-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 2 Pages 284-288A Pilot Clinical Study on Thiamine Hydrochloride as a New Mosquito Repellent: Determination of the Minimum Effective Dose on Human Skin Read moreEditor's pick
Mosquitoes that spread everywhere not only cause irritation, redness and discomfort after biting, but also can transmit contagious diseases. Many insect repellents have been used for decades, but were found either toxic or ineffective. Thiamine hydrochloride which is a water soluble vitamin was claimed to have certain insect repellent activity. However, there is a demand for a reassessment of the minimum required dose that is sufficient to perform a topical repellency on the human skin. The article by Badawi et al. estimated a dose response line through “probit plane analysis”. The repellent dose corresponding to percent protection of 50% and 99.9% was determined and validated.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 2 Pages 325-333Pharmacological Properties of JTE-952, an Orally Available and Selective Colony Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor Kinase Inhibitor Read moreEditor's pick
Colony stimulating factor 1 (CSF1) receptor (CSF1R) is a receptor protein-tyrosine kinase specifically expressed in monocyte-lineage cells. The article by Uesato et al. characterized the pharmacological properties of JTE-952, a novel CSF1R tyrosine kinase inhibitor. JTE-952 potently inhibited human CSF1R kinase activity and displayed no marked inhibitory activity against other kinases excluding tropomyosin-related kinase A. JTE-952 potently inhibited the CSF1-induced proliferation of human macrophages, and lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory cytokine production by human macrophages and in whole blood. In addition, orally delivered JTE-952 significantly attenuated arthritis severity in a mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis. These results indicate that JTE-952 is a potentially clinically useful agent for the treatment of a variety of human inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis.
-
Editor's pick
Oxaliplatin is the first-line chemotherapy for tumor treatment often accompanied with peripheral neuropathic pain. There are no specific drugs for the disease at present. Current studies have shown that curcumin has various biological activities like antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antitumor and so on, while few studies were conducted about its role in oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathic pain. The article by Zhang et al. demonstrated that curcumin could alleviate oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathic pain; the mechanism might be inhibiting oxidative stress-mediated activation of NF-κB and mitigating neuroinflammation. This study will provide an experimental foundation for the clinical application of curcumin in oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain.
-
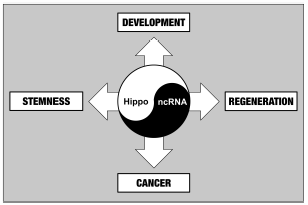
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 1 Pages 1-10The Emerging Link between the Hippo Pathway and Non-coding RNA Read moreEditor's pick
Extensive studies in recent years have revealed important functions of the Hippo intracellular signaling pathway in the control of organ development, stem cell biology, regeneration, and cancer. While a number of novel drugs are currently under development to modulate the Hippo pathway for cancer treatment and regenerative medicine, the molecular networks involving in the regulation of the Hippo pathway are just beginning to be elucidated. The review article by Shimoda and Moroishi summarizes the emerging understanding of the interplay between the Hippo pathway and non-coding RNAs, discussing a new approach to target this pathway for future drug discovery.
