-
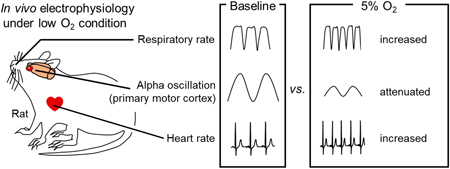
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 2 Pages 462-468Low Atmospheric Oxygen Attenuates Alpha Oscillations in the Primary Motor Cortex of Awake Rats Read moreEditor's pick
The authors investigated concurrent effects of hypoxia on physiological signals by simultaneously recording local field potentials in the primary motor, primary somatosensory and anterior cingulate cortices as well as electrocardiograms, electroolfactograms, and electromyograms of rats in acutely hypoxic environment. When they were exposed to acute hypoxia, alpha oscillations in the primary motor cortex were impaired. Moreover, the authors demonstrated that heart rate and respiratory rate were increased during acute hypoxia and high heart rate was maintained even after the oxygen level returned to the baseline. Altogether, this study characterizes a systemic effect of atmospheric hypoxia from physiological viewpoints.
-
Editor's pick
This study examined whether the approved sequence of vedolizumab and ustekinumab impacts the results of studies conducted in the EU, comparing the effectiveness of these drugs in Crohn's disease (CD) patients who failed anti-TNFα treatment. The authors conducted this study in Japan, where the approved sequence of drugs is different from that of the EU. They analyzed data from 256 CD patients from the Japanese claims database. The results suggested that ustekinumab is a more effective treatment option than vedolizumab for CD patients who failed anti-TNFα treatment, and this finding remains consistent across both Japan and the EU.
-
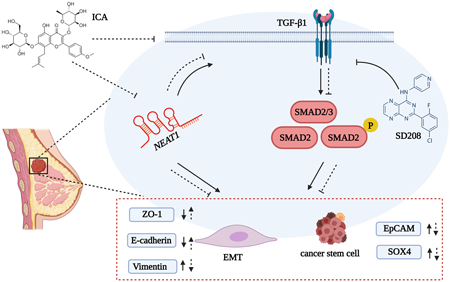
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 2 Pages 399-410Icariin Regulates EMT and Stem Cell-Like Character in Breast Cancer through Modulating lncRNA NEAT1/TGFβ/SMAD2 Signaling Pathway Read moreEditor's pick
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
Icariin(ICA) affects the EMT and cancer stem cell-like character of breast cancer cells. The main mechanism is to influence the characteristics of EMT and cancer stem cell-like character of breast cancer cells by regulating the TGFβ/SMAD2 signaling pathway, which in turn affects the migration of breast cancer cells. In addition, we have found not only ICA inhibits proliferation, EMT and stem cell-like character of breast cancer cells by silencing lncRNA NEAT1, but NEAT1 can exert anti-breast cancer effects through TGFβ/SMAD2 signaling pathway. Overall, we hypothesized that ICA could inhibit the proliferation, EMT and cancer stem cell-like character of breast cancer cells through the NEAT1/TGFβ/SMAD2 axis and suppress breast cancer migration. -
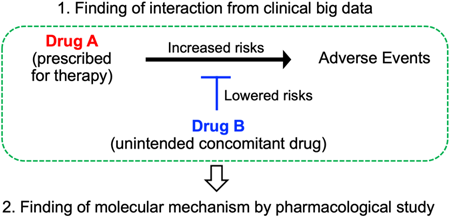
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 2 Pages 345-349A Novel Strategy for the Discovery of Drug Targets: Integrating Clinical Evidence with Molecular Studies Read moreEditor's pick
Recently, large amount of real-world data (RWD), such as insurance claims data and self-reports of adverse drug reactions become available. Statistical analysis of RWD has made it possible to identify novel and unexpected confounding factors that influence the occurrence of adverse events or spontaneous disease in humans. Such drug-drug interactions lead to the elucidation of adverse event mechanisms and the discovery of new drug targets. In addition, hypotheses derived from RWD may have high clinical predictive value. In this review, the author shows how RWD analysis can lead to the discovery of drug targets, by introducing examples of research reports.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 1 Pages 245-252Rheological Properties and Composition Affecting the Skin Permeation of a Model of a Hydrophilic Drug in Lecithin Reverse Wormlike Micelles Read moreEditor's pick
Lecithin reverse wormlike micelles (LRWs) are highly viscoelastic bodies and potentially useful for transdermal applications. The authors prepared LRWs with 6-carboxyfluorescein (CF) as a model for a hydrophilic drug, and investigated the effect of the rheological properties and composition of LRWs on the skin permeation of CF. The highest skin permeability of CF was observed when IPM was used as the oil, and the penetration of CF into hair follicles is influenced not only by the rheology of the formulation but also by the interaction between IPM and sebum in the hair follicles.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 1 Pages 104-111Ethoxyquin, a Lipid Peroxidation Inhibitor, Has Protective Effects against White Matter Lesions in a Mouse Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion Read moreEditor's pick
