-
-difference between wave-type cage and crown-type cage-
Shun TAKAGI
Session ID: S112p-04
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
As an effort to reduce energy loss, low torque rolling bearings are required. There are various types of rolling bearing cages with different materials and shapes. In this study, we investigate the influence of the cage on torque. Under oil lubrication and grease lubrication conditions, we measure torque of the wave-type and crown-type cage. Under grease lubrication conditions, the mass of grease is changed on basis of mass and space volume, torque is measured. Under oil lubrication condition, the crown-type cage exhibited lower torque. Under grease lubrication conditions, the wave-type cage exhibited lower torque when the amount of grease was low, and the crown-type cage exhibited lower torque when the amount of grease was high. Therefore, it can be said that it is appropriate to select wave-type cage when the mass of grease is small for high-speed rotation, and crown-type cage when the mass of grease is large for low-speed rotation and heavy load.
View full abstract
-
Yutaka HIRAO, Takuya KANO, Gang DENG
Session ID: S112p-06
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
If the maximum stress at the critical point is used to evaluate the bending fatigue strength of a crowned arc-notch three-point bend specimen, the fatigue strength will be greater than the yield point, and yielding is considered to occur in a small region near the critical point. In this study, in order to confirm the yielding phenomenon in bending fatigue tests, the stress-strain relationship during the loading and unloading process was investigated using nonlinear FEM analysis, and the residual strain at the critical point was measured using the presented back-cut method. As a result, the residual strain at the critical point was confirmed. So, it was clarified that small range yielding should be considered in the bending fatigue strength design of mechanical elements with stress concentration.
View full abstract
-
Rikuto SAWADA, Toshiyuki KAWAHARAMURA
Session ID: S112p-07
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
Tools for moving and transporting within walking distance are still under development. Certainly, there are tools such as belt conveyors and escalators. But these have high transportation costs and limited moving area, obviously there is still room for development. In fact, warehouses still require human intervention, for example, it is necessary of staffs’ hands for sorting at various points, even with installation of conveyors in factories. Moreover, special orders must be made each time because conveyor specifications must be changed according to the factories. In such a narrow area, it is thought that a transportation system by mechanical control that can flexibly respond and is good at versatility is necessary. Therefore, a movement and transportation supporting system “Euclitor” has been proposed in our laboratory, which has both flexibility and safety in neighborhoods and crowed area and has a low transportation cost. We are currently developing two types of mechanisms. One is a spherical type that emphasizes a high degree of freedom in the transportation direction and the other is a belt type that was derived with the purpose of increasing the transportable weight. In addition, since Euclitor requires the simultaneous control of multiple units, it is essential to establish communication control methods between units and develop control system programs. And we are also involved in such development.
View full abstract
-
Kazuhisa TAKEMOTO
Session ID: S113-01
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
In recent years, the number of motorcycle engines adopting cylinder offset has increased, but there is no literature that confirms the validity of the calculation formula for the slider crank mechanism with cylinder offset, which is the basis of dynamics. We need to establish the basis of the calculation formula used when adopting the cylinder offset to increase the certainty of the crank shaft design. As a result of verifying the approximation deployment method and the order of the variables used during approximation deployment based on mass production past record for motorcycle engines, it was confirmed that the piston inertia force is expressed by the following calculation formula.
View full abstract
-
Kazuhisa TAKEMOTO
Session ID: S113-02
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
In recent years, the number of motorcycle engines adopting cylinder offset has increased. But a formula for determining the amount and direction of unbalance added to the counterweight of the crank shaft necessary to achieve the desired ratio of crank shaft balance and the desired angle of principal axis of inertia used when adopting the cylinder offset is not shown even though that is important especially in the crank shaft design stage. As a result of verification using the actual product, it was confirmed that the amount and direction of unbalance required to achieve the desired ratio of crank shaft balance and the desired angle of principal axis of inertia are expressed by the following calculation formula.

View full abstract
-
Yoshihiko MATSUMOTO, Yasuhiro INOUE
Session ID: S113-03
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
Link mechanisms are advantageous for implementing complex motions by a simple structure and input. However, designing the structure of the link mechanisms to accomplish the desired movements through inverse analysis poses a significant challenge. This is primarily due to the inherent nonlinearity of the link mechanism equation. Although many methods have been proposed to address this issue, most of them focus on designing the link mechanisms to perform a desired movement using the trajectory as input. However, for certain mechanisms such as walking mechanisms, it is not always clear what an appropriate trajectory might be. Thus, we are developing the design method that uses the desired "function" as input, rather than a predefined trajectory. This method employs a genetic algorithm in conjunction with a 2D rigid body simulation. By combining the evaluation of the movements on the simulation with the genetic algorithm, it enables the design of the desired link mechanism without the need for a precise target trajectory. We show the result using the proposed method for designing walking mechanisms and discuss potential improvements to our method.
View full abstract
-
(Reset Control to Suppress Chaotic Disturbance for Pneumatic Control valve )
Masataka Iwai
Session ID: S113-04
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
In increasingly complex systems, it is becoming increasingly difficult to accurately identify the location of failures and the extent of their effects. Chaos engineering is a method to improve the reliability of the system by causing failures to reveal the problems. In this study, we propose a method of reset control that suppresses the failure of a pneumatic control valve by simulating the failure of the valve, incorporating the concept of chaos engineering. In this study, in order to investigate a new control method for the control parts of the positioner, simulations are conducted in which a chaotic signal is superimposed as a simulated disturbance on the input signal of a mathematical model of a pneumatic control valve with an electronic positioner. As an appropriate control method for control parts of the positioner, we apply the reset control, which autonomously generates pulses from the control deviation as a feedback control. The parameters of the reset control are adjusted for this model, and the simulation results show this reset control with these parameters can suppress failures caused by the superimposition of simulated chaotic signals.
