-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 6 Pages 932-937Ziyuglycoside II Inhibits Rotavirus Induced Diarrhea Possibly via TLR4/NF-κB Pathways Read moreEditor's pick
In the present study, Ziyuglycoside II inhibits rotavirus (RV) induced diarrhea via toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) signaling pathway. Ziyuglycoside II inhibited the proliferation of MA104 cells infected with RV via suppressing RV duplication. The combination of Ziyuglycoside II and Ribavirin protected against RV-induced diarrhea through regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Moreover, the combined treatment suppressed the level of pro-inflammation cytokines and overexpressed anti-inflammation cytokine. Moreover, the combined therapy improved the lesion changes and inhibited the cell apoptosis in vivo. Thus Ziyuglycoside II may function as protective role in RV-induced diarrhea.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 6 Pages 959-967Characterization and Immunological Activities of Polysaccharides from Polygonatum sibiricum Read moreEditor's pick
Polygonatum sibiricum first appeared in ancient Chinese medicine books around 1000 years ago and is used to tonify the spleen and nourish the lungs. The authors present here a kind of natural polysaccharides (PSP) extracted from Polygonatum sibiricum were purified, characterized and assayed both in vitro and in vivo for its immunomodulatory activity and mechanism. It is of interest to note that PSP not only regulated the immune function of normal mice, but participated in the protection against immunosuppression in cyclophosphamide-treated mice, highlighting its potential as an immunostimulant.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 6 Pages 968-975Potential Mechanisms Underlying the Hepatic–Protective Effects of Danshensu on Iron Overload Mice Read moreEditor's pick
Danshensu (3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-(2R)-lactic acid) is one of the water-soluble active ingredients of Salvia miltiorrhizae, a traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. This study investigated the protective effects of Danshensu on the acute liver injury induced by iron overload in mice. The results indicated that the underlying mechanisms at least partly involve anti-oxidation, anti-inflammation, anti-apoptosis, and decreasing hepatic iron deposition possibly through down-regulating the expression of iron uptake related proteins, such as DMT1, TfR, and L-type Ca2+ CP α1C. Therefore, they conclude Danshensu could be a promising prophylactic or therapeutic agent for iron overload diseases.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 6 Pages 1007-1015Detection of Abacavir-Induced Structural Alterations in Human Leukocyte Antigen-B*57 : 01 Using Phage Display Read moreEditor's pick
The interaction of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) with specific drugs induces structural alteration in HLA and delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions, which cause severe cutaneous toxicity. Shirayanagi et al. selected specific phage antibodies able to recognize HLA-B*57:01 and evaluated structural alterations in HLA-B*57:01 complexes induced by abacavir. The affinity of selected phage antibodies increased because of structural alterations in HLA-B*57:01 following exposure to abacavir, indicating that specific phage antibodies can identify drug-mediated structural changes in HLA complexes. These results suggest that phage display technology is a useful method for detecting structural changes in HLA complexes.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 5 Pages 823-830Predicting Method for the Human Plasma Concentration–Time Profile of a Monoclonal Antibody from the Half-life of Non-human Primates Read moreEditor's pick
Efficiency and animal welfare are important factors in the development of new drugs. Considering this, Nakamura et al. propose a new way of predicting human PK for mAbs that is more efficient than conventional methods. By collecting mAb PK data on linear elimination and analyzing a two-compartment model, they revealed that half-life during elimination is the main contributor to plasma clearance. Based on this feature, they developed a novel method that uses easy-to-obtain parameters from humans and non-human primates to predict human PK. Called the half-life method, it can improve animal welfare and potentially accelerate the drug development process.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 5 Pages 839-847Ethenzamide Exerts Analgesic Effect at the Spinal Cord via Multiple Mechanisms of Action Including the 5HT2B Receptor Blockade in the Rat Formalin Test Read moreEditor's pick
Ethenzamide (ETZ) is widely used as an OTC pain reliever, however, its site of action and mechanism underlying its analgesic action had not yet been fully elucidated. The article by Nikaido et al. provides evidence suggesting that the analgesic effect of ETZ in the rat formalin test was mediated by multiple mechanisms of action including the 5-hydroxytryptamine2B receptor blockade at the spinal cord.