-
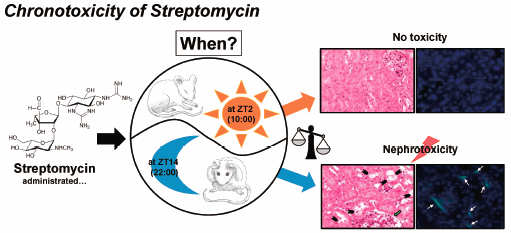
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 1 Pages 53-58Chronotoxicity of Streptomycin-Induced Renal Injury in Mice Read moreEditor's pick
Yoshioka and Miura et al. have focused on the relationship between the injection timings and the severity of toxicity, which they advocated as “chronotoxicology”. The aim of this study was to investigate the “chronotoxicity” of streptomycin (SM) in relation to its circadian periodicity. Both the mortality and the nephrotoxicity levels were severe by the SM injection during the “dark phase” than during the “light phase”, representing that SM showed evident chronotoxicity. The results indicated that chronotoxicology may provide valuable information on the importance of injection timings for evaluations of toxicity, and considering when determining any undesirable side effects.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 1 Pages 129-137Metformin Suppresses LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Macrophage and Ameliorates Allergic Contact Dermatitis in Mice via Autophagy Read moreEditor's pick
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is one of the most common skin diseases caused by hapten-modified proteins. The article demonstrated that metformin inhibited inflammatory responses in macrophages. Furthermore, metformin also enhanced autophagic flux, inhibited the phosphorylation of AKT/mTOR, MAPKs related protein levels and the level of miR-221 in macrophages. Besides, metformin attenuated 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene (DNFB) -induced ACD partly through the inhibition of macrophage activation and the induction of autophagic flux. Taken together, the results indicated that metformin ameliorates ACD through enhanced autophagic flux to inhibit macrophage activation and provides a potential contribution to ACD treatment.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 1 Pages 138-144The Synthetic Curcumin Derivative CNB-001 Attenuates Thrombin-Stimulated Microglial Inflammation by Inhibiting the ERK and p38 MAPK Pathways Read moreEditor's pick
Thrombin is a serine protease as a blood coagulation factor, but also has been implicated in the pathology of brain ischemia, stroke or neurogenerative diseases. In this study, Akaishi et al. have demonstrated that the synthetic curcumin derivative CNB-001 suppresses thrombin-induced NO production through the inhibition of ERK and p38 MAPK pathways in microglia. In contrast, the authors have previously reported that CNB-001 suppressed LPS-induced NO production through the inhibition of p38 MAPK, but not ERK. Therefore, additional studies on differences in signaling cascades by which thrombin and LPS promote ERK phosphorylation will help to identify the direct molecular target of CNB-001.
-
Volume 43 (2020) Issue 1 Pages 158-168Cloning, Expression, and Purification of a Pathogenesis-Related Protein from Oenanthe javanica and Its Biological Properties Read moreEditor's pick
Hypersensitive reaction to pathogenic attacks in plants triggers the expression of numerous plant genes encoding defense proteins. Pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins play an important role in inducing strong self-defense systems by getting accumulated in intercellular parts and vacuoles. Joo et al. cloned a PR protein gene from Oenanthe javanica (OJPR), which included PR-10 allergen without putative IgE binding residues, comprising 154-amino acids with a molecular mass of 16 kDa. The results of this study suggested that the newly identified and expressed OJPR may possess the biological activity and play a role in modulating host defense responses via Toll-like receptor signal cascades together with anti-viral activities in immune cells.
-
Volume 42 (2019) Issue 11 Pages 1926-1935Development of a Novel Intraocular-Pressure-Lowering Therapy Targeting ATX Read moreEditor's pick
Elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) is the major cause of glaucoma, which is the second leading cause of blindness. To develop new IOP-lowering treatments, the article by Nagano et al. generated a novel ATX inhibitor as an ophthalmic drug by high-throughput screening, followed by inhibitor optimization. Administration of the optimized ATX inhibitor (Aiprenon) reduced IOP in laser-treated mice exhibiting elevated IOP and higher level of ATX activity in AH and normal mice in vivo. The stimulation of ATX induced outflow resistance in the trabecular pathway; however, administration of Aiprenon recovered the outflow resistance in vitro.
-
Volume 42 (2019) Issue 10 Pages 1707-1712Acute and Direct Effects of Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition on Glomerular Filtration Rate in Spontaneously Diabetic Torii Fatty Rats Read moreEditor's pick
Recent clinical studies indicate that sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors exhibit a renoprotective effect. However, the mechanism underlying this effect has not been fully elucidated. The article by Takakura and Takasu found that single intravenous injection of ipragliflozin, a selective SGLT2 inhibitor, at a dose that increased glucose excretion reduced creatinine clearance without affecting systemic blood pressure in type 2 diabetic mellitus STD-fatty rats. These results suggest that SGLT2 inhibition directly reduces whole-kidney glomerular filtration rate, most likely due to a reduction in intraglomerular pressure, by altering local renal hemodynamics. This effect might explain the renoprotective effects demonstrated in clinical studies, at least partly.
