-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 4 Pages 630-635Apigenin Alleviates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Apoptosis in INS-1 β-Cells Read moreEditor's pick
Protection against impaired insulin secretion and β-cell apoptosis is an important strategy to prevent the progression of type 2 diabetes. The authors have reported the effects of apigenin, a dietary trihydroxyflavone, on pancreatic β-cell functions, underlying its anti-diabetic effects. The study demonstrated that apigenin exerts insulinotropic and anti-apoptotic effects in the β-cell line INS-1D. The anti-apoptotic effect of apigenin was further supported by reduced expression of apoptotic signaling proteins and pro-apoptotic protein. The results suggest and provide a basis for the development of apigenin as a potential therapeutic for type 2 diabetes through promoting β-cell survival and function.
-
Editor's pick
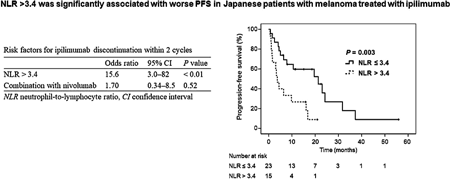
Studies have reported an association between elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and poor prognosis in patients with melanoma treated with ipilimumab. However, it remains unclear whether NLR is useful in Japanese. Authors retrospectively examined 38 patients, and found that baseline NLR>3.4 was an independent risk factor for ipilimumab discontinuation that was significantly associated with shorter progression-free survival. Because the NLR cut-off value in this study was lower than values in American and European studies, it possibly differs by race. Hence, it should be extrapolated to Japanese patients with caution.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 3 Pages 440-445Interference of New Antiseizure Agents with Hospital Transfer of Stroke Patients in Japan: A Retrospective Cohort Study Read moreEditor's pick
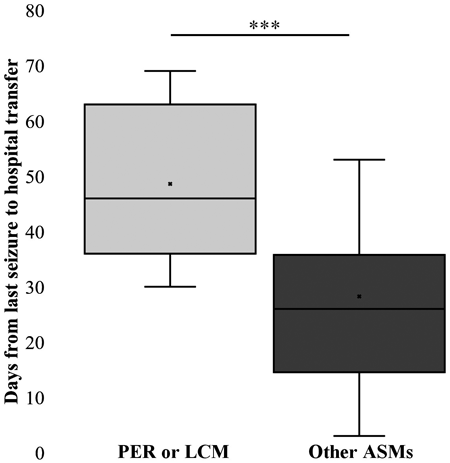
This investigation of the impact of antiseizure medications (ASMs) on hospital transfer was undertaken because chronic-care hospitals have refused to accept several post-stroke epilepsy patients using novel ASMs from acute-care hospitals. Patients with stroke receiving novel ASMs, i.e., perampanel and lacosamide, had longer times to hospital transfer than patients receiving other ASMs. Furthermore, a weak correlation was found between the cost of a patient's daily medications and the number of days to hospital transfer. These results indicate that considering the availability and cost of ASMs in the transfer destination hospital is important when choosing medications for patients requiring hospital transfer.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 3 Pages 446-454Enhancement of Neprilysin Activity by Natural Polyphenolic Compounds and Their Derivatives in Cultured Neuroglioma Cells Read moreEditor's pick
The authors found that amentoflavone, apigenin, kaempferol, and chrysin enhanced the activity and expression of neprilysin, one of the major Aβ-degrading enzymes, by screening a polyphenol library, and that chemical structures involving a double bond between positions 2 and 3 in the C ring of flavones were important for neprilysin enhancement. Moreover, natural compounds, such as quercetin, were not effective per se, but were changed to effective compounds by adding a lipophilic moiety. These findings provide a basis for the development of novel small molecules as disease-modifying drugs for Alzheimer’s disease.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 2 Pages 194-200Effect of Severe Renal Dysfunction on the Plasma Levels of DNA-Reactive Platinum after Oxaliplatin Administration Read moreEditor's pick
