-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 5 Pages 895-903New Directions for Advanced Targeting Strategies of EGFR Signaling in Cancer Read moreEditor's pick
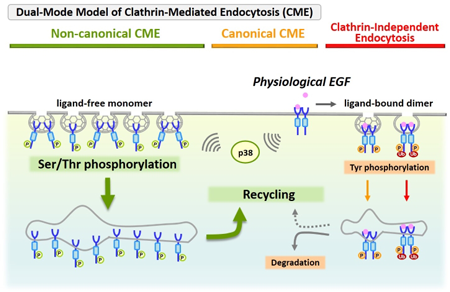
Since the first report of epidermal growth factor (EGF) in 1962, research on intracellular signaling through its receptor EGFR has greatly advanced. While the canonical activation of EGFR via tyrosine phosphorylation is well understood, the existence of a non-canonical activation via p38-dependent phosphorylation of serine/threonine residues has recently attracted attention. The authors have found that both of these mechanisms occur in parallel and are now analyzing them as a dual-mode activation model. This review summarizes new advances in EGFR signaling research and the latest status of EGFR inhibitor development for molecular targeted therapy of lung cancer.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 5 Pages 905-911From Glycolysis to Viral Defense: The Multifaceted Impact of Glycolytic Enzymes on Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Replication Read moreEditor's pick
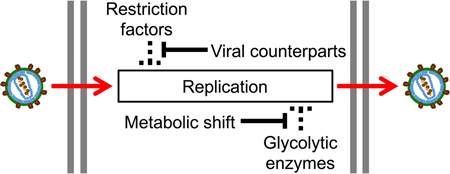
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) hijacks various cellular machinery to achieve efficient replication. HIV-1 infection induces a metabolic shift towards aerobic glycolysis as a cellular response to maintain homeostasis, yet the virus continues to replicate efficiently under these conditions. In this review, the authors introduce the regulatory role of glycolytic enzymes in HIV-1 replication and the impact of aerobic glycolysis on viral infection. In addition, the authors propose a novel strategy to eradicate latently HIV-1-infected cells.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 5 Pages 978-987The Influence of Emodin Succinyl Ethyl Ester on Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis Induced by a Diet High in Fructose, Cholesterol, and Fat in Mice Read moreEditor's pick
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a serious form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) that can lead to liver damage and inflammation. In this study, the authors focused on the therapeutic effects of emodin succinyl ethyl ester (ESEE) on NASH using a murine model induced by Special tailored diet. After four weeks of ESEE treatment, researchers observed significant improvements in glycolipid metabolism disorders, liver injury, and histopathological features of NAFLD/NASH. ESEE showed effectiveness in reducing cellular steatosis, inflammation, fat deposition in hepatocytes, and liver fibrosis in the model mice. These findings suggest that ESEE could serve as a novel therapeutic agent for NASH, providing protection against diet-induced liver abnormalities and injuries. -
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 5 Pages 1021-1027Short-Term Preexposure to Novel Enriched Environment Augments Hippocampal Ripples in Urethane-Anesthetized Mice Read moreEditor's pick
Exposure of animals to the enriched environments improves memory consolidation that requires extracellular ripples generated in the hippocampus during sleep. Natural sleep and general anesthesia are similar in terms of extracellular oscillations. However, whether the preexposure of animals to the enriched environment modulates neural activity in the hippocampus under subsequent anesthesia is not fully understood. The authors allowed mice to explore the enriched or standard environment, anesthetized them, and recorded local field potentials in the hippocampus, demonstrating that the amplitude of ripples and the number of successive ripples were larger in the novel enriched environment group.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 4 Pages 868-871Carbon Monoxide Alleviates Post-ischemia–reperfusion Skeletal Muscle Injury and Systemic Inflammation Read moreEditor's pick
Carbon monoxide (CO) exhibits versatile bioactivities; its preventive effect on the progression of ischemia-reperfusion injury in various organs has been reported. The authors developed CO-bound red blood cells (CO-RBC) as a bioinspired CO delivery donor and investigated the therapeutic potential of CO-RBC against ischemia-reperfusion injury in the hind limbs of rats. As a result, CO-RBC alleviated the skeletal muscle injury and systemic inflammation following ischemia-reperfusion in the rat model. The present study significantly contributes to the advancement of CO-based therapeutic strategies for treating skeletal muscle ischemia-reperfusion injury.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 4 Pages 840-847Maitake Beta-Glucan Enhances the Therapeutic Effect of Trastuzumab via Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity and Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity Read moreEditor's pick
