Abstract
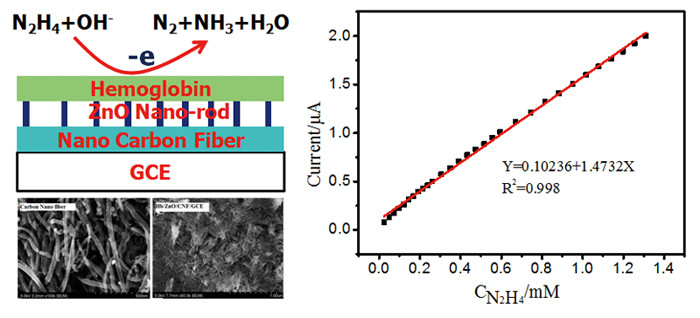
A novel biosensor was developed by immobilizing hemoglobin (Hb) on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) modified with a composite of ZnO nano-rods and carbon nanofiber (CNF), a strong reducer, hydrazine, was firstly used to evaluate the electrochemical behavior of Hb on Hb/ZnO/CNF/GCE. UV-vis and circular dichroism (CD) spectra indicated the conformational structure of Hb interaction with ZnO/CNF was predominantly an α-helical structure. The modified electrodes were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), electron impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and cyclic voltammetry. Electrocatalytic mechanism of Hb to oxidation reaction of hydrazine was suggested. The bioelectrocatalytic activity, kinetic parameters of Michaelis–Menten constant (Km), stability and reproducibility were also investigated. A linear dependence of peak currents to the concentrations of hydrazine was observed in the range from 1.98 × 10−5 to 1.71 × 10−3 mol L−1 with a correlation coefficient of 0.998, and a detection limit (S/N = 3) of 6.60 μmol L−1 was estimated.