-
Editor's pick
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the most frequent arrhythmias in patients with hypertension. The authors found that an L/N-type calcium channel blocker cilnidipine exerts anti-AF effects in the remodeled atria of Dahl salt-sensitive rats more potently than amlodipine. Since plasma catecholamine levels is lower in the cilnidipine-treated animals than those in amlodipine-treated ones, blockade of N-type calcium channels presumably contributes to the superior cardioprotective effect of cilnidipine. These findings provide important information for considering treatment of hypertension complicating AF.
-
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 4 Pages 507-514Overexpressed Hsa_circ_0001326 Contributes to the Decreased Cell Viability in SWAN71 Cells by Regulating MiR-186-5p/p27 Kip1 Axis Read more
-
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 4 Pages 522-527Dietary Fructooligosaccharides Reduce Mercury Levels in the Brain of Mice Exposed to Methylmercury Read moreEditor's pick
Fructooligosaccharides (FOS), typical nondigestible oligosaccharides, change the composition and/or activity of microbiota in the large intestine. Intestinal microbiota has important roles in the decomposition and fecal excretion of methylmercury (MeHg). Fecal Hg excretion was markedly higher in FOS-fed mice than in controls after oral administration of MeHg, but urinary Hg excretion was not. FOS-fed mice had lower total Hg levels in all tissues (including the brain) than controls. The possible mechanism on function of FOS is accelerated MeHg demethylation by intestinal bacteria and reduced MeHg absorption in the large intestine.
-
Editor's pick
Psoriasis is an inflammatory skin disease characterized by red scaly papules or plaques. It has been suggested that activation of immune cells such as T cells and abnormal differentiation and proliferation of keratinocytes are involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. IL-2-inducible T cell kinase (ITK) is a tyrosine kinase expressed in T cells that regulates T cell activation. Authors showed that topical application of BMS-509744, a selective ITK inhibitor, ameliorates psoriasis-like inflammation in the skin of mice. This study suggests that ITK inhibition in skin lesion is a promising candidate treatment for psoriasis.
-
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 4 Pages 544-549Increase in Blood Pressure by Local Injection of Ketamine into the Amygdala in Rats Read moreEditor's pick
Ketamine is known as a dissociative anesthetic that suppresses the cerebral cortex and activates the limbic system, and is unique as an anesthetic, since it induces blood pressure increase. Author examined the effect of ketamine, applied directly to the amygdala, on blood pressure. The results showed that the blood pressure was increased by ketamine injection into the basolateral and central nuclei of the amygdala, endopiriform nucleus and piriform cortex. Elucidation of the mechanism of ketamine-induced blood pressure increase will lead to understanding of the mechanism of side effects of ketamine, and will contribute to its appropriate use.
-
Editor's pick
The malignant potential of neuroblastoma is associated with elevated expression of β4-galactosyltransferase (β4GalT) 3. The transcription of the β4GalT3 gene is regulated by transcription factor Sp3 in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line, and Sp3 activates the β4GalT3 gene promoter. In this study, the authors demonstrated that the transcriptional activation of the β4GalT3 gene is mediated by the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling, and the phosphorylation of the serine residues in Sp3 is important for the transcriptional activation. The findings propose a therapeutic strategy for the regulation of the β4GalT3 gene in neuroblastoma by controlling the phosphorylation of Sp3.
-
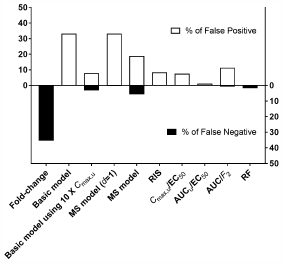
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 3 Pages 338-349Evaluation of Methods to Assess CYP3A Induction Risk in Clinical Practice Using in Vitro Induction Parameters Read moreEditor's pick
The authors evaluated the predictability of various methods used to assess clinical CYP3A induction risk based on various in vitro parameters, and demonstrated that correlation methods were better at predicting clinical induction risk than direct methods recommended in guidance/guidelines. Among correlation approaches, the Relative Factor (RF) and AUC/F2 methods showed an especially good correlation with clinical induction, and can be used to assess induction risk along with other correlation methods recommended in guidance/guidelines. These findings may allow researchers to more confidently determine whether or not a clinical induction study should be performed before clinical trials.
-
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 3 Pages 422-430Glucosyl Hesperidin Has an Anti-diabetic Effect in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice Read moreEditor's pick
Obese adipose tissue is characterized by increased immune cell infiltration. Adipocyte-immune cell interaction overproduces inflammatory adipokine, which contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus. The regulation of immune cells infiltration and inflammation in adipose tissue may exert preventive and therapeutic effects on obesity-related diseases. Flavonoids such as hesperidin have anti-inflammatory properties, but their low bioavailability limits their use as drugs and supplements. The authors report that glucosyl hesperidin (GH), a water-soluble derivative of hesperidin, ameliorated glucose intolerance and reduced macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue in high-fat diet-fed mice. These results suggest the usefulness of GH against obesity-related diseases.