-
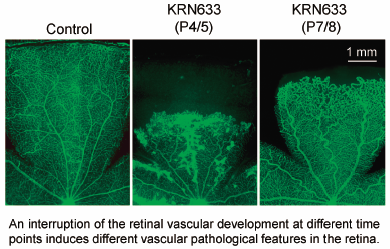
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 5 Pages 859-863Abnormal Vascular Phenotypes Associated with the Timing of Interruption of Retinal Vascular Development in Rats Read moreEditor's pick
Pathological angiogenesis is a leading cause of blindness in several retinal diseases. Kondo et al. demonstrated that only a 2-day treatment of neonatal rats with the VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor at different time points could induce abnormal blood vessels with different vascular pathological features (intravitreal neovascularization vs. tortuous arteries) in the retina. Pharmacological agents targeting the VEGF signaling pathway are useful for creating an abnormal retinal vasculature with various pathological features in order to study the mechanisms underlying abnormal retinal angiogenesis and evaluate the efficacy of anti-angiogenic compounds.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 5 Pages 873-878Cancer Cachexia May Hinder Pain Control When Using Fentanyl Patch Read moreEditor's pick
The transdermal fentanyl patch (FP) has been used worldwide to relieve cancer pain. However, no previous studies have examined the influence of cancer cachexia on pain control in cancer patients receiving FP treatment. Chiba et al. found that cancer cachexia may be a risk factor for poor pain control in patients receiving FP treatment, and that uncontrolled pain in FP treatment may be caused by the inhibition of fentanyl transdermal absorption due to dry skin.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 5 Pages 898-903Fluorinated Kavalactone Inhibited RANKL-Induced Osteoclast Differentiation of RAW264 Cells Read moreEditor's pick
To discover small molecules that affect osteoclastogenesis, Kumagai et al designed and synthesized styrylpyrone analogs, and discovered (E)-6-(2-fluorostyryl)-4-methoxy-2H-pyran-2-one (22) has osteoclast-inhibitory activities in murine RAW264 cells. A partial structure-activity relationship revealed that fluorine and its position within the styrylpyrone skeleton were important. Authors also revealed that compound 22 prevents osteoclastic bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis. Compound 22 downregulated mRNA expression levels of RANKL-induced nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 (NFATc1) and osteoclastogenesis-related genes. These findings may be useful for the desigh of antiresorptive agents for the treatment of bone disorders characterized by excessive osteoclastic activity .
-
Editor's pick
The 34th Annual Meeting of the Academy of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Technologies, Japan (APSTJ) was held in Toyama, Japan, May 16–18, 2019. In this meeting, a joint symposium was held with the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan and APSTJ. The theme of the symposium was “Recent Advances in Research on Particulate Formulations such as Lipoproteins, Liposomes, Extracellular Vesicles, and iPS Derived Cells.” The four invited speakers provide their review articles in the Current Topics of this issue.
-
Editor's pick
Interactions between drugs and pharmaceutical additives can cause problems when mixing multiple drugs in clinical settings. One example is aggregate formation between levofloxacin hydrate tablets and lansoprazole orally disintegrating tablets. Nakagawa et al investigated the factors involved in this aggregation, focusing on the role of pharmaceutical additives and electrostatic interaction. Levofloxacin, which is zwitterionic, formed aggregates with methacrylic acid copolymer LD, one of the pharmaceutical additives of lansoprazole orally disintegrating tablet. Other zwitterionic ingredients, including ampicillin, meropenem, cefepime, and cephalexin, also formed aggregates with methacrylic acid copolymer LD.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 4 Pages 688-692In Vitro Inhibitory Effects of Sesamin on CYP4F2 Activity Read moreEditor's pick
Sesamin is a major lignan in sesame seeds, and a recent meta-analysis of controlled trials showed that sesamin consumption reduces blood pressure. The antihypertensive effect of sesamin was suggested to be caused by suppression of cytochrome P450 4F2 (CYP4F2)-mediated 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid production. However, the detailed mechanism underlying inhibition of CYP4F2 function by sesamin was unclear. The article by Watanabe et al. characterized the in vitro inhibitory effects of sesamin on human CYP4F2 activity. The results indicated that sesamin is a mechanism-based inactivator of CYP4F2.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 4 Pages 697-706Transport Characteristics of 5-Aminosalicylic Acid Derivatives Conjugated with Amino Acids via Human H+-Coupled Oligopeptide Transporter PEPT1 Read moreEditor's pick
5-Aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) is used as first line therapy for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). However, a very high 5-ASA dose is required for IBD treatment because 5-ASA formula is relatively low delivery efficacy to local inflamed colonic sites. In this report, Yuri et al. focused on an intestinal H+-coupled oligopeptide transporter 1 (PEPT1) which is induced in the colon under IBD condition, and demonstrated that the newly synthesized dipeptide-like 5-ASA derivatives, which are coupling glycine, glutamic acid and valine to amino group of 5-ASA, were transportable substrates for PEPT1.