View full abstract
-
Takashi HARADA, Hayato YASE
Session ID: S113-05
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
The authors have proposed a novel six-DOF parallel robot, PEN2 (PEN-PEN), which consists of two five-DOF subparallel mechanisms with three-DOF translational and two-DOF tilting output node platforms and a one-DOF additional rotation mechanism. Mobility analysis of PEN2 has been performed using Gruebler's equation and screw theory. This paper reports the inverse kinematics analysis of PEN2 with an RH additional rotation mechanism inherent to a plate tilting sub-mechanism whose moving platforms are driven by one R(SU)2 limb and two RSU limbs. When the R(SU)2 limb is used for the sub-mechanism, tilting the MP causes the MP to rotate around the z-axis relative to the additional rotation mechanism. A vector loop equation was derived for the displacement analysis, including the rotation of this sub-mechanism. The equations were developed using Mathematica software, which uses convergence calculations to find the inverse kinematics solution numerically.
View full abstract
-
Daichi Habara, Nobuyuki Iwatsuki, Kotaro Hoshiba
Session ID: S113p-01
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
Over-constrained mechanisms, which can be operated with equal to or less than 0 degrees of freedom due to singularity in link dimensions or arrangement, are expected to be used in a wide range of applications such as space deployable structures for antenna or solar panel. However, over- constrained mechanisms lack sufficient equations for unknowns such as driving torque and joint forces, therefore they can be uniquely determined. In addition, the sensitivity of the driving torque to structural errors remains unclear. In this paper, the both the minimum norm solution and the minimum strain energy solution for the driving torque and joint forces for rigid links are derived. Furthermore, by considering a few elastic links with a structural error, driving torque and joint forces can be calculated.
View full abstract
-
Haruhito Hasegawa, Yuki Uemura, Shu Karube, Takuji Kousaka
Session ID: S113p-02
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
In this paper, an experimental apparatus was constructed to experimentally investigate whether the phenomenon of stepwise bifurcation occurs in mechanical vibration systems by applying periodic impact vibrations to a mass with a spring. In the experiment, the amplitude of the shaker was kept nearly constant, the frequency is varied, and the displacements of the shaker and the vibrating mass pushed by the shaker are measured. The results shows a trend similar to the stepwise bifurcation that occurred in the bouncing ball system. Before the stepwise bifurcation occurs, the vibrating body behaves similarly to a periodic vibration, but just before the stepwise bifurcation occurs, the amplitude of the vibration becomes smaller and non-periodic. After the stepwise bifurcation, the vibrating body vibrates non-periodically.
View full abstract
-
Riki Takano, Naoya Hashizume, Noritsugu Umehara, Takayuki Tokoroyama
Session ID: S114-01
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
To clarify the effect of precipitates on low friction, we conducted the friction test and in-situ observation of precipitates on contact point by reflectance spectroscopy. From the reflectance spectrum measured by reflectance spectroscopy, we observed and estimated the thickness of precipitates. From the viscosity measurement of lubricating oil, it was observed that the lubricating oil containing palmitic acid becomes turbid and rapidly increases in viscosity below a certain temperature. Friction tests showed that the lubricating effect was reduced when the temperature was below the melting point of palmitic acid. Oil film analysis revealed an abundant presence of palmitic acid in the frictional area. Moreover, the thickness of the oil film increased compared to the theoretical value, suggesting that the deposition of palmitic acid contributed to the increase in film thickness. Consequently, the deposition of palmitic acid led to an increase in oil film thickness, suppressing direct contact and reducing friction. A correlation was found between the thickness of the palmitic acid layer and the friction coefficient, with negative correlation at 30°C (below the cloud point) and positive correlation at 50°C (above the cloud point), suggesting the possibility of different friction reduction mechanisms depending on the temperature.
View full abstract
-
Rintaro OMIYA, Motoki TSUKADA, Ayuko SAITO, Satoru KIZAWA
Session ID: S114-03
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
In this research, we attempted to evaluate the cyclist's ability to maintain balance by using information from a 9-axis motion sensor attached to the cyclist's trunk, lower limbs, and bicycle body. The experiment is conducted on flat and uneven roads. First, the sensor fusion using a gyro sensor, an acceleration sensor, and a magnetometer is used to estimate the trunk posture during riding a bicycle. Then, we evaluate the coordination of acceleration between the rider’s trunk and the bicycle by using the singular value decomposition. Finally, the results of the three-dimensional posture of the trunk and the coordination of acceleration between trunk and the bicycle are used to verify the balance during riding a bicycle.
View full abstract
-
Takuji YOSHIDA, Ryo TUBOI
Session ID: S114-04
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
In this study, simulations were performed to reproduce a sliding surface with a convex texture in two dimensions. The effects of cavitation on sliding surfaces were investigated by simulating various texture geometries. The texture geometry was based on a rectangular shape and different size chamfers were added in the downstream side. A moving wall accelerating at 1 m/s2 on the top surface and a fixed wall with a convex texture on the bottom surface were addopted for boundary conditions. The upstream and downstream boundary conditions were fixed at a gauge pressure of 0 Pa. The gauge vapor pressure of the lubricant was set to -1325 Pa, below which cavitation would occur. The Schnerr and Sauer model was used to reproduce cavitation. To compare the effects of cavitation, calculations were also performed for single-phase flow without the occurrence of cavitation. As a result, it was clarified that the texture shape affects the occurrence of cavitation, and it affects the sliding performance.