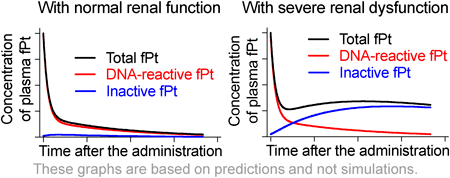
Oxaliplatin is a platinum (Pt)-based chemotherapeutic drug that is widely used to treat gastrointestinal and pancreatic cancers. The authors hypothesized that the DNA-binding capacity is one of the properties of reactive Pt species and aimed to evaluate the contribution of the kidney to the plasma levels of DNA-reactive Pt in an animal model and a hemodialysis patient. The results of this study showed that severe renal dysfunction has a limited effect on the plasma levels of DNA-reactive Pt after oxaliplatin administration.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 2 Pages 263-271Microbial Water Quality Assessment of Private Wells Using 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing with a Nanopore Sequencer Read more
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 2 Pages 272-278Effect of Topiroxostat on Reducing Oxidative Stress in the Aorta of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats Read moreEditor's pick
Vascular damage is often seen in patients with diabetes and is thought to be caused by oxidative stress. Xanthine oxidoreductase exists both intracellularly and extracellularly and causes vascular injury by producing reactive oxygen species. The authors investigated the effects of topiroxostat, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, and its mechanism of action in a rodent model of diabetes. They found that topiroxostat inhibited anchored xanthine oxidase bound to the surface of vascular endothelial cells in the thoracic aorta and suppressed damage to these cells, suggesting that topiroxostat could potentially have a vasoprotective effect in patients with diabetes-induced macrovascular disease.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 2 Pages 301-308Use of Iontophoresis Technology for Transdermal Delivery of a Minimal mRNA Vaccine as a Potential Melanoma Therapeutic Read moreEditor's pick
mRNA has many challenges including insufficient delivery owing to the high molecular weight and high negative charge. Authors chemically synthesized a minimal mRNA vaccine encoding human gp10025-33 peptide (KVPRNQDWL), as a potential treatment for melanoma and iontophoresis (IP) was used for its delivery into the skin. After combining IP with the newly synthetized minimal mRNA vaccine, successful intradermal and intracellular delivery of the minimal mRNA was achieved. Results showed stimulation of the immune system which led to tumor inhibition and infiltration of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells in the tumor tissue. This is the first report combining IP and chemically synthesized minimal mRNA vaccine.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 2 Pages 320-333Plantainoside B in Bacopa monniera Binds to Aβ Aggregates Attenuating Neuronal Damage and Memory Deficits Induced by Aβ Read moreEditor's pick
Cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain are known to degenerate early stage of Alzheimer's disease (AD), and amyloid-β (Aβ) oligomers are suggested to be deeply involved in AD pathogenesis. Authors here established an Aβ oligomer-induced neurodegeneration model using human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cholinergic neurons and demonstrated the neuroprotective effect of plantainoside B identified from herbal extracts as an Aβ-binding small molecule. Radioisotope-labeled plantainoside B showed affinities to Aβ oligomers and brain sections from a mouse model of AD. Results suggest the potential of developing “theranostics” in AD that simultaneously performs diagnoses (Aβ detection) and therapy (neuroprotection).