-
Editor's pick
Cutting-edge contributions from invited poster presentations providing significant research works in the fifth International Symposium for Medicinal Sciences (ISMS) in the 139th Chiba annual meeting in 2019 are assembled for the Current Topics section in this issue of the Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin.
-
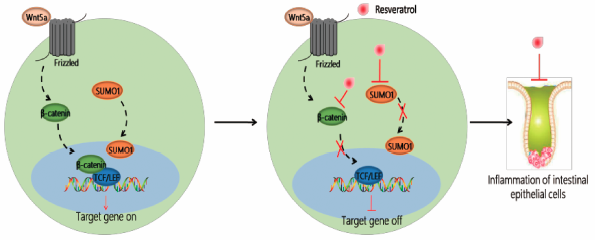
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 3 Pages 450-457Resveratrol Attenuates Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Mice by Regulating SUMO1 Read moreEditor's pick
Mao et al. found that resveratrol can significantly inhibit the expression of SUMO1. They demonstrate that resveratrol alleviates inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in mice by inhibiting the expression of SUMO1 molecule, and by modulating the activation of wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Clinical analysis also proves that the expression of SUMO1 and β-catenin molecules increased with the worsening of the disease, which also provides a new method for clinical diagnosis and treatment of IBD.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 3 Pages 458-462Risk Factors for Major Bleeding and Clinically Relevant Non-major Bleeding in Japanese Patients Treated with Edoxaban Read moreEditor's pick
Edoxaban is an oral anticoagulant used for preventing and treating stroke or systemic embolism. Bleeding is the most common complication associated with anticoagulants. In particular, severe bleeding is assumed to be related to mortality in patients treated with anticoagulation therapy. However, few studies have examined the risk factors for bleeding in Japanese patients receiving edoxaban. The article by Takase et al. revealed that a low baseline hemoglobin level was a significant risk factor for major and clinically relevant bleeding in Japanese patients receiving edoxaban.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 3 Pages 516-525Involvement of A2B Receptor in DNA Damage Response and Radiosensitizing Effect of A2B Receptor Antagonists on Mouse B16 Melanoma Read moreEditor's pick
The article by Tanaka et al. proposed a novel mechanism of radioresistance and candidate for use as radiosensitizers in radiation therapy of melanoma. A2B receptor was involved in radioresistance via DNA damage response in B16 cells. A2B receptor antagonist enhances tumor growth-inhibitory effect by gamma-ray and shows radiosensitizing effect in vivo. These findings proposed that A2B receptor contributes to radioresistance, and could be a new target for the development of agents to increase the efficacy of radiotherapy.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 3 Pages 540-545The Lysosome Pathway Degrades CD81 on the Cell Surface by Poly-ubiquitination and Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis Read moreEditor's pick
CD81 is important for regulating biological processes such as B cell receptor signaling and B cell differentiation. However, little is known about degradation mechanism of CD81. Hosokawa et al. demonstrated that CD81 on the cell surface is degraded by lysosome via K63- and K29-linked poly-ubiquitination. The poly-ubiquitinated CD81 is translocated from the cell surface into endosomes and is degraded by lysosomes. This is the first report showing that the lysosomal degradation of CD81 requires poly-ubiquitination and clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 2 Pages 195-206Toxicological Property of Acetaminophen: The Dark Side of a Safe Antipyretic/Analgesic Drug? Read moreEditor's pick
Acetaminophen (paracetamol, N-acetyl-p-aminophenol; APAP) is undoubtedly a well-recognized and highly used antipyretic/analgesic in the world. However, some experts have misunderstood that APAP is a type of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) with weak-to-moderate effects, since the adverse reaction profiles of APAP described in package insert in Japan are almost the same as classical NSAIDs. Even clinicians and researchers might actually have a wrong perception regarding it. The review by Ishitsuka et al. the safety profiles of APAP particularly in terms of respiratory tract and ductus arteriosus-related toxicity. We also introduce some recent findings about molecular mechanisms of APAP hepatotoxicity.
-
Editor's pick
Microbes are important for pharmacists, biologists, and chemists, because some environmental microbes cause infectious diseases, but also produce beneficial compounds for our health. Understanding environmental microbes are necessary to live with them and also contributes to preventing infectious diseases. This current topic summarized the recent progress on controlling environmental pathogenic microbes by disinfection methods, sterilization methods, vaccines, antibiotics, and developing new technologies.