View full abstract
-
Toshiki WATANABE, Ken NAKANO
Session ID: S114-07
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
Sliding between solids always causes friction. In general, frictional force can be divided into two components: attractive force and repulsive force. In this study, we focus on the frictional force of the repulsive component arising from the viscoelasticity of solids. To represent the viscoelasticity of solids, the viscoelastic foundation was used: It is a simple modeling method in which the solid is described by an array of rheological elements that deform only in the perpendicular direction to the rigid base. In previous studies, the Kelvin-Voigt model was used as a rheological model, whereas in this research, the standard linear solid model (SLS model) capable of representing major viscoelastic properties (e.g., relaxation and retardation) was employed. We numerically obtained the velocity dependence of friction in steady states using the SLS foundation model. We found that the velocity range can be divided into three distinctive regions by asymptotes obtained theoretically. In conclusion, the Kelvin-Voigt foundation is effective in the low to medium velocity range, while the SLS foundation is effective in all velocity ranges.
View full abstract
-
Keisuke KISU, Motohiro KOZAWA, Keiichi WATANUKI
Session ID: S114-08
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
This study assesses the impact of varying objects and artistic techniques in viewing paintings on stress reduction using biometric measurements. A multi-physiological sensor combined with a tabletop eye-movement measurement device was utilized during the study. The evaluation indices included skin conductance response (SCR), low-to-high frequency ratio (LF/HF), and pupil diameter. We found a significant reduction in SCR, LF/HF, and pupil diameter while participants (n = 13) viewed paintings, regardless of the specific objects or artistic techniques depicted. These findings suggest that viewing paintings effectively reduce stress, irrespective of the content or artistic techniques utilized in the artwork. Finally, the questionnaire results revealed that individuals without extensive art expertise were still able to appropriately classify paintings in terms of abstraction.
View full abstract
-
Yusei YAMAMOTO, Naoya HASHIZUME, Noritsugu UMEHARA, Takayuki TOKOROYAM ...
Session ID: S114-10
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
To enhance the friction reduction characteristics of MoDTC are desired to reduce a friction loss of automobile engines. In this research, we focused on the carbon structures and doped metal of DLC coatings as factors that affect the friction reduction effect of MoDTC. We prepared two types of DLC coatings with different carbon structures: ta-C coating with an amorphous carbon structure and GNC coating with nano-crystals of graphite. Each coating was doped with different concentrations of Ta. The Raman analysis of the as-deposited DLC coatings revealed that GNC:Ta coatings consistently had a higher ID/IG ratio of around 1.2, regardless of the concentration of Ta. On the other hand, the ID/IG ratio of ta-C:Ta coatings increased with the addition of Ta. In order to evaluate the friction characteristics, we conducted friction tests and performed in-situ observations of the tribofilm at the contact point using reflectance spectroscopy. From the reflectance spectrum measured by reflectance spectroscopy, we observed and estimated the thickness and the composition of tribofilm. Interestingly, we found that the tribofilm on the DLC coating with a higher ID/IG ratio contained more MoS2 and exhibited a low friction coefficient of under 0.10. Based on our findings, we proposed that DLC coatings with higher ID/IG ratios contributed more to the reaction of MoDTC, resulting in a larger friction reduction effect of the tribofilms derived from MoDTC.
View full abstract
-
Ryuto KONISHI, Tomomi HONDA, Tomohiko KON
Session ID: S114-11
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
The purpose of this study is to clarify the relationship between dimple shape and seizure resistance and to derive the optimal design solution for the texture shape. The authors conducted ring-on-plate tribotests with five different dimpled specimens and measured the seizure load. The results showed that the dimple depth and area ratio had a greater influence on the seizure load than the other parameters, suggesting that elliptical dimples have higher seizure resistance than circular ones. We analyzed the maximum load-carrying capacity and fluid pressure using the TED/CPA when multiple dimples were subjected to load and sliding velocity in oil lubrication in order to clarify the effect of oil film pressure on seizure resistance. By comparing these values with the seizure load obtained from tribotests, a correlation was found between the maximum load-carrying capacity and the seizure load for dimples of similar area. This suggests that using the maximum load-carrying capacity as an indicator is effective in designing dimples with high seizure resistance.
View full abstract
-
Ryota TAKASAKA, Noritsugu UMEHARA, Takayuki TOKOROYAMA, Koichi OKAMURA ...
Session ID: S114-12
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
In an environment where glycol-based hydraulic fluid flows at high speed through a hydraulic circuit, the seat of a linear solenoid valve wears due to the synergistic effects of cavitation erosion and corrosion of the metal surface caused by the hydraulic fluid. The wear of the seat of a linear solenoid valve causes leakage of hydraulic fluid in the circuit, so there is a need to elucidate the wear factors and to reduce the wear. Focusing on the additives in the hydraulic fluid, tests were conducted in which hydraulic fluid containing different additives flowed in a hydraulic circuit. As a result, it was found that the hardness of the sheet surface after the test differed depending on the additive contained, and that the amount of wear was affected by the additive. The results of surface observation by FE-SEM and elemental analysis by EDS showed that the wear patterns were different depending on the additives contained.
View full abstract
-
Kenya NAKAYAMA, Kaisei SATO, Shinya SASAKI
Session ID: S114-14
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
To extend the cruising range of electric vehicles (EVs), it is necessary to improve the efficiency of EVs. As one method to improve the power consumption of EVs, the increase of motor speed is expected. The increase of motor speed makes it possible to reduce the size and weight, which leads to increase power output of EVs. However, the fatigue life of the bearings and gears will decrease; therefore, micropitting will increase. Diamond-like carbon (DLC) film is expected as one way to prevent the micropitting of bearings and gears. DLC has various excellent tribological properties such as low friction and high wear resistance. However, evaluation method for micropitting in DLC has not yet been established. In addition, in the contact surface of gears, sliding and rolling contact occur at the same time. In previous studies, it has been reported that fatigue surfaces are eliminated by wear due to sliding. Therefore, to clarify the effect of rolling contact on the occurrence of micropitting, it is necessary to conduct tests under pure rolling contacts, where the effect of sliding is minimal. In this study, we applied two types of DLC film (a-C:H, ta-C) to the surface of balls. Ball-on-disk tests were conducted under the conditions of lubrication of base oil and pure rolling contact to investigate the effect of these types of DLC film on micropitting resistance. We confirmed that the ta-C type DLC film suppresses micropitting.
