-
47 巻 (2024) 3 号 p. 698-707Lymphatic Endothelial Cells Produce Chemokines in Response to the Lipid Nanoparticles Used in RNA Vaccines もっと読む
-
47 巻 (2024) 3 号 p. 641-651Oxidized-LDL Induces Metabolic Dysfunction in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells もっと読む
-
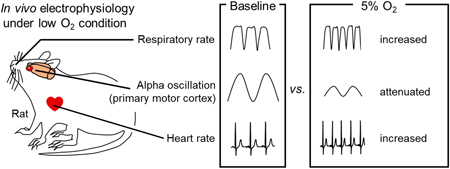
47 巻 (2024) 2 号 p. 462-468Low Atmospheric Oxygen Attenuates Alpha Oscillations in the Primary Motor Cortex of Awake Rats もっと読む
-
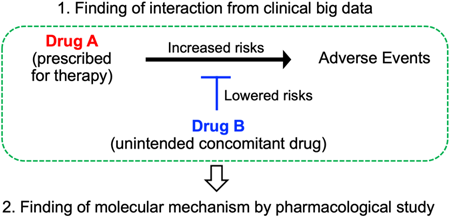
47 巻 (2024) 2 号 p. 345-349A Novel Strategy for the Discovery of Drug Targets: Integrating Clinical Evidence with Molecular Studies もっと読む
-
-
編集者のコメント
Genetic engineering now enables generation of artificially modified antibodies having higher diagnostic utilities. The authors developed single-chain Fv fragments (scFvs) against cortisol with >55-fold improved affinity (Ka, 2.0-2.2 ´ 1010 M-1) by inserting additional amino acid(s) site-directedly into the framework region 1 of the VH domain. These scFvs were fused with NanoLuc luciferase for the use in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) system. The resulting luminescent ELISAs generated dose-response curves with >150-fold higher sensitivity than the colorimetric ELISAs using the scFv without insertion and >8,000-fold higher sensitivity than the ELISA using the mouse antibody from which the scFvs were derived.
-
46 巻 (2023) 12 号 p. 1676-1682Method for Preparing Recombinant Galectin-2 Protein without Escherichia coli-Specific Post-translational Modifications もっと読む編集者のコメント
E. coli is often employed for the cost-effective production of large quantities of recombinant proteins. Conventionally, it is believed that post-translational modifications, including glycosylation, do not transpire during protein expression in E. coli. However, in the course of preparing recombinant galectin-2 protein using E. coli, the authors discovered that phosphogluconoylation of Lys residues and mistranslation of termination codons occurred. The authors have elucidated strategies to mitigate these occurrences, proposing the addition of tags, substitution of Lys residues, and modification of termination codons. These methods offer valuable means to prevent undesired modifications, ensuring the production of homogeneous recombinant proteins in E. coli.
-
編集者のコメント
The authors focused on cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) as penetration enhancers for ocular drug delivery. This study suggested that the CPPs evaluated in this study can be penetration enhancers based on in vitro intracellular uptake using a reconstructed human corneal epithelial model. The CPPs could enhance the penetration of drug molecules into the cornea in cases of coexistence as well as conjugation between CPPs and drug molecules. The result of surface plasmon resonance showed that the electrostatic interaction plays an important role. The authors expect that this fundamental information in this article will support the development of new penetration enhancers in eye drop formulations for ocular drug delivery.
-
46 巻 (2023) 12 号 p. 1753-1760Arid5a/IL-6/PAI-1 Signaling Is Involved in the Pathogenesis of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Kidney Injury もっと読む編集者のコメント
Inflammation is responsible for the development of various kidney diseases. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) is involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory kidney injury; however, the regulatory mechanism of PAI-1 in injured kidneys remains unclear. The authors found that PAI-1 expression was increased in endothelial cells after lipopolysaccharide (LPS, an inflammation inducer) treatment, and pharmacological inhibition of PAI-1 reduced LPS-induced kidney injury. Moreover, IL-6 exacerbated kidney injury concomitant with increased PAI-1 expression, and Arid5a deficiency partially suppressed the expression of IL-6 and PAI-1 in the kidneys after LPS treatment. These findings indicate that the Arid5a/IL-6/PAI-1 signaling is involved in LPS-induced kidney injury.
-
46 巻 (2023) 12 号 p. 1778-1786Identification of the Acidification Mechanism of the Optimal pH for RNase He1 もっと読む編集者のコメント
Hericium erinaceus secretes an acidic ribonuclease (RNase) He1 belonged to RNase T1 family. The authors decided on the structure of He1 apo form and He1/guanosine complex. The mechanism of acidification of optimal pH in He1 was, in neutral environment, to form the hydrogen bond between Asp 31 on α1β3- loop and His 34 (catalytic residue), and repulsive each other Glu 92 and Asp 93 on β6,7- loop. Structure comparison of He1 with other acidic RNases, Ms and U2, suggested that the acidic residues on α1β3- and β6,7- loop may contribute to the acidification of optimal pH in Ms and U2.