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 1 Pages 1-11Chemical Activation of Piezo1 Alters Biomechanical Behaviors toward Relaxation of Cultured Airway Smooth Muscle Cells Read moreEditor's pick
Inspired by the well-known phenomenon of stretch-induced airway dilation in normal lung and the emerging stretch-responsive Piezo1 channels, the authors in this study demonstrated that chemical activation of Piezo1 channels by agonist YODA1 dramatically reduced the contractility of cultured ASMCs in terms of cells stiffness, traction force, migration, and expression of molecules associated with cell mechanics. These findings indicate that chemical activation of Piezo1 can indeed modulate biomechanical behaviors of ASMCs towards relaxation. And this novel regulatory mechanism as alternative to the conventional b2-adrenergic receptor for relaxation of ASMCs may provide a potentially new target for bronchodilation in asthma therapy.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 1 Pages 19-25Impact of Drugs and Patient Characteristics on Life Expectancy during the Induction Phase of Dialysis Read moreEditor's pick
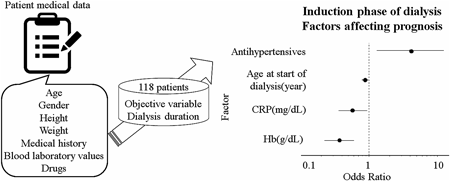
Various factors affect the prognosis of dialysis patients. Analysis of the drugs used and clinical and demographic characteristics of the patient at the time of dialysis initiation is a useful means of estimating prognosis. The authors investigated the drugs used by dialysis patients during the induction phase of dialysis and performed a detailed analysis of variables predictive of prognosis. As a result, antihypertensives, hemoglobin, and age at start of dialysis were found to have significant effects on dialysis duration. It was posited that antihypertensives prolong dialysis duration, thereby improving life expectancy. These findings may be used to improve drug adherence in dialysis patients and guide physicians in their treatment.
-
Editor's pick
Tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) may be a key modulator of the pharmacological effects of barbiturates. Suzuki, et al., used a TrkB agonist 7,8-dihydroxyflavone (DHF) in the animal study for phenobarbital-induced general anesthesia, demonstrating that rats receiving the DHF pretreatment readily fell into anesthesia in a shorter time than those without the pretreatment. They then showed that DHF promotes the TrkB to be phosphorylated and that the protein expression of the potassium chloride transporter KCC2 was consequently suppressed. It was thus revealed that DHF potentiates the pharmacological effects of phenobarbital as it causes the functional activation of the TrkB.
-
Editor's pick
Bortezomib is widely used in treating multiple myeloma, but causes serious adverse effects, such as peripheral neuropathy, leading to discontinuation of Bortezomib treatment. To explore the mechanism, the authors, unlike previous reports, applied relatively low concentrations of bortezomib at clinical concentration, to primary cultured Schwann cells, satellite glial cells, macrophages, and dorsal root ganglion neurons. The results showed that bortezomib caused Schwann cell dedifferentiation, increased GFAP levels in satellite glial cells without inducing inflammatory responses, and decreased ion channel expression in dorsal root ganglion neurons. This may explain the mechanism of bortezomib-induced peripheral neuropathy.
-
Volume 46 (2023) Issue 1 Pages 111-122Transforming Growth Factor-β1 and Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Inhibit Differentiation into Mature Ependymal Multiciliated Cells Read moreEditor's pick
Ependymal cilia on the ventricular surface play pivotal roles in cerebrospinal fluid flow. Authors newly constructed the polarized primary culture system of ependymal multiciliated cells (MCCs) from undifferentiated glial cells using a permeable filter in which they retained ciliary movement. Fetal bovine serum (FBS) on the ventricular side of culture inhibited the differentiation with ciliary movement. Transforming growth factor-b1 (TGF-b1) and Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-2 mimic the inhibitory action of FBS. The inhibition on the differentiation by FBS was recovered by the TGF-b1 and BMP-2 inhibitors in combination. Taken together, TGF-b1 and BMP-2 are found to be major inhibitors in the differentiation of ependymal MCCs.