View full abstract
-
Kanta ONIMARU, Keiichi WATANUKI, Kazunori KAEDE, Yusuke OSAWA
Session ID: S114-17
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
This paper aims to explore the influence of advertisements displayed during visual display terminal (VDT) work on workers' concentration and examine the appropriate conditions for presenting advertisements to both consumers and advertisers. A cognitive memory task was specially designed and presented to participants on a monitor, alongside mock advertisements. The effects on concentration were assessed through task performance, subjective evaluations of concentration, and eye-gaze data. We observed that variations in the level of interest in the advertisements had an impact on the participants' ability to concentrate. The results suggest that the use of colors with high visibility and attractiveness is more suitable than the use of movement as a condition for presenting advertisements. This paper highlights the implications of advertisement placement during VDT work and provides valuable insights for optimizing advertising strategies and promoting sustained focus among workers.
View full abstract
-
Kazushi ITO, Xiaoxu LIU, Satoru MAEGAWA, Fumihiro ITOIGAWA
Session ID: S114-18
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
The frictional properties of rubber materials are strongly influenced by the viscoelasticity of the rubber itself. When a rubber block slides on a rough surface, the bulk region near the sliding surface repeatedly deforms up and down following the surface roughness, and part of the vibration energy is dissipated as heat inside the rubber. This frictional work loss corresponds to frictional force. We have been studying a method to increase friction force by utilizing the enhancement of bulk vibration by filling inside hard particles. In this study, we studied whether our proposed method apply tire rubber used in actual products. Tire rubber is filled with fillers to improve wear resistance and strength. We investigated the effect of the size and density of these particles on the friction force, and the results showed that the coefficient of friction increased when the filled particles mechanically interlock with the unevenness of the mating surface.
View full abstract
-
Feature of AE Signal Detected at Sliding Wear under Electric Current in Rainy Weather
Kouki OZAWA, Alan HASE
Session ID: S114-20
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
Wear under electric current causes more damage than normal friction due to the effects of arc discharge and melting. In this study, the characteristics of AE signal waveforms during wear under current application are extracted from the amplitude and the frequency spectrum, and the phenomena occurring in rainy weather (water lubrication) are analyzed. As a result, it was found that the state of arc discharge and melting can be evaluated from the change of AE signals even in the presence of water. In this report, the results of an investigation of the energized wear mechanism based on the characteristics of the AE signals are described.
View full abstract
-
(Design and Experiment)
Ryoto NAGATA, Zixin LIN, Peiran NIU, Shoichi HASEGAWA, Yoshihiro KAI
Session ID: S114-21
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
When persons carry a heavy object, a large burden is exerted on their arms. Therefore, there is a need for a device that reduces the burden. In this paper, we describe the development of an elbow joint assist suit with a mechanical brake (MB) considering energy consumption and safety. When a user lifts a heavy object up, the assist suit’s motor is used to assist the user's elbow joint. When the user holds the heavy object in the arms at a raised position, the MB is used to support the elbow joint without consuming electric power. After the assist suit’s computer breaks down, if the elbow joint is moved at high speeds by the assist suit, the MB turns off the motor and stops the assist suit. First, the features of the elbow joint assist suit are presented. Next, the elbow joint assist suit which we designed and developed is introduced. Furthermore, the structure and the mechanism of the MB are explained. Finally, experimental results to verify the effectiveness of the MB are presented in the elbow joint assist suit.
View full abstract
-
Masamitsu NAGAYOSHI, Keiichi WATANUKI, Kazunori KAEDE, Yusuke OSAWA
Session ID: S114-23
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
This study investigated the impact of various minimum risk maneuver (MRM) alarm tones on drivers of following vehicles during automatic driving. The necessity of MRM alarm tones was assessed, and drivers' impressions and stress levels were examined based on differences in the waveform of the alarm tones. Twelve participants were engaged in a driving simulation on a highway, and they were required to avoid collisions after the collision avoidance support function (MRM) was activated in an autonomous vehicle driving ahead of them. The experimental conditions included sine wave, triangle wave, square wave, sawtooth wave, and no alarm sound. The results indicated that the presence of alarm tones has a significant effect on preventing abrupt braking and reducing feelings of anxiety in the following vehicle drivers. Additionally, a positive correlation was observed between the perception of the alarm sound and the amount of high-frequency components in the waveform.
View full abstract
-
Tomoki ODA, Noritsugu UMEHARA, Takayuki TOKOROYAMA, Naoya HASHIDUME, D ...
Session ID: S114-25
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
In recent years, environmental pollution and depletion of energy resources have been discussed as problems, and technologies for higher efficiency are required. Lubricants are used in gasoline vehicle transmissions to reduce friction, and ester mixed lubricants are used in boundary lubrication conditions where solid contact is severe. Ester mixted lubricants increase oil film thickness by adhering to metal surfaces to reduce friction, but it has been found that esters containing unsaturated fatty acids undergo thermal denaturation during friction. In this study, the effects of thermal denaturation of esters on friction properties were elucidated. Friction tests were conducted at 23°C, 60°C, and 80°C using lubricants with unsaturated fatty acids (TMPTO) added to the base oil (PAO), and the friction coefficient was the largest at 60°C and the smallest at 80°C. The oil film thickness was the smallest at 60°C and the friction coefficient was the largest at 80°C. The coefficient of determination between the friction coefficient and oil film thickness is 0.73, which means that the assumed oil film model is correct. This suggests that the effect of surface adsorption is stronger at low temperatures, while the effect of thermal denaturation of TMPTO with high viscosity is stronger at high temperatures, suggesting that more thermal modification products may be produced at high temperatures.