HER2 overexpression is observed in 15-20% of breast cancers and is associated with an aggressive phenotype and poor prognosis. Trastuzumab is the primary treatment for HER2-positive breast cancers. However, trastuzumab resistance is often observed, highlighting the need for novel therapeutic approaches to improve clinical benefits. This study showed that Maitake beta-glucan MD-Fraction enhanced the therapeutic effect of trastuzumab in HER2-positive xenograft models. MD-Fraction enhances trastuzumab-induced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, complement-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, and complement-dependent cytotoxicity. These findings suggest that the combination of trastuzumab and MD-Fraction could be beneficial for the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 4 Pages 764-770Monocarboxylate Transporters 1 and 2 Are Responsible for L-Lactate Uptake in Differentiated Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells Read moreEditor's pick
Lactate transport via monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs) in the central nervous system is crucial for the memory formation. The present study aimed to identify transporters that contribute to lactate transport in differentiated human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells, which are used as a model for neurons. Kinetic analysis suggested that lactate transport was biphasic. Selective inhibitors for MCT1 and MCT2 significantly inhibited lactate transport. Therefore, the authors found that MCT1 and MCT2 are major contributors to lactate transport in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. These results lead to a better understanding of the involvement of MCTs in the memory formation and central nervous system disease.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 4 Pages 791-795Interactions between Age-Related Type 2 Diabetes and the Small Intestine Read moreEditor's pick
This study examined the pathological mechanisms in the small intestine and the aging effects using a mouse model of type 2 diabetes (KK-Ay/TaJcl) aged 10 and 50 weeks. The results showed that Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and mast cell expression increased, whereas diamine oxidase (DAO) decreased in the small intestine with age. Increased TNF-α and histamine levels occurred in plasma and the small intestine. The cell adhesion molecules ZO-1 and claudin-1 expression decreased in the small intestine. These findings may explain the pathological mechanisms and complications of type 2 diabetes.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 4 Pages 809-817Angiotensin II Is Involved in MLKL Activation During the Development of Heart Failure Following Myocardial Infarction in Rats Read moreEditor's pick
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
Angiotensin II is known to be an important factor in the development of chronic heart failure. The authors showed that angiotensin II is involved in the induction of necroptosis, a type of programmed necrosis-like cell death, during the development of heart failure in rats following myocardial infarction and in cultured cells. This finding suggests a new mechanism of action for angiotensin II inhibitors and is expected to contribute to a novel therapeutic strategy for heart failure by targeting necroptosis. -
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 3 Pages 698-707Lymphatic Endothelial Cells Produce Chemokines in Response to the Lipid Nanoparticles Used in RNA Vaccines Read moreEditor's pick
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
The study examined which cells are responsible for responding to the LNPs used in the approved COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. In this study, the authors incubated immortalized mouse lymphatic endothelial cells (mLECs) or professional antigen presenting cells (APCs) such as RAW 264.7 monocyte/macrophage cells with SM-102 LNPs that contained no mRNA. As a result, chemokines involved in the recruitment of monocytes/neutrophils were produced only by the mLECs following the empty LNP treatment. These findings indicate that LECs appear to serve as the cells that send out initial signals to response LNPs. -
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 3 Pages 641-651Oxidized-LDL Induces Metabolic Dysfunction in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Read moreEditor's pick
Mitochondrial dysfunction is recognized as a key factor in the pathological progression of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and can disrupt the balance of intracellular metabolic pathways (e.g., oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis). The authors focused on oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL), reported to a primary component accumulated in the retina of AMD patients, and elucidated its effect on metabolic alterations with increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production in retinal pigment epithelial cells. It was discovered that prolonged exposure to ox-LDL is crucial for the induction of these metabolic alterations. These significantly contribute to understanding the mechanisms underlying AMD metabolic alterations.
