-
Volume 41 (2018) Issue 10 Pages 1567-1573Characteristics of Bone Strength and Metabolism in Type 2 Diabetic Model Nagoya Shibata Yasuda Mice Read moreEditor's pick
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) animal models are often used in basic research on diabetic osteoporosis. The article by Tanaka et al. elucidated hyperglycemia contributed to a decrease in bone metabolism turnover in the T2DM animal model NSY mice, resulting in a thinner and shorter femur, lower cortical and trabecular area, and lower bone mass. Their results suggest that these effects contribute to the deteriorated bone strength of the femur in NSY mice, and the NSY mouse could serve as an appropriate T2DM animal model for examining the specific effect of hyperglycemia on bone integrity, using the ICR mouse as a control.
-
Volume 41 (2018) Issue 9 Pages 1456-1462Effects of Supplementary Seleno-L-methionine on Atopic Dermatitis-Like Skin Lesions in Mice Read moreEditor's pick
Seleno-L-methionine (SeMet) is a major form of selenium compounds in foods. The article by Arakawa et al. demonstrated that ear thickness was increased by repeated application of 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene (TNCB) to the ear, and SeMet significantly suppressed ear thickness in mice. SeMet inhibited epidermal hyperplasia and dense infiltration of inflammatory cells. Serum total immunoglobulin (Ig) E levels were suppressed by SeMet. Interleukin (IL) 4 expression in the ear and superficial parotid lymph node was inhibited by SeMet. These results demonstrated that SeMet suppresses atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions and inhibits the expression of total IgE and IL-4.
-
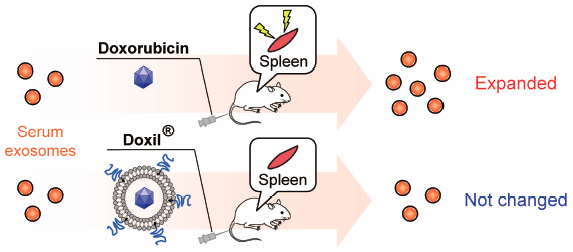
Volume 41 (2018) Issue 7 Pages 1078-1083Doxorubicin Expands in Vivo Secretion of Circulating Exosome in Mice Read moreEditor's pick
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles released by various types of cells, including immune cells and cancer cells. The article by Emam et al evaluated in vivo secretion of exosomes following intravenous injection of free doxorubicin (DXR) or liposomal DXR (Doxil®) was evaluated using normal mice. Free DXR treatment markedly increased the serum exosome level, while Doxil® treatment did not change. Interestingly, splenectomy significantly suppressed the exosomal secretions induced by free DXR treatment. Their results suggest that conventional anticancer agents induce the secretion of exosomes via stimulating immune cells of the spleen, and might contribute to the antitumor effect of chemotherapeutic agents.
-
Volume 41 (2018) Issue 6 Pages 925-936A Novel Mechanism of γ-Irradiation-Induced IL-6 Production Mediated by P2Y11 Receptor in Epidermal Keratinocytes Read moreEditor's pick
The article by Ohsaki et al. proposed a novel mechanism of cytokine production in γ-irradiated cells. γ-Ray irradiation induced sustained IL-6 production in HaCaT epidermal cells from 33 h after irradiation. Extracellular ATP-induced activation of P2Y11 receptor was involved in the production of IL-6. At the downstream of P2Y11 receptor activation, the p38 MAPK and NF-kB signaling was involved in IL-6 production. The protein level of G9a, which inhibits IL-6 production, was decreased after g-irradiation. These findings should be helpful to understand the pathogenesis of radiation-induced inflammation, as well as the potential side effects of therapeutic irradiation.
-
Volume 41 (2018) Issue 5 Pages 761-769Protective Effect of Ipragliflozin on Pancreatic Islet Cells in Obese Type 2 Diabetic db/db Mice Read moreEditor's pick
Ipragliflozin is a selective sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor that increases urinary glucose excretion, and subsequently improves glucolipotoxicity. The article by Takasu et al. demonstrated that the treatment with ipragliflozin decreased pancreatic cells positive for 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4HNE), an oxidative stress marker, in obese type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) db/db mice. Histopathological examination of pancreatic islet cells revealed strong insulin staining, whereas reduced glucagon staining, accordingly pancreatic insulin content tended to be higher in the ipragliflozin 10 mg/kg-treated group compared with the DM-control group. It was demonstrated that ipragliflozin has a protective effect on the pancreas by reducing oxidative stress.