View full abstract
-
Satoshi MINO, Yuta SUNAMI, Kazuyoshi TSUTIYA
Session ID: S114-26
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
Web is a generic term for thin, flexible, continuous material such as plastic film and metal foil. The R2R production method is used for web production. In this system, a lot of rollers support and transport the web from the unwinding to the winding. In this production system, the winding section is the most important process that determines the quality of the web. Inappropriate winding conditions are winding defects such as slippage and wrinkles can occur. Slippage and wrinkles are situations where changes in interlaminar frictional forces and tangential direction stresses suggest winding defects. In recent years, webs have become increasingly multilayered, thinner, and more precise. Therefore, web thickness variation more likely to occur. Thickness variation causes a difference in the internal stress in the web width direction due to the change in contact area between the web layers. Therefore, quality of the web may be affected. A theoretical prediction model that considers thickness variation is the winding model proposed by Hakiel that considers thickness variation in the width direction. This winding model is assumed to exist only in the web width direction, it is possible to prevent winding defects by calculating the internal stresses of the winding rolls. However, the actual web has thickness variation in the transport direction. Therefore, in my study, the web roll internal stresses were compared with the theoretical prediction model. As a result, the need to account for thickness irregularities in the transport direction was confirmed.
View full abstract
-
(Rotation Speed 4000min-1 or Less and Constant Speed)
Hironori YAJIMA, Tomoya HOTTA
Session ID: S114-27
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
In general, when bearings are operated under no load or very light loads, slippage may occur between the rolling element and the raceways. Thus, certain amount of load is required for normal operation of bearings. However, the calculation method of the minimum load differs from manufacturer, and no clear value is currently stated. In this research, in order to clarify the relationship between the radial load and slip at the rolling element, measuring the rolling element orbital speed using the cylindrical roller bearing (N305) and comparing it with the theoretical orbital speed. As a results, the rolling element are slip at loads of less than 250 N, and that a 15% reduction in velocity at 50 N. This corresponds to 1% of the basic static load rating.
View full abstract
-
Kazuya INOSHITA, Satoru KIZAWA, Yoshikazu KOBAYASHI, Ayuko SAITO
Session ID: S114-29
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
A squat is an exercise in which the knee is repeatedly flexed and extended from an upright position. It has been reported that a decrease in the velocity of the center of gravity of the body is one of the causes of falls during standing up motion in the elderly. Clarifying the contribution of each muscle to exercise speed during squatting requires quantification of the relationship between exercise speed and lower limb muscle forces, which is useful for evaluating motor function. Therefore, in this study, we construct a squat model that estimates the velocity of the center of gravity using lower limb muscle forces that contribute to hip and knee flexion and extension, and ankle dorsiflexion and plantarflexion. Furthermore, by applying the proposed method to squats with different stance widths, we verify the contribution of each muscle to the motion velocity.
View full abstract
-
Simultaneous measurements of film thickness and viscoelasticity
Daiki KAGIWATA, Hikaru OKUBO, Yoshinobu TSUJII, Ken NAKANO
Session ID: S114-32
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
In this study, a homemade apparatus conducting time-resolved simultaneous measurements of the film thickness and viscoelasticity at the contact interface using optical interference and contact dynamics was developed. Two types of tests, the indentation and friction tests, were alternately conducted on a substrate coated with CPB and a steel ball. From the indentation tests, the presence of dilute, middle, and concentrated layers was quantitatively confirmed by measuring the film thickness about the change in viscoelasticity. From the friction tests, the wear of the CPB was detected from a decrease in the film thickness of the CPB. The thickness of each layer decreased at a constant value with sliding, indicating that the dilute layer was continuously formed due to sliding. Therefore, it is concluded that wear occurs randomly at the friction interface, resulting in the formation of a layer of low density and low stiffness on the surface.
View full abstract
-
Hidetaka Tsuchiya, Noritsugu Umehara, Takayuki Tokoroyama, Jaeil Kim, ...
Session ID: S114-33
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
About 15% of the available energy in automobile engine is dissipated as mechanical, mainly frictional loss. In automobile engine, friction coefficient of boundary lubrication mode should be expected to be reduced less than 0.05 under reciprocating sliding parts. Recently, in order to overcome this problem, the synergy effect of specific DLC (Diamond-Like-Carbon) coating doped with various elements and friction modifier as MoDTC are expected under boundary oil lubrication. Therefore we prepared carbonaceous hard coatings doped with Ta and N by a combination coating equipment combined with FCVA (Filtered Cathodic Vacuum Arc) deposition and a gas ion implantation source. And a reciprocation sliding friction tests against SUJ2 roller were conducted under PAO base oil and PAO oil including MoDTC. We have prepared 4 different carbonaceous hard coatings as ta-C, ta-CNx, ta-C:Ta and ta-CNx:Ta and reciprocation sliding test was carried out in various sliding conditions. And normal load was decreased by 0.5 N after each 100 sliding cycle up to 0.5 N. For PAO base oil, all of carbonaceous hard coatings showed lower friction coefficient compared with SUJ2 disk. Minimum average friction coefficient was 0.11 for ta-C and ta-C:H. On the other hand, for MoDTC including PAO oil, Nitrogen and Tantalum doping ta-C showed lower friction coefficient.