-
Editor's pick
Management of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) after delayed periods presents a significant challenge in cancer chemotherapy. This study represents the first attempt to compare the administration of fosnetupitant (F-NTP), fosaprepitant (F-APR), or aprepitant (APR) from 0 to 168 hours following the initial doses of cisplatin-based regimens. The authors demonstrated that F-NTP was significantly more effective than F-APR and APR in reducing CINV after anticancer drug administration from 0 to 168 hours, without significant side effects. The efficacy of F-NTP was particularly effective in the beyond-delayed periods (120-168 hours), which is the focus of attention of the revised Japanese antiemetic guidelines.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 3 Pages 732-738Risk Factors of Cetuximab-Induced Hypomagnesemia and the Effect of Magnesium Prophylaxis in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer: A Retrospective Study Read moreEditor's pick
The authors mainly investigated the risk factors and preventive strategies of cetuximab-induced hypomagnesemia in head and neck cancer (HNC) patients. Their results indicated that a low pre-treatment serum magnesium level emerges as the only risk factor, and this risk can be effectively mitigated through intravenous prophylactic magnesium sulfate administration from initiating cetuximab treatment. This preventive intervention exhibits minimal adverse events and is thus recommended for managing cetuximab-induced hypomagnesemia. Given that cetuximab interruption due to adverse events directly impacts prognosis, the insights gleaned from their study hold significant relevance for the optimal care of HNC patients undergoing cetuximab treatment.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 3 Pages 739-749Alteration of Sweet and Bitter Taste Sensitivity with Development of Glucose Intolerance in Non-insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Model OLETF Rats Read moreEditor's pick
Diabetes patients are well-known to exhibit alteration of taste sensitivity, but the alteration profiles have not been clarified in detail yet. In brief-access tests with a mixture of sucrose and quinine hydrochloride, the lick ratios of control, but not non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM)-model, rats for the mixture and quinine hydrochloride solutions decreased aging-dependently. Metagenomic analysis of gut microbiota revealed strain- and aging-dependent alteration of mucus layer-regulatory microbiota. These findings suggested that control, but not NIDDM-model, rats exhibited an aging-dependent increase of bitter taste sensitivity with alteration of gut microbiota.
-
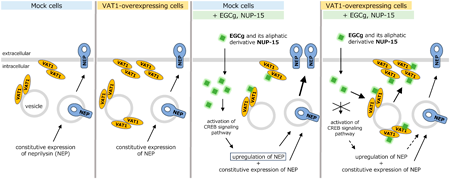
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 2 Pages 509-517Identification and Characterization of Synaptic Vesicle Membrane Protein VAT-1 Homolog as a New Catechin-Binding Protein Read moreEditor's pick
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCg) is known to upregulate neprilysin, an Aβ-degrading enzyme. To clarify the mechanism underlying this process, the authors screened catechin-binding proteins by pull-down assay with magnetic beads and LC-tandem mass spectrometry and identified synaptic vesicle membrane protein VAT-1 homolog (VAT1). Surface plasmon resonance analysis revealed a direct binding of recombinant VAT1 protein to EGCg or its alkylated derivative NUP-15 with comparable affinity to the other EGCg binding proteins reported previously. Furthermore, the authors found that VAT1 prevented the upregulation of neprilysin by EGCg or NUP-15 through binding to and inactivating them in the cells overexpressing VAT1.
-
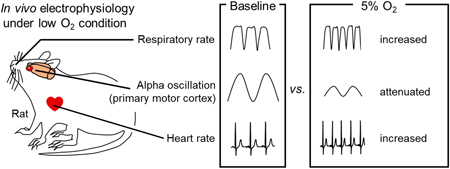
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 2 Pages 462-468Low Atmospheric Oxygen Attenuates Alpha Oscillations in the Primary Motor Cortex of Awake Rats Read moreEditor's pick
The authors investigated concurrent effects of hypoxia on physiological signals by simultaneously recording local field potentials in the primary motor, primary somatosensory and anterior cingulate cortices as well as electrocardiograms, electroolfactograms, and electromyograms of rats in acutely hypoxic environment. When they were exposed to acute hypoxia, alpha oscillations in the primary motor cortex were impaired. Moreover, the authors demonstrated that heart rate and respiratory rate were increased during acute hypoxia and high heart rate was maintained even after the oxygen level returned to the baseline. Altogether, this study characterizes a systemic effect of atmospheric hypoxia from physiological viewpoints.