-
Editor's pick
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) recruits diverse cellular factors into viral particles during its morphogenesis, which apparently play roles in modulating its infectivity. The article by Mouree et al. evaluated that a key glycolytic protein, pyruvate kinase muscle type 2 (PKM2) is incorporated into viral particles. Furthermore, the virion-packaged PKM2 significantly reduces the viral infectivity by affecting the selective packaging of intravirion tRNALys3, which primes the initiation of reverse transcription, along with other nonpriming tRNAs, such as tRNALys1,2 and tRNAAsn, without affecting the cytoplasmic level of these tRNAs. These findings proposed that PKM2 is a vital host factor that negatively affects HIV-1 infectivity by targeting the tRNALys3-mediated initiation of reverse transcription in target cells.
-
Volume 41 (2018) Issue 3 Pages 419-426Identification and Characterization of a Novel NADPH Oxidase 1 (Nox1) Inhibitor That Suppresses Proliferation of Colon and Stomach Cancer Cells Read moreEditor's pick
NADPH oxidase (Nox) isozymes are implicated in the diseases associated with oxidative stress, and search of their selective inhibitors has been a focus of attention. By screening microbial metabolites, Nakano and colleagues identified a novel Nox1 inhibitor (NOS31) produced from actinomyces. NOS31 inhibited Nox1-mediated hydrogen peroxide production with high Nox1 selectivity and suppressed proliferation of colon and gastric cancer cells that up-regulate Nox1. Thus, NOS31 may have the therapeutic potential for treating cancer involving the over-activation of Nox1.
-
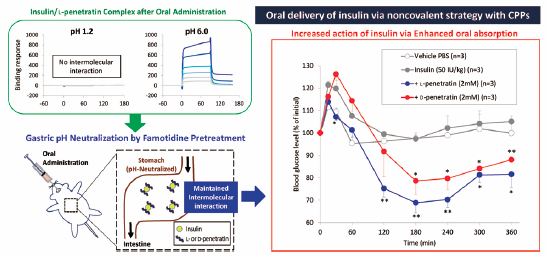
Volume 41 (2018) Issue 2 Pages 239-246Exploration of the Key Factors for Optimizing the in Vivo Oral Delivery of Insulin by Using a Noncovalent Strategy with Cell-Penetrating Peptides Read moreEditor's pick
Based on the binding characteristics, Kamei et al. attempted to increase the bound concentration of penetratin, cell-penetrating peptide (CPP), by increasing the concentration of mixed insulin, however the effect of L-penetratin on the oral absorption of insulin was not boosted by increasing the dose of insulin. The investigation in the gastric pH-neutralized mice showed that the dissociation of noncovalent complexes of insulin and CPPs at the low gastric pH was prevented in these mice, and clearly suggested that a noncovalent theoretical strategy with CPPs represents an effective approach for the L-form of CPP to attain greater absorption of insulin.
-
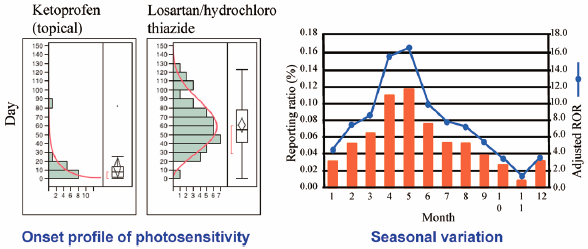
Volume 40 (2017) Issue 12 Pages 2158-2165Evaluation of Drug-Induced Photosensitivity Using the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER) Database Read moreEditor's pick
Drug-induced photosensitivity (DIP) is a cutaneous adverse event caused by the combined effects of a medication and exposure to light. The article by Nakao et al. evaluated the association between drugs and DIP by using the reporting odds ratio and time-to-onset analysis data from the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER) database. More than half of the reports of DIP onset following ketoprofen administration were recorded within 10 days of initiation of treatment. The seasonal variation of DIP was shown to follow an annual sinusoidal pattern with peaks observed in April and May. The results of this study suggest close monitoring of patients taking suspected drugs, especially during the peak season of photosensitivity reactions.
-
Editor's pick
Because tyrosine kinases mainly localize to the cytoplasm or the plasma membrane, most studies have focused on their roles in the cytoplasm. However, emerging evidence has revealed that tyrosine kinases also localize to the nucleus and regulate nuclear events, such as DNA damage responses, gene expression, and chromatin structural changes. In this paper, Takakura et al. showed that the truncated isoform of the receptor tyrosine kinase ALK (ALK ATI), which only has the intracellular kinase domain, regulates chromatin structural changes, heterochromatinization, and gene expression in the nucleus. This paper is the first report shedding light on the nuclear roles of ALK.