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion can cause white matter lesions, leading to vascular dementia. Recently, these diseases have been reported to be associated with lipid peroxidation. In this research, the authors revealed that ethoxyquin, a lipid-soluble antioxidant, had a protective effect against a glutamate-stimulated mouse hippocampal cell line and was comparable to the ferroptosis inhibitor. Additionally, when applied to a mouse model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion, ethoxyquin suppressed white matter lesions and inflammatory responses. Overall, the authors demonstrated that inhibiting lipid peroxidation could be a helpful therapy for chronic cerebrovascular disease. -
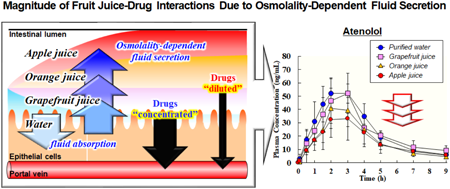
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 1 Pages 72-78Magnitude of Fruit Juice–Drug Interactions Due to Osmolality-Dependent Fluid Secretion: Differences among Apple, Orange, and Grapefruit Juices Read moreEditor's pick
The authors revealed that changes in gastrointestinal fluid volume due to solution osmolality can explain the differences in the magnitude of beverage-drug interactions depending on the type of beverage. Osmolality-dependent fluid secretion and consequent decrease in luminal concentrations and absorption of drugs were observed in the rat intestine after administration of apple juice, orange juice, and grapefruit juice. Further, in vivo oral experiments showed that plasma concentrations of atenolol, a low-permeability drug, after oral administration decreased in dependence upon the magnitude of osmolality of ingested beverages, while the plasma concentrations of antipyrine, a high-permeability drug, did not change.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 1 Pages 60-71Involvement of Cannabinoid Receptors and Adenosine A2B Receptor in Enhanced Migration of Lung Cancer A549 Cells Induced by γ-Ray Irradiation Read moreEditor's pick
The article by Oyama et al. suggested a novel mechanism of radiation-induced acquisition of malignant profile in lung cancer. Authors have shown that activation of adenosine A2B receptor and cannabinoid receptors (CB1, CB2 and GPR55) are involved in enhancement of cell migration after g-irradiation in A549 cells. And authors have shown that enhancement of cell migration by activation of adenosine A2B receptor is mediated by activation of CB2 and GPR55 receptor. These findings proposed that the A2B-CB2 and A2B-GPR55 pathways contributes to the radiation-induced acquisition of malignant profile in lung cancer and could be a novel molecular target to improve the efficiency of radiation therapy for lung cancer.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 1 Pages 28-36Identification of Azalamellarin N as a Pyroptosis Inhibitor Read moreEditor's pick
Pyroptosis is a type of regulated cell death, and its dysregulation is detrimental and implicated in various diseases. The authors screened chemical compounds and identified azalamellarin N (AZL-N), a hexacyclic pyrrole alkaloid, as an inhibitor of pyroptosis induced by the intracellular multiprotein complex NLRP3 inflammasome. The inhibitory effects of AZL-N differed depending on the type of stimulus, which was different from those of MCC950, a well-established NLRP3 inhibitor. Considering that many studies have been focusing on the general mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis, AZL-N is a unique tool for uncovering the differential mechanisms of pyroptosis depending on the type of inflammatory stimulus.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 12 Pages 1661-1665Framework-Directed Amino-Acid Insertions Generated over 55-Fold Affinity-Matured Antibody Fragments That Enabled Sensitive Luminescent Immunoassays of Cortisol Read moreEditor's pick
Genetic engineering now enables generation of artificially modified antibodies having higher diagnostic utilities. The authors developed single-chain Fv fragments (scFvs) against cortisol with >55-fold improved affinity (Ka, 2.0-2.2 ´ 1010 M-1) by inserting additional amino acid(s) site-directedly into the framework region 1 of the VH domain. These scFvs were fused with NanoLuc luciferase for the use in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) system. The resulting luminescent ELISAs generated dose-response curves with >150-fold higher sensitivity than the colorimetric ELISAs using the scFv without insertion and >8,000-fold higher sensitivity than the ELISA using the mouse antibody from which the scFvs were derived.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 12 Pages 1676-1682Method for Preparing Recombinant Galectin-2 Protein without Escherichia coli-Specific Post-translational Modifications Read moreEditor's pick