-
Editor's pick
This study examined whether the approved sequence of vedolizumab and ustekinumab impacts the results of studies conducted in the EU, comparing the effectiveness of these drugs in Crohn's disease (CD) patients who failed anti-TNFα treatment. The authors conducted this study in Japan, where the approved sequence of drugs is different from that of the EU. They analyzed data from 256 CD patients from the Japanese claims database. The results suggested that ustekinumab is a more effective treatment option than vedolizumab for CD patients who failed anti-TNFα treatment, and this finding remains consistent across both Japan and the EU.
-
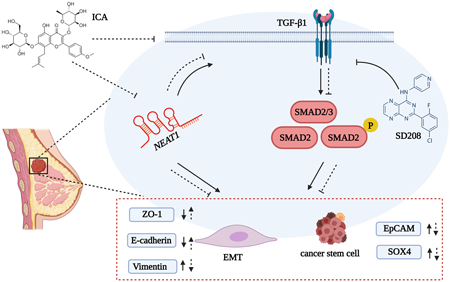
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 2 Pages 399-410Icariin Regulates EMT and Stem Cell-Like Character in Breast Cancer through Modulating lncRNA NEAT1/TGFβ/SMAD2 Signaling Pathway Read moreEditor's pick
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
Icariin(ICA) affects the EMT and cancer stem cell-like character of breast cancer cells. The main mechanism is to influence the characteristics of EMT and cancer stem cell-like character of breast cancer cells by regulating the TGFβ/SMAD2 signaling pathway, which in turn affects the migration of breast cancer cells. In addition, we have found not only ICA inhibits proliferation, EMT and stem cell-like character of breast cancer cells by silencing lncRNA NEAT1, but NEAT1 can exert anti-breast cancer effects through TGFβ/SMAD2 signaling pathway. Overall, we hypothesized that ICA could inhibit the proliferation, EMT and cancer stem cell-like character of breast cancer cells through the NEAT1/TGFβ/SMAD2 axis and suppress breast cancer migration. -
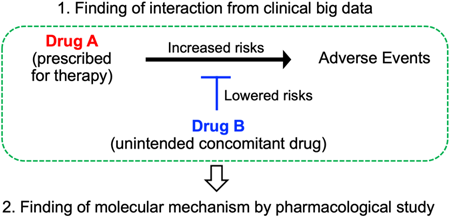
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 2 Pages 345-349A Novel Strategy for the Discovery of Drug Targets: Integrating Clinical Evidence with Molecular Studies Read moreEditor's pick
Recently, large amount of real-world data (RWD), such as insurance claims data and self-reports of adverse drug reactions become available. Statistical analysis of RWD has made it possible to identify novel and unexpected confounding factors that influence the occurrence of adverse events or spontaneous disease in humans. Such drug-drug interactions lead to the elucidation of adverse event mechanisms and the discovery of new drug targets. In addition, hypotheses derived from RWD may have high clinical predictive value. In this review, the author shows how RWD analysis can lead to the discovery of drug targets, by introducing examples of research reports.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 1 Pages 245-252Rheological Properties and Composition Affecting the Skin Permeation of a Model of a Hydrophilic Drug in Lecithin Reverse Wormlike Micelles Read moreEditor's pick
Lecithin reverse wormlike micelles (LRWs) are highly viscoelastic bodies and potentially useful for transdermal applications. The authors prepared LRWs with 6-carboxyfluorescein (CF) as a model for a hydrophilic drug, and investigated the effect of the rheological properties and composition of LRWs on the skin permeation of CF. The highest skin permeability of CF was observed when IPM was used as the oil, and the penetration of CF into hair follicles is influenced not only by the rheology of the formulation but also by the interaction between IPM and sebum in the hair follicles.