-
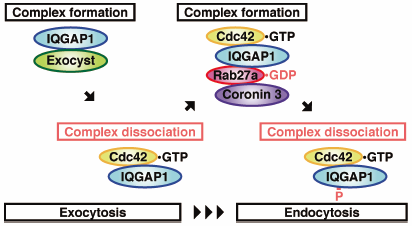
Volume 42 (2019) Issue 9 Pages 1532-1537GDP-Bound Rab27a Dissociates from the Endocytic Machinery in a Phosphorylation-Dependent Manner after Insulin Secretion Read moreEditor's pick
Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion is controlled by both exocytosis and endocytosis in pancreatic β-cells. Although endocytosis is a fundamental step to maintain cellular responses to the secretagogue, the molecular mechanism of endocytosis remains poorly defined. Kimura et al. have demonstrated the regulatory mechanisms of the IQGAP1/GDP-bound Rab27a endocytic machinery. PKCε, which was activated by glucose stimulation, phosphorylated IQGAP1 on Ser-1443, thereby promoting the dissociation of the IQGAP1/GDP-bound Rab27a complex in pancreatic β-cells. Insulin secretion is controlled by stage-specific complex formation and the dissociation of IQGAP1 from its specific binding partners.
-
Editor's pick
Reconstituted discoidal high-density lipoprotein particles are called lipid nanodisks, which can be developed for biocompatible delivery vehicles. The article by Tanaka et al. designed lipid nanodisks using a peptide (LpA peptide) with the LDL receptor-binding region of apolipoprotein E (apoE). Discoidal LpA nanodisks of approximately 10 nm in size were successfully prepared. In addition, the uptake of LpA nanodisks was higher than that of apoE nanodisks especially under the condition where the expression of LDL receptor was increased (LPDS) compared with the normal condition (FBS). Thus, LpA nanodisks are potential biocompatible delivery vehicles targeting LDL receptors.
-
Volume 42 (2019) Issue 7 Pages 1140-1145Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Induced by Repeated Forced Swimming in Mice Read moreEditor's pick
Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) has few beneficial treatments for patients. Recently, the involvement of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) in ME/CFS has been reported. However, it is little known whether PDH could be a therapeutic target of ME/CFS. In this paper, Ohba et al. established ME/CFS model in mice and investigated the involvement of PDH. In an ME/CFS group, PDH activity was decreased in the mitochondrial fraction of the gastrocnemius muscle. Sodium dichloroacetate (DCA), which is a PDH activator, recovered fatigue-like behavior in ME/CFS group. These findings indicate that PDH might be an important therapeutic target for treatment of ME/CFS.
-
Volume 42 (2019) Issue 6 Pages 944-953Selective Protein Expression Changes of Leukocyte-Migration-Associated Cluster of Differentiation Antigens at the Blood–Brain Barrier in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Systemic Inflammation Mouse Model without Alteration of Transporters, Receptors or Tight Junction-Related Protein Read moreEditor's pick
Leukocyte migration across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a key step in the progression of brain dysfunction in systemic inflammation. The key regulatory molecules at the BBB involved in leucocyte-endothelial interaction would be promising druggable targets. Sato et al. have established the LC-MS/MS-based comprehensive absolute protein quantification system for the cluster of differentiation (CD) antigens and identified the key molecules at mouse BBB in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced systemic inflammation based on their absolute protein expressions. Their findings should be helpful in the development of BBB-targeting drugs to block leukocyte migration associated with central nervous system disorders.
-
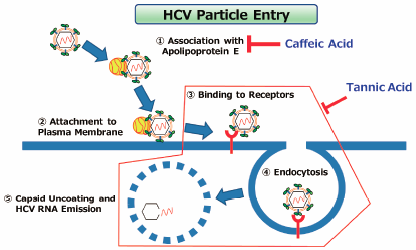
Volume 42 (2019) Issue 5 Pages 770-777Inhibition Mechanisms of Hepatitis C Virus Infection by Caffeic Acid and Tannic Acid Read moreEditor's pick
The article by Shirasago et al demonstrated that the coffee-related compounds caffeic acid and tannic acid act on hepatitis C virus (HCV) particles and abrogate their infectivity. Particularly, the authors demonstrated that caffeic acid significantly reduced cellular attachment of HCV particles and their interaction with host apolipoprotein E, which is essential for HCV infectivity. Intake of coffee or the coffee-related compounds caffeic acid and tannic acid, which are inexpensive and easy to supply, might lead to prevention of HCV infection and slower disease progression after HCV infection.