E. coli is often employed for the cost-effective production of large quantities of recombinant proteins. Conventionally, it is believed that post-translational modifications, including glycosylation, do not transpire during protein expression in E. coli. However, in the course of preparing recombinant galectin-2 protein using E. coli, the authors discovered that phosphogluconoylation of Lys residues and mistranslation of termination codons occurred. The authors have elucidated strategies to mitigate these occurrences, proposing the addition of tags, substitution of Lys residues, and modification of termination codons. These methods offer valuable means to prevent undesired modifications, ensuring the production of homogeneous recombinant proteins in E. coli.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 12 Pages 1720-1730Exploring Cell-Penetrating Peptides as Penetration Enhancers in Eye Drop Formulations Using a Reconstructed Human Corneal Epithelial Model Read moreEditor's pick
The authors focused on cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) as penetration enhancers for ocular drug delivery. This study suggested that the CPPs evaluated in this study can be penetration enhancers based on in vitro intracellular uptake using a reconstructed human corneal epithelial model. The CPPs could enhance the penetration of drug molecules into the cornea in cases of coexistence as well as conjugation between CPPs and drug molecules. The result of surface plasmon resonance showed that the electrostatic interaction plays an important role. The authors expect that this fundamental information in this article will support the development of new penetration enhancers in eye drop formulations for ocular drug delivery.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 12 Pages 1753-1760Arid5a/IL-6/PAI-1 Signaling Is Involved in the Pathogenesis of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Kidney Injury Read moreEditor's pick
Inflammation is responsible for the development of various kidney diseases. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) is involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory kidney injury; however, the regulatory mechanism of PAI-1 in injured kidneys remains unclear. The authors found that PAI-1 expression was increased in endothelial cells after lipopolysaccharide (LPS, an inflammation inducer) treatment, and pharmacological inhibition of PAI-1 reduced LPS-induced kidney injury. Moreover, IL-6 exacerbated kidney injury concomitant with increased PAI-1 expression, and Arid5a deficiency partially suppressed the expression of IL-6 and PAI-1 in the kidneys after LPS treatment. These findings indicate that the Arid5a/IL-6/PAI-1 signaling is involved in LPS-induced kidney injury.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 12 Pages 1778-1786Identification of the Acidification Mechanism of the Optimal pH for RNase He1 Read moreEditor's pick
Hericium erinaceus secretes an acidic ribonuclease (RNase) He1 belonged to RNase T1 family. The authors decided on the structure of He1 apo form and He1/guanosine complex. The mechanism of acidification of optimal pH in He1 was, in neutral environment, to form the hydrogen bond between Asp 31 on α1β3- loop and His 34 (catalytic residue), and repulsive each other Glu 92 and Asp 93 on β6,7- loop. Structure comparison of He1 with other acidic RNases, Ms and U2, suggested that the acidic residues on α1β3- and β6,7- loop may contribute to the acidification of optimal pH in Ms and U2.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 11 Pages 1498-1505Suppression of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced IL-1β Gene Expression by High-Molecular-Weight Adiponectin in RAW264.7 Macrophages Read moreEditor's pick
Although most previous studies in this area used recombinant adiponectin, herein, the author used native high-molecular-weight (HMW) adiponectin purified from human plasma, which is considered the most active form of circulating adiponectin. The current results clearly demonstrate that native HMW adiponectin preferentially inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-1β expression but not tumor necrosis factor-α expression by inhibiting the Akt-C/EBPβ inflammatory signaling pathway in macrophages. Furthermore, HMW adiponectin preconditioning is essential for achieving the anti-inflammatory effects of adiponectin. Thus, these findings highlight the regulatory mechanisms underlying the anti-inflammatory function of adiponectin.