-
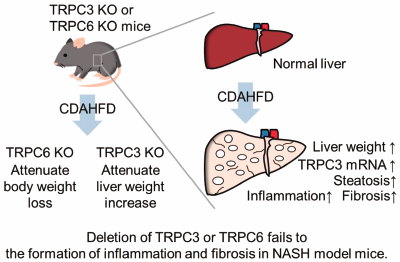
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 3 Pages 431-436Deletion of TRPC3 or TRPC6 Fails to Attenuate the Formation of Inflammation and Fibrosis in Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis Read moreEditor's pick
Two transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) subfamily members, TRPC3 and TRPC6, reportedly participate in the development of fibrosis in cardiovascular and renal systems. This study is to investigate whether TRPC3 and TRPC6 channels also contribute to the formation of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) which includes liver fibrosis, using TRPC3 or TRPC6 systemic knockout mice fed with the choline-deficient, L-amino acid-defined, high-fat diet. The authors found that systemic deletion of TRPC3 or TRPC6 gene alone failed to attenuate liver dysfunction and fibrosis in NASH model mice.
-
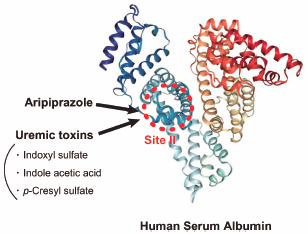
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 3 Pages 437-441Effects of Uremic Toxins on the Binding of Aripiprazole to Human Serum Albumin Read moreEditor's pick
Aripiprazole (ARP), an antipsychotic drug, binds strongly to site II on human serum albumin (HSA). In this study, the issue of how uremic toxins (indoxyl sulfate, indole acetic acid and p-cresyl sulfate) affect the binding of ARP to HSA were investigated. Authors demonstrated that these uremic toxins inhibit the binding of ARP to diazepam subsite within site II, and these inhibitory effects were more significant, comparing with those on the drug binding to arylpropionic acids subsite. These findings provide important information for considering the pharmacokinetics of ARP and the drugs that bind to site II during renal diseases.
-
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 3 Pages 442-447Altered Functional Connectivity of the Orbital Cortex and Striatum Associated with Catalepsy Induced by Dopamine D1 and D2 Antagonists Read moreEditor's pick
By combining whole-brain activation mapping of neurons activated in response to dopamine D1 and D2 receptor antagonists with non-bias analysis, Niu et al. provide the direct evidence that the orbital cortex in addition to the striatum are important brain areas associated with DA antagonists-induced movement abnormality.
-
Editor's pick
Transient receptor potential melastatin 3 (TRPM3) is Ca2+-permeable channel that is highly expressed in the brain and activated by the neurosteroid pregnenolone sulfate (PS) and body temperature. Here, it is shown that TRPM3 was expressed in cultured rat oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs) and activated by PS, resulting in extracellular Ca2+ influx. Moreover, TRPM3 expression was increased by treatment with tumor necrosis factor a. In demyelinated lesions of endothelin-1-induced ischemic rat model (lacunar infarction model), TRPM3 was upregulated in OPCs, a type of glial cells that differentiate into myelinating oligodendrocytes. These imply that TRPM3 is involved in the regulation of specific behaviors of OPCs in inflammatory pathological conditions. Scale bar shows 200 mm.
-
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 2 Pages 197-210Involvement of CD73 and A2B Receptor in Radiation-Induced DNA Damage Response and Cell Migration in Human Glioblastoma A172 Cells Read moreEditor's pick
The article by Kitabatake et al. suggested a novel mechanism of radiation resistance and radiation-induced acquisition of malignant profile in glioblastoma. Authors have shown that CD73, an enzyme that metabolizes extracellular ATP to adenosine, and activation of adenosine A2B receptor (CD73-A2B receptor pathway) are involved in radiation-induced DNA damage response, cell death, and enhancement of cell migration in A172 cells. These findings proposed that the CD73-A2B receptor pathway contributes to the resistance of the antitumor effect of radiation in glioblastoma and could be a novel molecular target to improve the efficiency of radiation therapy for glioblastoma.
-
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 2 Pages 251-258In Vitro and in Vivo Comparative Study of Oral Nanoparticles and Gut Iontophoresis as Oral Delivery Systems for Insulin Read moreEditor's pick
Most of therapeutic peptides like insulin are administered parenteral because of rapid hydrolysis and enzymatic degradation after oral administration. Many techniques have been investigated for overcoming the problems and meeting the shortage of current conventional dosage forms such as iontophoresis.In this study, authors investigated if iontophoresis can be used to enhance permeation of insulin nanoparticles across the intestinal membrane and thus enhance the oral delivery of insulin.Gut iontophoresis is a promising technology that can substantially improve the transport of insulin nanoparticles across the intestinal membrane barrier.