-
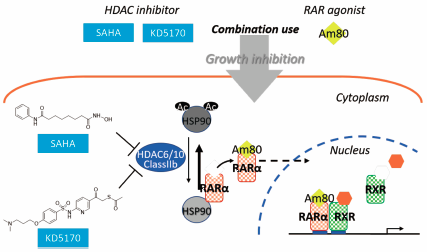
Volume 42 (2019) Issue 3 Pages 448-452Class IIb HDAC Inhibition Enhances the Inhibitory Effect of Am80, a Synthetic Retinoid, in Prostate Cancer Read moreEditor's pick
The growth-inhibitory effects of Am80 (tamibarotene), a specific retinoic acid receptor (RAR) α/β agonist, in combination with a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) on androgen receptor positive or negative prostate cancer cell lines were investigated. Ishigami-Yuasa et al. found that the combination therapy of Am80 and SAHA showed an enhanced growth-inhibitory effect on LNCaP cells. Studies with various HDAC isotype-selective inhibitors indicated that the Class IIb HDACs, especially HDAC6, had significant roles in the enhanced effect of the combination. Thus, dual targeting of Class IIb HDAC and RARα would be useful therapeutic strategy for prostate cancer.
-
Volume 42 (2019) Issue 2 Pages 273-279Hepatic and Intrahepatic Targeting of Hydrogen Sulfide Prodrug by Bioconjugation Read moreEditor's pick
The delivery of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) to liver is expected for the treatment of hepatic diseases. K. Sakai et al. developed two types of sulfo-albumins, macromolecular H2S prodrugs, for hepatic and intrahepatic targeting of H2S. Sulfide groups (source of H2S) were covalently bound to succinylated (Suc) and galactosylated (Gal) bovine serum albumin (BSA) for targeted delivery of H2S to hepatic nonparenchymal cells and parenchymal cells, respectively. Their results demonstrated targeted delivery of H2S prodrug to a specific type of liver cells using the chemical modification of targeting ligands.
-
Volume 42 (2019) Issue 1 Pages 57-65Forced Expression of CXCL10 Prevents Liver Metastasis of Colon Carcinoma Cells by the Recruitment of Natural Killer Cells Read moreEditor's pick
CXC chemokine ligand (CXCL) 10 is a chemokine that binds to CXCR3 expressed on natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. In this paper, Kikuchi et al. showed that forced expression of CXCL10 in murine colon carcinoma CT26 cells prevents their in vivo proliferation and liver metastasis by recruiting NK cells, suggesting that forced expression of CXCL10 in the colon tumors by gene delivery should lead to a favorable clinical outcome.
-
Volume 41 (2018) Issue 12 Pages 1853-1858Skin Sensitization to Fluorescein Isothiocyanate Is Enhanced by Butyl Paraben in a Mouse Model Read moreEditor's pick
Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-induced contact hypersensitivity is a mouse model of skin allergy to chemicals. In this model, chemicals such as phthalate esters are known to enhance skin sensitization to FITC. The article by Matsuoka et al. demonstrated that butyl paraben (BP), a common preservative, enhances skin sensitization as revealed by ear-swelling response to FITC. Mechanistically, BP facilitates dendritic cell trafficking from skin to lymph nodes, and enhances cytokine production from lymph node cells. Their results provide direct in vivo evidence that BP, like phthalate esters, enhances sensitization to other chemicals.
-
Volume 41 (2018) Issue 11 Pages 1716-1721Analysis of Glycoforms and Amino Acids in Infliximab and a Biosimilar Product Using New Method with LC/TOF-MS Read moreEditor's pick
How can you know the structural difference between biosimilar and reference product? The structure of biosimilar products is not the same as their original product because of post-translational modifications. In the article by Tsuda et al., a valuable method with a papain digestion and LC/TOF-MS analysis was established. Their new method can analyze not only carbohydrate chains but also amino acids of bio-medicines including biosimilar antibodies. This technology will provide a useful strategy to evaluate bio-medicines including biosimilar antibodies.