-
Volume 40 (2017) Issue 9 Pages 1468-1474Up-Regulation of the Voltage-Gated KV2.1 K+ Channel in the Renal Arterial Myocytes of Dahl Salt-Sensitive Hypertensive Rats Read moreEditor's pick
Salt-sensitive hypertension induces renal injury via decreased blood flow in the renal artery. Voltage-gated, delayed-rectifier K+ (KV) channels play key roles in the regulation of vascular tone, and their dysfunction in arterial myocytes may be involved in the higher vascular resistance. In their report, Ogiwara et al. described that there is a large contribution of KV2.1 to the resting tension maintenance of renal artery in Dahl salt-sensitive hypertensive rats and suggested the up-regulation of the KV2.1 channel in renal artery might be involved in the compensatory mechanisms against decreased renal blood flow in salt-sensitive hypertension.
-
Volume 40 (2017) Issue 8 Pages 1183-1191Characterization of Membrane Integrity and Morphological Stability of Human Salivary Exosomes Read moreEditor's pick
In their report, Kumeda et al. examined Membrane integrity and morphological stability of salivary exosomes using dipeptidyl peptidase IV and CD9 as membrane makers, and Alix and Tsg101 as lumen markers. Neither localization nor levels of these marker proteins were changed in isolated exosomes after long-term storage at 4°C or multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Moreover, intact exosomes could be isolated from whole saliva refrigerated for a month. Components inside the exosomes were stable even after solubilization of membrane components with detergents such as Triton X-100. These results indicate that human saliva-derived exosomes are very stable, maintaining their membrane integrity over a long storage period.
-
Volume 40 (2017) Issue 7 Pages 1029-1034Antioxidative Protection of Squalene Adjuvant and Rabies Vaccine with Adjuvant Read moreEditor's pick
The composition of the adjuvant emulsions was 2.5% squalene, 6% detergents, 0.5% antioxidant – α-tocopherol or β-carotene and 91% water phase. Antioxidant effectivity was testing by determination of peroxide value. α-tocopherol acted as a prooxidant, β-carotene was an effective antioxidant. Effectiveness of rabies vaccine with squalene adjuvant was testing on mice. Adjuvanted vaccine with β-carotene was compared to vaccine without antioxidant and induced a slower but prolonged immunity response with protective levels of rabies antibodies (0.5 IU/mL).
-
Volume 40 (2017) Issue 6 Pages 815-823Effective-Loading of Platinum–Chloroquine into PEGylated Neutral and Cationic Liposomes as a Drug Delivery System for Resistant Malaria Parasites Read moreEditor's pick
In their report, Ibrahim et al. described that generating platinum chloroquine diphosphate dichloride (PtCQ)-loaded polyethylene glycol (PEG)-modified (PEGylated) cationic liposomes exhibiting high drug encapsulation and high drug retention. PtCQ was encapsulated in PEGylated cationic liposomes comprising various amounts of cationic lipids using the remote-loading method. PEGylated neutral liposomes and cationic liposomes exhibited minimum leakage of PtCQ after two months’ storage at 4˚C, and further exhibited little release under in vitro culture conditions at 37˚C for 72 hours. These results provide a useful framework for the design of future liposome-based in vivo drug delivery systems targeting the drug-resistant malaria parasite.
-
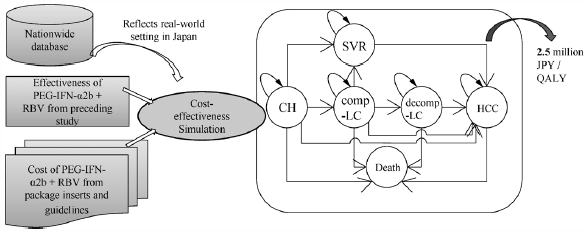
Volume 40 (2017) Issue 5 Pages 594-597Cost-Outcome Description of PEG-IFN-α2b+RBV for Hepatitis C: Results Based on the Interferon Database Read moreEditor's pick
Economic evaluation has been recently carried out using real-world data instead of clinical trial data. Akutagawa et al. conducted a cost-outcome description based on a nationwide registry providing information on hepatitis treatment in Japan and estimated the utility of the analysis. Specifically, they evaluated the cost-outcome description of a 48-week peginterferon plus ribavirin treatment in patients infected by the hepatitis C virus. Simulations were based on a Markov model. After setting the cohorts using data from the registry, and assuming a societal perspective for the calculation of costs, they estimated 2.5 million JPY per quality-adjusted life years (QALY) for treatments over a 10-year period. They analyzed patients’ statistics at each disease stage using their registry data and calculated the costs. Their results reflect more closely a real-world clinical situation as compared to the widely used clinical trial method.
