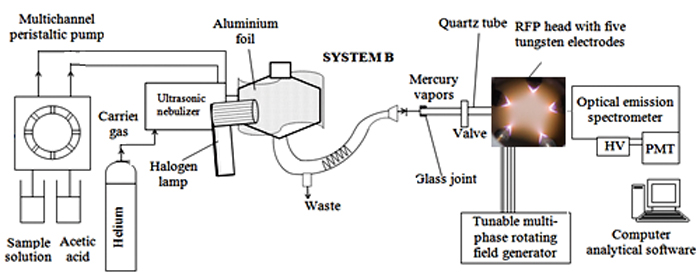
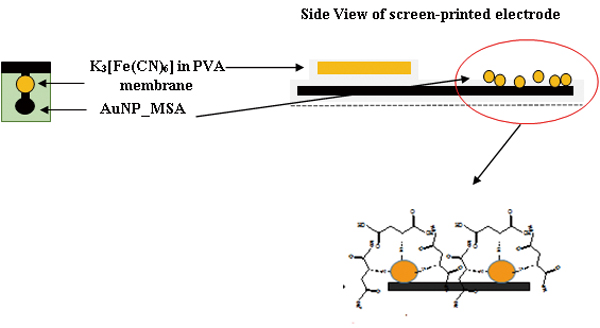
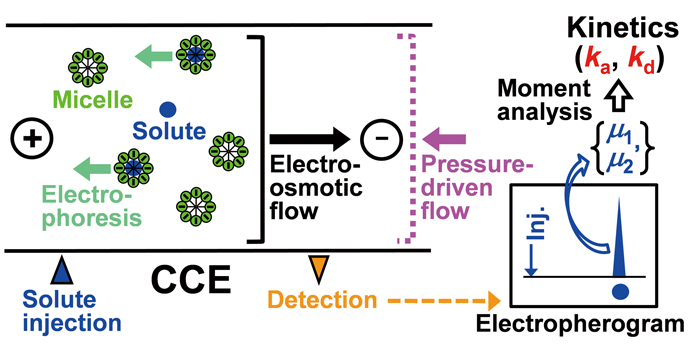
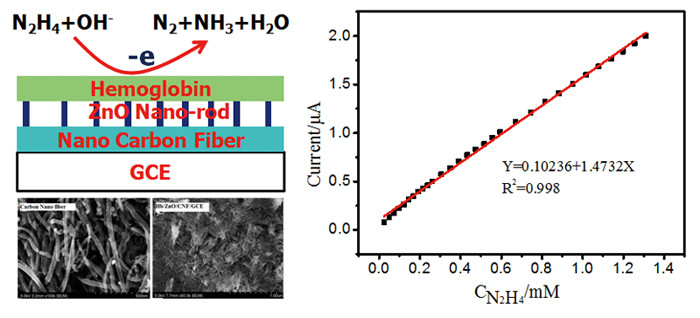
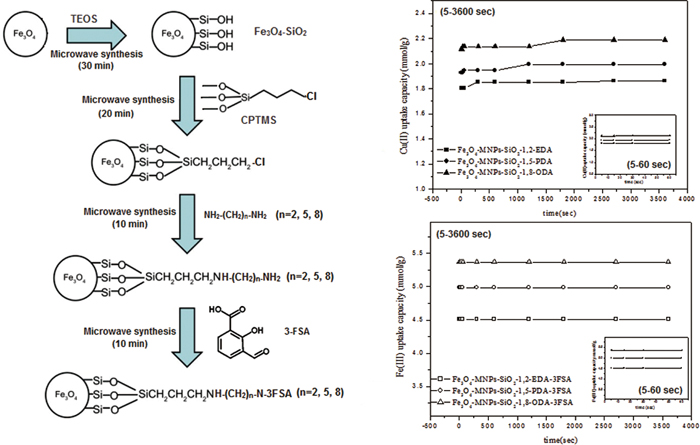
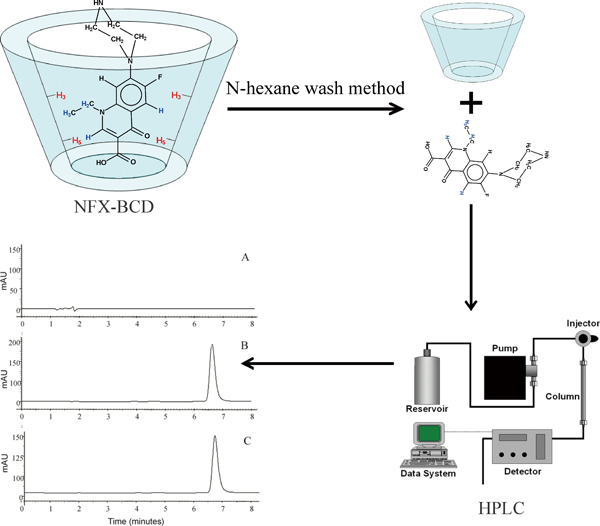
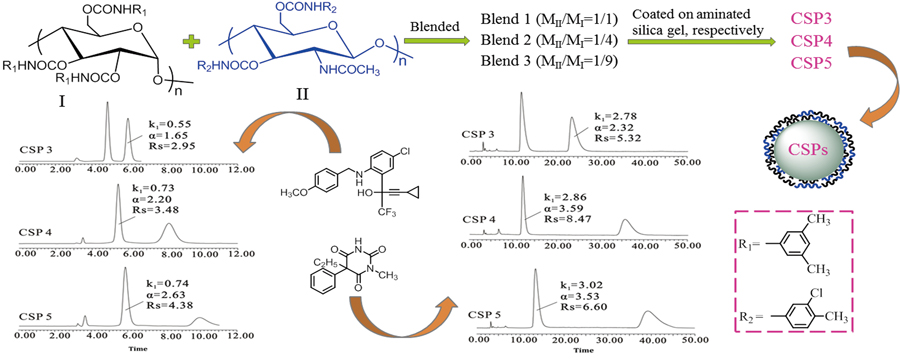
Volume 31, Issue 10
Displaying 1-21 of 21 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 955-960
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (8743K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 961-969
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (4173K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 971-977
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (2318K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 979-986
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (817K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 987-995
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (11482K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 997-1003
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (1471K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 1005-1010
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (1816K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 1011-1017
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (8727K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 1019-1025
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (2820K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 1027-1033
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (2609K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 1035-1039
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (1380K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 1041-1045
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (864K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 1047-1054
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (1906K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 1055-1059
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (1059K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 1061-1068
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (2757K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 1069-1074
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (1197K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 1075-1081
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (1601K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 1083-1089
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (604K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 1091-1097
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (736K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 1099-1103
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (460K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2015Volume 31Issue 10 Pages 1105
Published: October 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2015
Download PDF (2723K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|