View full abstract
-
Kazuya TAKAHASHI, Masahiro FUJII, Masahiko YAMAKI, Yusuke SUGIURA
Session ID: S114-35
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
Plastic gears are used in a wide range of fields, and various studies have been conducted to improve their performance. The plastic gears have some advantages - for example, light weight and low vibration. It has significantly lower bending fatigue strength than metal gears. In recent years, Meatal-insert plastic-molded gears which combines metal and plastic have been attracting attention as one of ways to increase the fatigue strength of plastic gears. In this paper, we conducted fatigue test to investigate the durability and failure mode using the Metal-inset plastic-molded gears. The plastic coated to metal gears was polyether ether ketone filled with 20% carbon fiber. Failure mode of the gears was not tooth breakage due to bending fatigue, but peeling in the plastic coating layer. Maximum depth of the peeling was close to the depth which maximum shear stress and orthogonal shear stress ware maximum. Therefore, it was suggested that the evaluation could be similar to that of metal gears.
View full abstract
-
Tohma OKADA, Kazuyoshi TSUCHIYA, Yuta SUNAMI, Satoshi KANEKO, Shoto TO ...
Session ID: S114-36
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
A web is a general term for thin and flexible continuous media, and there is a roll-to-roll production method that can consistently perform from unwinding to winding as a web production method. In this production method, the core is wound in a roll shape, and from the viewpoint of cost reduction, it is often wrapped around a paper core. However, winding defects occur during winding, and in order to prevent winding defects, it is necessary to accurately predict changes in the internal state of the winding roll and wind under appropriate winding conditions. Therefore, Hashimoto performed a theoretical calculation of the internal stress state of the roll, and confirmed a difference between the theoretical value and the measured value in the radial stress near the core. This is because the anisotropy of the core in Young's modulus and humidity expansion is not considered.Therefore, in this study, we measured the Young's modulus of the paper tube in dry and wet conditions for the purpose of evaluating the effect of the anisotropy of the Young's modulus on the humidity dependence of the paper tube on the radial stress near the core. After that, we calculated the theoretical value of the radial stress and compared it with the measured value. The measurement confirmed that the anisotropy in the Young's modulus of the paper tube and the humidity dependence of the paper tube affected the Young's modulus. Furthermore, it was confirmed that the Young's modulus of the paper tube affects the radial stress.
View full abstract
-
Yoshihiro SEJIMA, Takuya WAKATSUKI, Shota HASHIMOTO, Tomio WATANABE
Session ID: S121-01
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
In human communication, a listener's active attitude brings comfort to the speaker and promotes acceptance and empathy. Especially in the counseling, in addition to linguistic and semantic understanding, it is important to generate the acceptive and empathetic attitude based on nonverbal information. Therefore, it is expected that the listening mechanism that actively relates to the speaker can be constructed by introducing the listener's attitude into social robots. We focused on the pupil response that is closely related to human interests, and developed a pupil response robot called Pupiloid. Pupiloid can generate various pupil responses based on the speech. In this study, focusing on eyelids that are related to the human internal state and interest, and developed a listening expression method that controls the degree of eye opening using the Pupiloid. This method expresses the strength of robot's interest by controlling the angle of eyelids in addition to the size of pupils. The effectiveness of the method was confirmed by the questionnaire at an exhibition.
View full abstract
-
Saki INAGAKI, Daiki MORITA, Yoshihiro SEJIMA
Session ID: S121p-01
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
Humans often use a metaphor to describe activated communication as a heat. We focused on this metaphor and developed an estimation model for activated interaction and communication by regarding an interactive communication space as a heat conduction in a virtual temperature space. In addition, we developed a communication system that changes the background color based on the model. This system supports sharing an interactive atmosphere even in spatially separated online communication by changing the background color from the black to the warm color. However, when the background color suddenly changes from the warm color to the black, it brings a negative impression of the silence of the conversation. In this study, we developed a new method that expresses the afterglow of the interaction atmosphere in the system. This method generates slowly changing the background color from the warm color to the black when the conversation is finished.
View full abstract
-
Ryoya OBA, Keiichi WATANUKI, Kazunori KAEDE, Yusuke OSAWA
Session ID: S121p-02
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
Invasive methods of core body temperature measurement pose challenges to the assessment and supervision of human health. Although non-invasive methods are available, they frequently involve the use of medical equipment. To address this issue, some methods have been proposed various types of biological data. However, existing systems often require large measurement devices and complex calculations, limiting their practicality. In this paper, we present an estimation model that leverages machine learning to predict core body temperature using a hand-mounted wearable sensor. In the preprocessing stage, we identified features based on the peak-to-peak interval derived from a volume pulse wave and created lagged datasets using biological data. To account for non-linearity in the machine learning component, we used support vector regression. Our proposed method displayed an error of 0.078 ℃ in core body temperature estimation. On the other hand, the application conditions of this model are limited, and it is necessary to acquire biological data considering various environments, such as hot and humid conditions or during physical activities.
View full abstract
-
Kohei KANAMARU, Toru EGUCHI, Takeshi MURAYAMA
Session ID: S141p-01
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
This paper deals with job shop scheduling problem with consideration for multi-objective evaluation related to due dates. An effective priority rule is constructed for this problem using a neural network. The neural network is trained using input-output pairs extracted from schedules optimized using a genetic algorithm incorporating the priority rule. The numerical experiments demonstrate that effective priority rules can be automatically constructed by training using the input-output pairs.