-
Editor's pick
Acidified extracellular pH (pHe) characterized of tumor microenvironment (TME) impairs the responses of tumors to anti-cancer chemotherapies. In this study, the authors showed that daily oral dosing of sodium potassium citrate (K/Na citrate) increased blood bicarbonate concentrations and then neutralized the tumor pHe. In addition, this tumor neutralization potentiated the therapeutic effect of anticancer agent TS-1 on Panc-1 pancreatic cancer-xenograft murine model. The authors strongly propose that the neutralization of acidic TME by oral dosing of K/Na citrate must be a smart approach for enhancing the therapeutic effects of anticancer agents for pancreatic cancer in the end stage.
-
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 2 Pages 275-278Analysis of α-Defensin 5 Secretion in Differentiated Caco-2 Cells: Comparison of Cell Bank Origin Read moreEditor's pick
α-Defensin 5 has a particularly broad antibacterial spectrum, eliminates pathogenic microorganisms and regulates intestinal flora. There are few reports of measuring the secretory capacity of α-defensin 5 in vitro. In this study, author found Caco-2 cells, which are gastrointestinal model cells, secreted α-defensin 5 and examined the relationship between α-defensin 5 secretion and cytokines mRNA levels such as TNF-α. These results suggest that Caco-2 cells may be a simple model for screening health food components and drugs that affect α-defensin 5 secretion.
-
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 1 Pages 1-6Design of Functional Nanoparticles for Intractable Disease Therapy Read moreEditor's pick
Synthetic polymers have the potential to work as protein affinity reagents by mimicking protein–protein interactions. The authors report the recent research in the design of synthetic polymer nanoparticles (NPs) that capture and neutralize target molecules for intractable disease therapy. The authors found that lightly crosslinked (2%) N-isopropylacrylamide (pNIPAm)-based NPs bind to target small molecules, peptides, and proteins in vivo by the inclusion of several functional monomers, such as charged and hydrophobic monomers. In addition, modification of linear polymer onto lipid nanoparticles improved polymer circulation time in vivo and binding affinity for the target. These results will provide information for the in vivo application of synthetic polymers.
-
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 1 Pages 82-87Role of Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acids in Acetylcholine-Induced Dilation of Rat Retinal Arterioles in Vivo Read moreEditor's pick
Acetylcholine (ACh) dilates retinal blood vessels through nitric oxide (NO)-dependent and NO-independent mechanisms. In the rat retinal arteriole, NO stimulates the cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1)/prostaglandin I2 (PGI2)/prostanoid IP receptor/cAMP signaling pathway and activates 4-aminopyridine-sensitive KV channels (KV). The article by Mori et al. provides evidence suggesting that cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenase-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) activate large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels (BKCa) in rat retinal arterioles. The NO-independent component of ACh-induced retinal vasodilator response is mediated partly by an endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization mechanism, through CYP epoxygenase-derived EETs. EETs may function as an endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor in rat retinal arterioles.
-
Editor's pick
Snail-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) enhanced P-glycoprotein (P-gp) function and drug resistance to P-gp substrate anticancer drug in a human NSCLC cell line, HCC827. This study indicates that multidrug resistance-associated proteins (MRPs) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) are regulated differently in HCC827 cells with Snail-induced EMT. Specifically, the function of MRP5 appears to be enhanced via an increase in membrane localization, whereas the function of BCRP is reduced via a decrease in the expression level. Therefore, it was suggested that MRPs and BCRP are regulated differently in HCC827 cells with Snail-induced EMT.
-
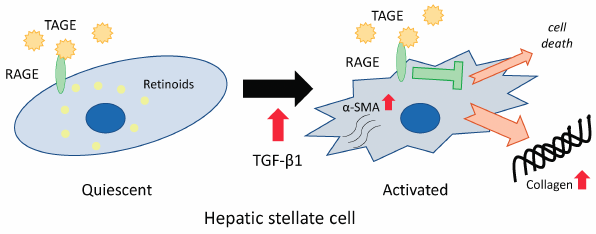
Volume 44 (2021) Issue 1 Pages 112-117Suppression of Hepatic Stellate Cell Death by Toxic Advanced Glycation End-Products Read moreEditor's pick
Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) are produced by the non-enzymatic reaction of sugars with proteins. It has been revealed that glyceraldehyde-derived toxic AGEs (TAGE) are elevated with the non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) that causes such as liver fibrosis. Liver fibrosis is caused by activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Herein, it was found that the suppression of apoptosis in activated LX-2 cells which are HSCs by TGF-β1 and TAGE co-treatment is related to an increase in the production of the extracellular matrix such as collagen Ⅰ. This result suggests that TAGE might aggravate the liver fibrosis of chronic hepatitis, such as NASH.