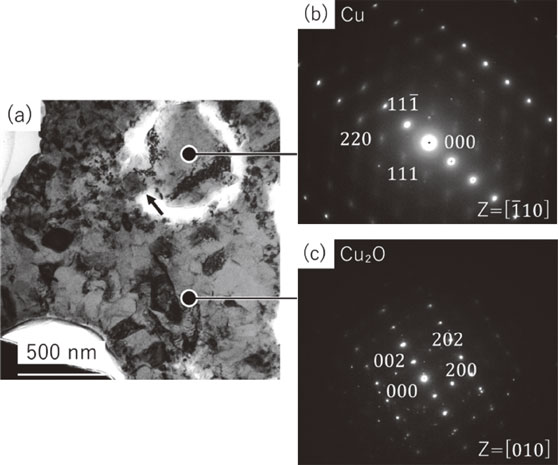
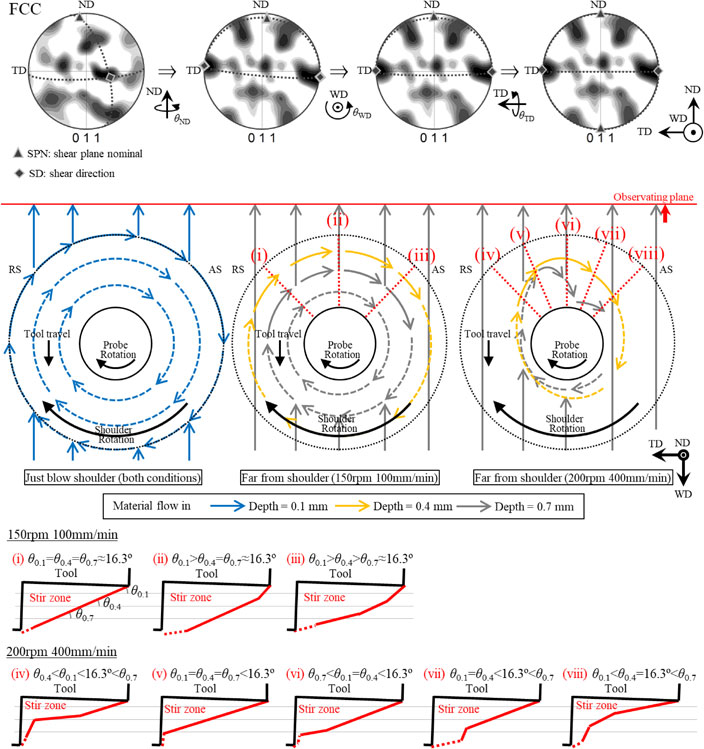
日本金属学会誌
日本金属学会誌は、1937年に創刊し、金属のみならず関連する電子材料、磁気材料、超電導材料、
セラミックス等の先端材料に関する幅広い分野の研究成果を対象とする貴重な和文学術論文誌であり、
研究成果を幅広く国内外へ情報発信しています。
もっと読む
公益社団法人 日本金属学会
が発行
収録数 13,069本
(更新日 2025/06/05)
(更新日 2025/06/05)
Online ISSN : 1880-6880
Print ISSN : 0021-4876
ISSN-L : 0021-4876
Print ISSN : 0021-4876
ISSN-L : 0021-4876
0.500
2023 Journal Impact Factor (JIF)
2023 Journal Impact Factor (JIF)
ジャーナル
査読
フリー
HTML
早期公開
Scopus
Scopus