View full abstract
-
(Learning Priority Rule Using Neural Network)
Takumi YOSHIDA, Toru EGUCHI, Takeshi MURAYAMA
Session ID: S141p-02
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
This paper deals with a job shop scheduling problem that considers the skill difference of operators. A priority rule for this problem is constructed using a neural network. A neural network learns from input-output pairs extracted from a schedule optimized using an IP solver for small-scale problem instances. Through numerical experiments, it was found that trained neural network by the proposed method showed better performance than the existing priority rules even in larger scale problem instances.
View full abstract
-
Experimental Study on Diagnostic Mechanism
Noi Kurimoto, Takumi Hibi, Tatsuru Asai, Souichi Saeki
Session ID: S141p-03
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
In fuel cells manufacturing process, there remains a problem of Fe micro-particles buried into Membrane Electrode Assemblies (MEA). In this study, the authors propose a non-contact rapid diagnosing system of Fe contamination, which is composed of an electro-magnetic impact generators and laser displacement sensors, namely EMA-LDS. EMA-LDS was experimentally applied to both samples of MEA with and without burying Fe micro-particle. As an experimental result, the oscillation under Fe-contaminated MEA was experimentally confirmed to have different phase in the natural frequency, although the normal MEA had the same phase. These results are attributed to the additional generation of Fe magnetic force and the spatial-temporal changes of Lorentz force by the existence of Fe micro particle. Therefore, EMA-LDS has an effective potential as a diagnosing system of metallic micro-particle into MEA.
View full abstract
-
Kohei MIYATA, Norisuke FUJII, Noboru FUJITA, Taisei MASSAKI, Tatsumasa ...
Session ID: S142-02
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
Recently, In the manufacturing industry, in order to respond to changes of business environment quickly, it is required to realize variable-variety variable-volume production. Along with this, flexible production methods which can produce a wide-variety products on any line are focused on. In the flexible production methods, it is important to make an appropriate production schedule to maintain productivity because bottleneck resources fluctuate. In addition, it is also required to make production schedule quickly to respond daily demand fluctuations. In this research we develop simulation-based scheduling methods that enable high-speed and high-productivity scheduling by providing planning logic that corresponds to the characteristics of the manufacturing line. In this talk, we will discuss planning logic and numerical experiment results especially for manufacturing lines with parallel line configuration.
View full abstract
-
Koki JIMBO, Sara SEYAMA, Shinya MORITA
Session ID: S142-04
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
In this study, we propose a design method for compliant mechanisms using material extrusion-based additive manufacturing, with the aim of producing robot hands as one part. A compliant mechanism that performs through elastic deformation of the material simplifies the assembly process and has the potential to achieve oil-less and zero backlash operation. Our proposed design method is based on a two-dimensional bellows-like structure and a beam between its walls. The stiffness of this structure can be designed by changing the dimensions of a unit structure. It allows the fabrication of complex three-dimensional mechanisms that would be difficult to achieve through traditional manufacturing methods. In our evaluation experiments, we fabricated specimens using 6 design parameters and conducted wire-driven experiments to evaluate the effectiveness of our design method. We confirmed not only that the proposed design parameters allow for the design of the stiffness of the flexible structure both in-plane and out-of-plane, but also that the structure can be fabricated without the use of support materials by material extrusion. Finally, a single flexible structure simulating the behavior of a parallel link mechanism was designed by the proposed method. The results of the experiment confirm that the deformation of the entire structure can be designed by the proposed method.
View full abstract
-
(DfAM Trial on a Heat Exchanger)
Takahiro KONO, Kayo MIGITA, Koji TAKAHATA, Daisuke MITSUOKA
Session ID: S142-06
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
Additive Manufacturing (AM) is a powerful tool that allows parts to enhance their performance and combine into one part because of its high shape flexibility comparative to conventional production methods. It is not only the production innovation, but also design is needed to be changed so that getting these benefits. We focused on DfAM (Design for AM) and performed a trial on a heat exchanger to assess positive effects of DfAM. After AM building with AlSi10Mg powder bed fusion, heat transfer per volume 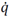 was evaluated. A DfAM prototype recorded nearly doubled
was evaluated. A DfAM prototype recorded nearly doubled 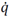 of a conventional heat exchanger with the restrictions of conventional production, besides measurement and prediction were well matched. We have considered that pursuing of an ideal shape based on ideas and simple physical models are keys of DfAM.
of a conventional heat exchanger with the restrictions of conventional production, besides measurement and prediction were well matched. We have considered that pursuing of an ideal shape based on ideas and simple physical models are keys of DfAM.
View full abstract
-
Katsunari IKEZAWA, Atsuya KAWAI, Shingo AKASAKA, Jiahua WENG
Session ID: S142-07
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
Efforts to reduce resource waste and utilize limited resources effectively have been a primary concern in the manufacturing industry. Circular supply chain models were developed to collect and reuse products in the market. However, traditional models have mainly focused on reusing collected parts for the same product. This paper proposes a novel operation model that reduces the wastage of parts by converting the recovered parts into different products according to their degree of functional deterioration. The conversion of electric-vehicle lithium-ion batteries to forklift and storage batteries was considered, and the performance of the model was verified using an event simulator.
View full abstract
-
Hiroki MITSUTA, Masataka TANAKA, Ryo TAKAHASHI, Yu TAJIRI
Session ID: S142-08
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
High-mix low-volume production is required highly efficient manufacturing because frequent changes in manufacturing conditions increase setup time and equipment idle time. In the surface mounting process of high-mix low-volume production, multiple surface mounters are connected in order to improve efficiency. The allocation of parts to these surface mounters was determined based on the know-how of the operator, but the large number of parts made it difficult to plan the optimal layout, leading to the problem of longer manufacturing lead time. In this research, we developed an optimization technology for component placement using mixed integer programming and local search in order to plan the placement of electronic components to reduce manufacturing lead time in high-mix low-volume production with a large number of components. In this presentation, I will talk about the optimization technology of the component placement of the surface mounter and the evaluation results of the test line.
