
- Issue 6 Pages 464-
- Issue 5 Pages 403-
- Issue 4 Pages 237-
- Issue 3 Pages 149-
- Issue 2 Pages 105-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Alexander R. Gabelli2024Volume 19Issue 5 Pages 403-412
Published: July 31, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 31, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe static load rating of hybrid bearings is a performance parameter used in designing hybrid bearings applications. The calculation of this load capacity factor is specified by the International Standard ISO 20056-2:2017. In this article, the static load rating of hybrid bearings is analysed using a novel experimental method for both point and line contact bearings. From the obtained measurements, an assessment of the ISO equations used for hybrid rolling bearings static load ratings is carried out. The comparison of the analytical and experimental results indicates good agreement and the overall validity of the current ISO formulation. The practical use of the ISO static load rating in designing hybrid bearing applications is also discussed. Using an actual hybrid bearing application case, it is shown when the static rating becomes the critical parameter in the design of hybrid bearings applications.
View full abstractDownload PDF (5944K) -
―Proposal of Liquid State Equation and Estimation of High Pressure Density―Masato Kaneko2024Volume 19Issue 5 Pages 413-427
Published: July 31, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 31, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe physical properties of lubricant under high temperature and high pressure include high pressure viscosity, high pressure density, bulk modulus, coefficient of thermal expansion, etc. It is important to know these high pressure physical properties in machine design. However, almost no discussion has been made on the liquid state equation, which is the basis of the high pressure physical properties of these lubricants. Therefore, in this report, using the high pressure density measuring device, the volume was obtained from the measurement of the density at each temperature and pressure, and the PVT relational equation was derived. Further, Vt=0 (absolute experiments, and it was found that this equation could be utilized as a liquid state equation of high utility. In addition, we can estimate the high pressure density which is one of the high pressure physical properties of the lubricant by this liquid state equation.
View full abstractDownload PDF (3795K) -
Mahathep Sukpat, Worawut Kunghun, Pudsadee Chupong, Karuna Tuchinda2024Volume 19Issue 5 Pages 428-436
Published: July 31, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 31, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSImpact wear (repetitive impact-induced wear) has been identified as a significant issue in various engineering components, such as valves, electrical contacts, and pumps. This study investigates the impact wear behavior of martensitic stainless steel, a commonly used material for valves. Understanding the wear behavior is crucial for minimizing losses and enhancing component performance. Repetitive impact tests were conducted using a custom-built testing machine with a well-defined impact position. Four impact loads were applied (10 N, 20 N, 30 N, and 40 N) at 30,000 impact cycles. It was observed that plastic deformation precedes the transition to fatigue wear after multiple impact cycles under loads 20 N and over. However, under 10 N, plastic deformation was not observed clearly, and the initial damage mode primarily involved pitting, followed by delamination wear. Wear rates were found to correlate well with the contact pressure, and the equation for predicting the wear rate was derived from such a relation. A valuable guideline for minimizing wear and designing operating contact pressure in martensitic stainless-steel components is achieved via the upper and lower bound curves.