-
Volume 40 (2017) Issue 4 Pages 495-503Growth Inhibition of Refractory Human Gallbladder Cancer Cells by Retinol, and Its Mechanism of Action Read moreEditor's pick
In their report, Li et al. described that vitamin A (retinol) inhibits cancer cell growth via endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Retinal is a more potent suppressor of refractory human gallbladder cancer cell growth linked to tumor progression than retinoic acid (RA). Although cellular incorporation of RA is higher than retinol, it was not correlated with anti-proliferative activity. Retinol did not induce apoptosis or suppress MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways. However, it significantly increased the expression of ER stress related genes and autophagy-associated protein (LC3-II) and the number of cells in the G0/G1 phase. This result indicates that retinol suppresses gallbladder cancer cell growth by mechanisms involving ER stress, autophagy, and cell cycle delay. Retinol might be useful for the prevention and treatment of cancer.
-
Volume 40 (2017) Issue 3 Pages 297-302An Activatable Fluorescent γ-Polyglutamic Acid Complex for Sentinel Lymph Node Imaging Read moreEditor's pick
Sentinel lymph nodes (SLN) are the first LN where cancer cells metastasize from the primary tumor. As an activatable fluorescence probe to detect the SLNs, Hagimori et al. developed ternary anionic nanoparticles constructed with fluorophore (TAMRA)-labeled polyamidoamine dendrimer conjugated with diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (TAMRA-G4-DTPA), quencher-labeled polyethyleneimine (PEI-QSY7 or PEI-BHQ2), and g-polyglutamic acid, namely TAMRA-G4-DTPA/PEI-QSY7/g-PGA and TAMRA-G4-DTPA/PEI-BHQ2/g-PGA by the electrostatic self-assembly system. The fluorescence of these complexes was quenched by a strong stacking interaction of TAMRA and quenchers, but was dequenched by dissociation of complexes when taken up by inflammatory cells (high populations in LN). They performed fluorescence imaging at 24 h after intradermal injection of TAMRA-G4-DTPA/PEI-QSY7/g-PGA into mouse footpads. Then, TAMRA fluorescence signal was clearly visualized in popliteal lymph node with high contrast.
-
Editor's pick
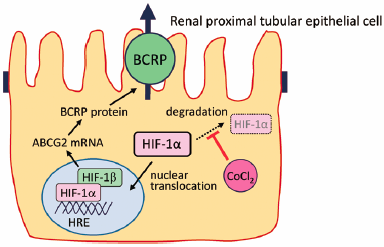
In their report, Nishihashi et al. describe in detail that cobalt chloride-induced activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) increases not only mRNA and protein expression but also function of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) in a human renal proximal tubular epithelial cell line. HIF-1 consists of an inducible a-subunit (HIF-1a) and a constitutive b-subunit (HIF-1b). The stabilization of HIF-1a under hypoxia and various biochemical stimuli leads to nuclear translocation, dimerization with HIF-1b and binding to hypoxia response element (HRE) sequences in the promoter of various target genes. The present results indicate that HIF-1 plays an important role in modulating BCRP-mediated transport activity in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells.
-
Volume 39 (2016) Issue 11 Pages 1868-1875Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis Is Part of the Skin Flora on the Hands of Both Healthy Individuals and Hospital Workers Read moreEditor's pick
In their report, Watanabe et al. described the prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE), one of the major nosocomial pathogens, on the hands of healthy individuals and hospital workers. The detection rates of MRSE in community pharmacists (92.3%) and students (87.5%) were higher than those in hospital workers (66.7% to 81.8%). Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) analysis strongly suggested that the MRSE strains on the hands of hospital workers and students were normal inhabitants of each subject. Their results lead to a new finding that MRSE is commonly colonized on the hands of not only hospital workers but also of healthy individuals.
-
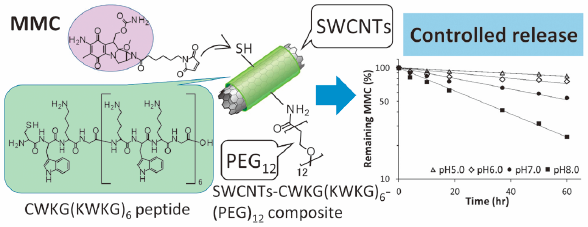
Volume 39 (2016) Issue 10 Pages 1687-1693Sustained Release of Mitomycin C from Its Conjugate with Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Associated by Pegylated Peptide Read moreEditor's pick
In their report, Ohta et al. described that single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) with superior dispersion stability in water are expected to serve as a good drug delivery system carrier in various biomedical applications. The SWCNTs composites with designed peptide having polyethylene glycol (PEG) modification were further conjugated with mitomycin C (MMC) for achieving its controlled release. The obtained conjugate of SWCNTs composites and MMC showed good dispersion stability even under physiological conditions. The release of MMC followed the first-order kinetics with half-lives of 32.2-256.2 hours being accelerated by the pH increase. In addition, the MMC conjugate demonstrated the antitumor activity with delayed growth inhibition comparing with free MMC.