-
Editor's pick
Although inhaler drugs are the mainstay of treatment for obstructive lung diseases, some of these patients have inadequate skills in inhaler use, and pharmacists have limited time to provide inhaler instruction in daily clinical practice. The authors aimed to investigate the instruction methods provided by community pharmacists and their influence on inhaler handling techniques. They found that patients without critical handling errors received demonstration instructions from pharmacists combined with leaflets and verbal explanations more frequently than those with critical errors. The finding of this study indicates combined instructional approach including pharmacist demonstration may be effective in improving inhaler treatment outcomes.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 12 Pages 1791-1797Testicular Hypoplasia with Normal Fertility in Neudesin-Knockout Mice Read moreEditor's pick
Neudesin is a secretory protein, originally identified as a neurotrophic and neuroprotective factor. Although neudesin is widely expressed in various organs in mammals, its function in the tissues other than the nervous system and adipose tissues remains unknown. In this manuscript, the authors examined the phenotype of Neudesin-knockout mice and found a testicular hypoplasia emerging from early postnatal stages. Despite the smaller testes in the adult Neudesin-knockout males, they produced healthy sperm and retained their fertility. This study revealed a novel function and versatility of neudesin.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 12 Pages 1798-1804OX40 Ligand-Mannose-Binding Lectin Fusion Protein Induces Potent OX40 Cosignaling in CD4+ T Cells Read moreEditor's pick
T cells play important roles for protection against infection and cancer. Upon interaction with OX40 ligand (OX40L, TNFSF4), OX40 expressed by activated T cells promotes the production of long-lived memory T cells. However, it remains unclear how better activity of OX40 can be induced by a designer OX40L protein. A soluble OX40L possessing a collagenous trimerization domain from mannose-binding lectin was prepared in this study, and this novel protein functioned as a superior agonist both in vitro and in vivo. The authors propose that activity of OX40L can be engineered to elicit robust T cell responses by rational structural design.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 12 Pages 1805-1811Central Nervous System Ischemia Associated with Bevacizumab: An Analysis of the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report Database Read moreEditor's pick
Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody that blocks VEGF receptors, thereby inhibiting angiogenesis in cancer cells and stopping tumor growth. However, bevacizumab inhibits signaling pathways involved in angiogenesis, which may lead to central nervous system (CNS) ischemia. However, its definitive characteristics have not been elucidated. Therefore, authors analyzed the JADER database to determine the incidence and characteristics of CNS ischemia in patients receiving VEGF inhibitors. Significant signals associated with CNS ischemia were detected in patients receiving bevacizumab. The results also suggested that bevacizumab-associated CNS ischemia was associated with a diagnosis of glioma, underlying hypertension, and aging.
-
Editor's pick
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment induces hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis(HLH)-like features, including pancytopenia, in senescence-accelerated mice (SAMP1/TA-1). Prolonged hyper-inflammation in LPS-treated SAMP1/TA-1 severely impaired the hematopoietic microenvironment in the bone marrow (BM), disrupting the dynamics of hematopoiesis. Macrophages are major components of hematopoietic microenvironment, and the balance of pro-inflammatory macrophages (M1) and anti-inflammatory macrophages (M2) governs the inflammatory process. In this study, the authors showed that LPS treatment led to severely imbalanced M1 and M2 macrophage polarization and prolonged monocyte-macrophage hyper-production in the BM of SAMP1/TA-1, resulting in severe and persistent inflammation in the BM hematopoietic microenvironment, and disruption of the dynamics of hematopoiesis.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 11 Pages 1627-1635The Impact of Eribulin on Stathmin Dynamics and Paclitaxel Sensitivity in Ovarian Cancer Cells Read moreEditor's pick
Stathmin, a microtubule destabilizing protein, may modulate the antiproliferative activity of eribulin, a microtubule dynamics inhibitor, in ovarian cancer. The authors investigated the function of stathmin in the antitumor effect of eribulin in ovarian cancer. In the cancer xenograft model and cultured cancer cells, eribulin treatment decreased tumor weight and increased phosphorylated stathmin mediated in part by downregulation of protein phosphatase 2A. Eribulin-induced phosphorylation of stathmin may also enhance the antiproliferative effect of paclitaxel. These results suggest that eribulin may inhibit proliferation of ovarian cancer cells in part by modulating stathmin activity.