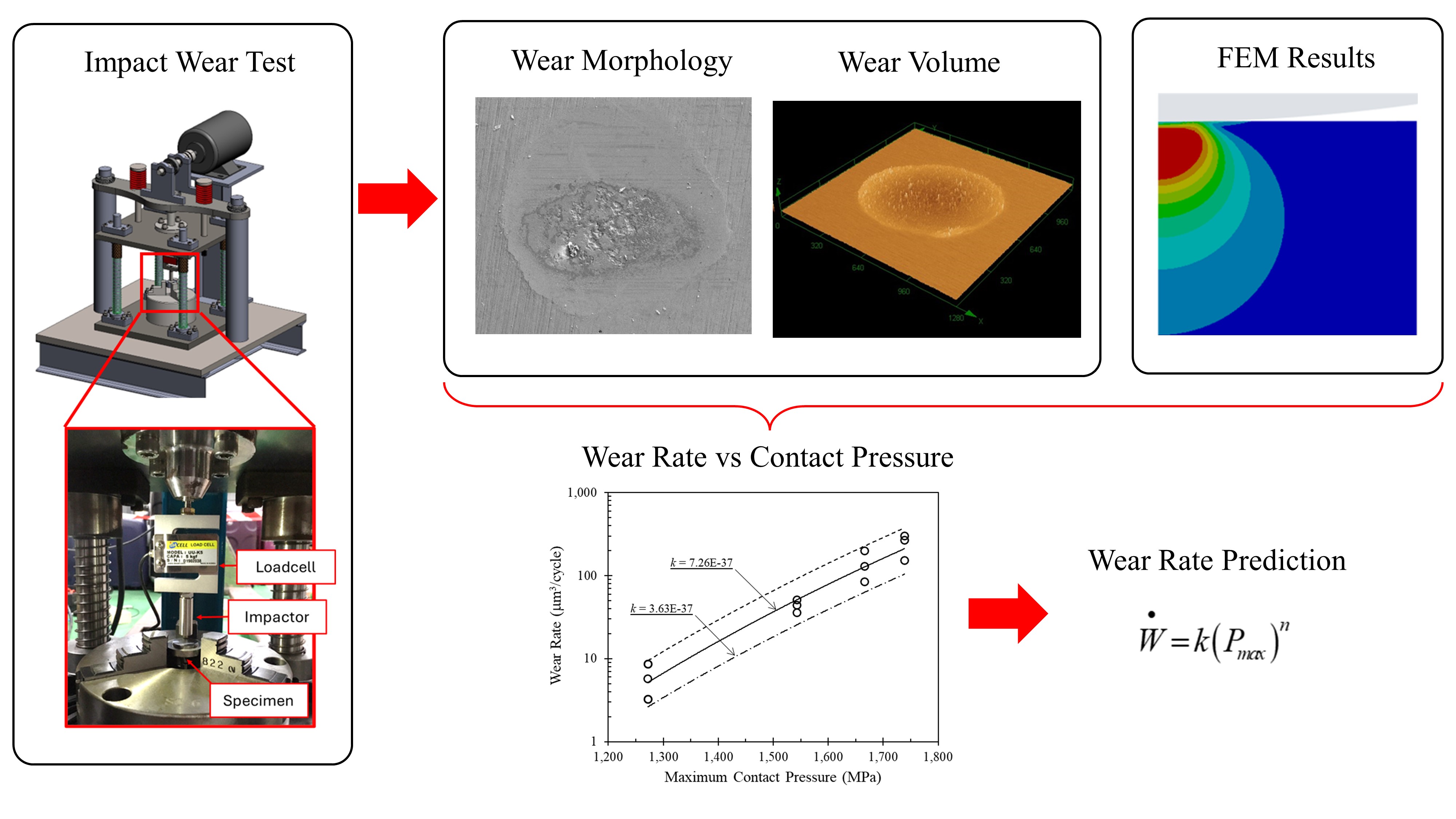 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (6258K)
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (6258K)
-
Shahnaza Akhter, M. Jebran Khan, M.F. Wani, Mohammad Arif Parray, Shuh ...2024Volume 19Issue 5 Pages 437-447
Published: July 31, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 31, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe cryogenic engineering is a vast and important field of engineering. The effect of cryogenic treatment on performance parameters of cutting tools directly affects the tool life and productivity and same has been analyzed in this review paper. The tool wear increase, dimensional inaccuracy, rough surface finish and increased production cost is encountered by cryogenic treatment of tool materials. This review gives analysis about the cryogenic treatment process, cryogenic fluid used, temperature/pressure maintained, and desired improvements achieved. The literature survey applied clearly signifies that cryogenic treatment improves the machinability characteristics compared to the untreated tools. A lot has been achieved and further improvements are poised with future challenges to be encountered. The paper analyses the studies on HSS, and carbide tools done through cryogenic treatment and ascertains that better tool life and productivity can be achieved by cryogenic treatment through reduced tool wear.
View full abstractDownload PDF (620K)
-
Supreeth Shivakumar, Thipaaiah NagaRaju, Rattehalli Ningachar Ravikuma ...2024Volume 19Issue 5 Pages 448-453
Published: September 15, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: September 15, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSStudies on non-contact hydrodynamic foil thrust bearings (FTB) with a diameter of 224 mm were fabricated and tested for operating speeds up to 20,000 rpm. Single layer top foils and stepped / multiple foils with steel and copper foil materials were used in the present study that eliminates the complexity of foil design and manufacturing. Thrust loads of the FTB for various foil configurations were determined for two foil thicknesses and foil sector angles (SA) thereby optimizing the best foil stiffness. The paper also enlightens on the life of these bearings tested for about 50 cycles that ensures their application in air cycle machines and food processing industries.
View full abstractDownload PDF (4771K)
-
Kai Xing, Shingo Ozaki2024Volume 19Issue 5 Pages 454-463
Published: September 30, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: September 30, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSIn various dynamic systems, accurately predicting frictional stick–slip motion is critical for maintaining stability. To address this issue, we integrated a particle filter with a rate- and state-dependent friction model to enhance the prediction of stick–slip dynamics. Our method assimilates the experimental data and iteratively updates the parameter distributions to align with the observed stick–slip events. Using the proposed approach, we demonstrate parameter estimation for different dynamic behaviors of a one-degree-of-freedom system, enabling a robust simulation of stick–slip motion. Specifically, as the particle filter assimilates data, the prediction interval for the candidate parameter set becomes narrow, thereby yielding increasingly precise forecasts. Subsequently, by utilizing the posterior parameter distributions obtained through Bayesian updates, our approach successfully simulated and predicted the experimental stick–slip outcomes. This validation underlines the capability of the rate- and state-dependent friction model to describe complex frictional motions, and suggests the potential of the particle filter as a powerful Bayesian tool for predicting nonlinear dynamics, including stick–slip motion.
View full abstractDownload PDF (4474K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|