View full abstract
-
Tatsuhiko SAKAGUCHI, Ryo FUJITA
Session ID: S142-09
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
In the wiring design of electrical equipment construction such as buildings, it is necessary to design the optimal cable route by considering various conditions such as constraints on the building structure and constraints due to the electrical equipment itself. Concretely, it is necessary to determine the shortest possible wiring route in order to prevent voltage drop while avoiding structures such as beams and pillars. In this study, we propose a graph algorithm for searching for the shortest route by modeling the candidate paths of cable routes on architectural drawings as a Steiner tree in order to search for the shortest route whose total length is minimized for one floor of a building. First, candidates for switchboards and wiring routes are modeled in a graph structure, and the shortest route is searched by applying an algorithm that is an extension of the KMB method. In order to validate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, we conducted the numerical experiments on one floor of the actual building.
View full abstract
-
- Automatic Diagnosing System based on Machine Learning
Tatsuru Asai, Takumi Hibi, Noi Kurimoto, Souichi Saeki
Session ID: S142p-02
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
In the manufacturing process of Membrane Electrode Assemblies (MEA) of fuel cell, there remains a problem of metallic micro-particles buried into Gas Diffusion Layer (GDL). It leads to the performance drop-down of fuel cells. In this study, we propose a real-time diagnosing system introducing Machine Learning to EMA-LDS, which is composed of electro-magnetic impact generators and laser displacement sensors. EMA-LDS was experimentally applied to both samples of gas diffusion layer (GDL) with or without burying Fe micro-particle with a diameter of 100 μm. As an experimental result, the contaminated GDL was estimated to have a high probability of metallic micro-particles, although the normal GDL had lower probability. In conclusions, the proposed method can discriminate metallic micro-particles according to Machine learning. Therefore, EMA-LDS has an effective potential as a diagnosing system of metallic microparticle into MEA.
View full abstract
-
Eri MORITA, Masayuki TANAKA, Hideaki MORISHIMA, Yasuaki HADAME, Moeha ...
Session ID: S161-01
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
In web handling, some defects such as wrinkles occur due to the non-uniform strain distribution in the web. Hence it leads to the deterioration in quality and manufacturability. In order to improve the web handling productivity by clarifying the phenomena of defects generation and optimizing the handling conditions, the method of measuring the strain distribution of the web is needed. DIC(Digital Image Correlation) can measure a wide range of strain without contact, therefore we conducted a basic study to apply DIC to the web handling. One of the problems in measuring strain during web handling by DIC is the effect of large in-plane movement and out-of-plane vibration. In this study, we verified the strain measurement accuracy when a rigid body moves in and out of the plane. First, 2D-DIC and 3D-DIC measurements were performed while the web sample was moved rigidly. By applying 3D-DIC, it was found that the strain error due to unwanted movement and equipment vibration can be sufficiently reduced. Next, the strain during web handling in undeform web was measured by 3D-DIC using a simple handling system. The absolute value of strain error was 2.03×10-5. Results of these experiments suggest that the strain can be measured with small error due to rigid body movement by using 3D-DIC.
View full abstract
-
Hiroshi TANI, Ryo KAWAKAMI, Shouhei KAWADA, Renguo LU, Shinji KOGANEZA ...
Session ID: S162-01
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
As part of the development of intelligent tires, a method for estimating the slip condition between the tire and the road surface was studied. The output waveform of a piezoelectric film attached to the inner surface of the tire was measured when the film passed the contact patch, and it was confirmed that the waveform changed as the slip ratio changed. The results indicated the possibility of estimating the slip ratio by monitoring changes in the voltage peaks corresponding to the entrance and exit of the contact patch.
View full abstract
-
Wako TAKANASHI
Session ID: S162-02
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
This paper is described that it is possible to decipher the undeciphered Indus script for characterizing and organizing relatively long character information such as sentences for the three elements of shape, pronunciation, and culture.For the content related to the event, the concept of digital twins of astronomy, weather, and custom is employed. As a result, it was found that the word order of the Indus script is SOV, SVO, and VSO, and the sentence pattern resembles that of kanji-kana mixed sentences.
View full abstract
-
Shinji KOGANEZAWA, Takuma HAYASHI, Hiroshi TANI, Renguo Lu, Shouhei KA ...
Session ID: S162-03
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
We have been developing a self-powered vibration sensor for bridge structural health monitoring systems using a magnetostrictive material. In this study, a novel sensor structure was investigated to adjust the bias magnetic field of the magnetostrictive rod to a uniform value that maximizes the voltage generated by passing medium-sized vehicles. The improved sensor was designed so that the magnetic field within the magnetostrictive material was in the range of 3000-4000 A/m.
View full abstract
-
Yoshiyuki ISHIHARA, Sinji TAKAKURA, Makihiko ISHITANI
Session ID: S162-04
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
RESTRICTED ACCESS
For nearline HDDs used in data centers, it is important to improve the positioning accuracy of read/write heads and track seeking speed in one-track seeking control, which is continuously invoked during large data read/write operations. This paper proposes a one-track seeking control that uses iterative learning control to shape the feedforward input waveform of a PZT actuator of a dual-stage actuator at each seek. The effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by one-track seeking simulation using the HDD benchmark problem for a dual-stage actuator. The proposed method shows better read/write head positioning accuracy than the conventional method. In addition, the error 2-norm of the learning control can be easily monotonically decreased by adjusting the learning gain.
View full abstract



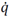 was evaluated. A DfAM prototype recorded nearly doubled
was evaluated. A DfAM prototype recorded nearly doubled