-
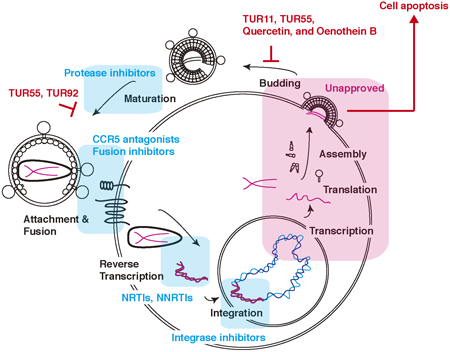
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 11 Pages 1535-1547Turkish Plants, Including Quercetin and Oenothein B, Inhibit the HIV-1 Release and Accelerate Cell Apoptosis Read moreEditor's pick
Authors suggest that plant extracts, including quercetin and oenothein B, reduce the amount of virus in the cell supernatants and induce cytotoxicity in HIV-1-infected T cells but not HTLV-1-infected T cells. The large amount of oenothein B were detected in Onagraceae. Thus, the plant extracts might block the HIV-1 release and kill the HIV-1-infected cells. Consequently, the plant extracts from the plant library of Turkey might be suitable candidates to develop novel anti-retroviral drugs that target the late phase of the HIV-1 life cycle.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 11 Pages 1583-1591Endothelium-Independent Vasorelaxant Effects of Sudachitin and Demethoxysudachitin, Polymethoxyflavone from the Peel of Citrus sudachi on Isolated Rat Aorta Read moreEditor's pick
Citrus sudachi is a popular fruit in Tokushima Prefecture, Japan, and its peel contains high amounts of polymethoxyflavones with the most abundant being sudachitin (SDC) followed by demethoxysudachitin (DMSDC). The effects of SDC and DMSDC on the cardiovascular system have not been investigated. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of SDC and DMSDC on vascular tonus and to investigate mechanism of action of SDC using aorta preparations isolated from rats. The results demonstrated that SDC and DMSDC cause endothelial-independent relaxation, and that the mechanism of vasorelaxation by SDC is associated with the enhancement of cAMP- and cGMP-dependent pathways.
-
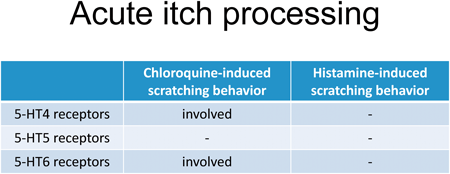
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 11 Pages 1601-1608Differential Contribution of 5-HT4, 5-HT5, and 5-HT6 Receptors to Acute Pruriceptive Processing Induced by Chloroquine and Histamine in Mice Read moreEditor's pick
Antidepressants, such as milnacipran, a serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor, and mirtazapine, a noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant attenuate the induction of scratching events by chloroquine (CQ) or histamine. However, it remains unclear whether serotonin or noradrenaline is involved in attenuating effects of these antidepressants. Miyahara and colleagues show that 5-HT4 and 5-HT6 receptors are involved in the amelioration of CQ-induced scratches, but not histamine-induced scratches, engendered by the antidepressants. These findings suggest that 5-HT4, 5-HT5, and 5-HT6 receptors play differential roles in acute pruriceptive processing after administration of CQ or histamine.
-
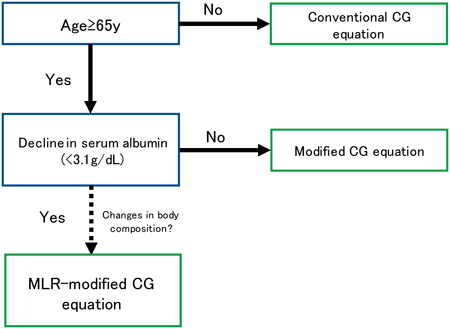
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 11 Pages 1609-1618Effects of Body Composition on Renal Function Estimates in Older Patients Read moreEditor's pick
The authors validated the modified Cockcroft-Gault equation, developed previously for aged-oriented cohort, in a newly obtained dataset and found that good renal function estimates were obtained for patients exceeding 65 years of age. Using statistical analysis, estimates for a subset of patients in this cohort were identified to be inadequate and this deviation from estimates was attributed to a decreased albumin level. A multivariate linear regression estimating equation was developed for this region by incorporating body composition parameters. A flow diagram was proposed to select an appropriate renal function estimating equation particularly for older patients.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 10 Pages 1365-1370Comparison of Incidence of Hyponatremia between Linezolid and Vancomycin by Propensity Score Matching Analysis Read moreEditor's pick
Linezolid (LZD) has been reported to cause severe hyponatremia, but infection per se is also a potential cause of hyponatremia by increasing vasopressin secretion. The author compared the incidence and risk of developing hyponatremia between LZD and vancomycin (VCM) using propensity score analysis to demonstrate that hyponatremia is associated with LZD rather than infection. The analysis indicated a significantly higher incidence and 3.7-fold higher risk of developing hyponatremia associated with LZD than with VCM, regardless of patient background characteristics. Regularly monitoring serum sodium and infusing sodium promptly when the level decreases would be required when administering LZD.