-
編集者のコメント
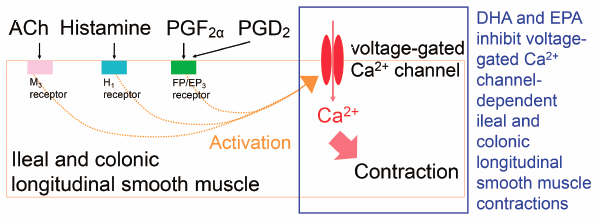
DHA and EPA have been reported to improve lower gastrointestinal (LGI) disorders through their anti-inflammatory effects. However, few studies examine the effects of DHA and EPA on LGI tract motility. To elucidate this, authors evaluated their effects on guinea pig ileal/colonic longitudinal smooth muscle (LSM) contractions. DHA and EPA significantly inhibited ileal/colonic LSM contractions induced by acetylcholine/histamine/PGF2α/PGD2/CaCl2. All ileal/colonic LSM contractions were completely suppressed by verapamil. These findings suggest that DHA and EPA could improve the abnormal contractile functions of the LGI tract associated with inflammatory diseases, partly through inhibition of voltage-gated Ca2+ channel-dependent ileal/colonic LSM contractions.
-
44 巻 (2021) 7 号 p. 910-919PC3-Secreted Microprotein Is Expressed in Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells and Human Glioma Tissues もっと読む編集者のコメント
The authors established single cell-derived tumorsphere clone, named P4E8, from human glioblastoma U87MG cells and indicated that P4E8 cells had the CSC-like phenotype such as self-renewal capacity, expression of CSC markers, resistance to several anti-cancer agents and high tumorigenicity in vivo. Furthermore, DNA microarray analysis identified that PC3-secreted microprotein (MSMP) was the highest expressed gene in P4E8 cells compared to U87MG cells. In addition, authors first indicated the expression of MSMP protein in patient-derived glioma stem cells (GSCs) and human glioma tissues. These findings raised the possibility that MSMP may contribute to glioma development and/or progression.
-
編集者のコメント
Transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8) is a non-selective cation channel activated by mild cooling temperature and chemical cooling agents, including menthol. The authors demonstrate the mucosal protective and anti-inflammatory effects of TRPM8 expressed in sensory afferent neurons via in-vivo studies using TRPM8-deficient mice and specific TRPM8 agonist, and also immunohistochemical studies using TRPM8-enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) transgenic mice. The TRPM8-mediated protective and anti-inflammatory effects are accounted for by a protective neuropeptide calcitonin gene-related peptide released from sensory afferent neurons. These findings propose that TRPM8 is a potential target for the treatment of NSAID-induced enteropathy and inflammatory bowel diseases.
-
編集者のコメント
Authors demonstrate that pyoluteorin can inhibit cell proliferation by inducing autophagy and apoptosis in NSCLC cell lines through the JNK/Bcl2 pathway. Inhibition of autophagy via 3-MA or Beclin1 knockout enhance pyoluteorin-induced apoptosis. Authors believe that pyoluteorin combined with autophagy inhibitor may be a potential anticancer drug for human NSCLC.
-
編集者のコメント
Kitamura et al. have developed a new human immortalized cell-based multicellular spheroidal blood-brain barrier (BBB) model, in which astrocytes and pericytes form a spheroid core that is covered with an outer monolayer of brain microvascular endothelial cells. This layered structure is likely to play a critical role in bringing out high levels of BBB characteristics in the model and allows researchers to examine various BBB functions, including drug permeability assays. Therefore, the work opens up new avenues for accelerating in vitro BBB modeling, which in turn significantly contributes to CNS drug development as well as elucidation of molecular bases of CNS diseases.
-
編集者のコメント
Nicotine is known to enhance recognition memory in various species. However, the brain region where nicotine acts and exerts its effect remains unclear. In this study, using the novel object recognition test in mice, authors provide evidence that nicotine acts on α4β2 and α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed in the medial prefrontal cortex, a brain region associated with memory, and enhances object recognition memory.
-
44 巻 (2021) 6 号 p. 747-761Chrono-Drug Discovery and Development Based on Circadian Rhythm of Molecular, Cellular and Organ Level もっと読む編集者のコメント
This review describes the chronotherapeutic strategies based on molecular clock system of chronopharmacokinetic, chronopharmacodynamic and cancer chronopathological factors in the xenobiotic detoxification, transporter, receptor and molecular target. Chronotherapeutic strategies focus on the monitoring of rhythm, overcoming rhythm disruption, manipulation of rhythm, chrono-therapeutic drug monitoring, chrono-drug delivery system and chrono-drug discovery. The screening for small molecules targeting the clock genes is now in progress to stabilize circadian phase and enhance circadian amplitude, thereby consolidating and coordinating circadian organization,. The academic research along with a combination of chemical and biological information is essential to promote the research and development of new modality drug discovery such as clock genes.
-
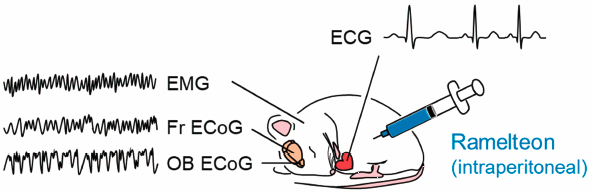
44 巻 (2021) 6 号 p. 789-797Acute Ramelteon Treatment Maintains the Cardiac Rhythms of Rats during Non-REM Sleep もっと読む編集者のコメント
Ramelteon, a melatonin receptor agonist, has a sleep-promoting effect by modulating sleep-wake rhythms. To examine the effect of ramelteon on cardiac function, authors simultaneously recorded electrocardiograms, electromyograms, and electrocorticograms in the frontal cortex and the olfactory bulb of unrestrained rats treated with ramelteon. Authors demonstrated that during non-REM sleep, heartrate variability was maintained by ramelteon treatment. Analysis of the electromyograms confirmed that neither microarousal during non-REM sleep nor the occupancy of phasic periods during REM sleep was altered by ramelteon. Thus, authors propose a remedial effect of ramelteon on cardiac activity by keeping the heartrate variability.
-
編集者のコメント
Numerous studies have confirmed that the sFlt1/PlGF ratio is a good predictor of the signs and symptoms of Pre-Eclampsia. However, its usefulness is limited to diagnosis after 20 weeks of gestation. To address this issue, in the present study the authors used plasma samples collected at gestational weeks 14-24 weeks from subjects who were subsequently diagnosed as Pre-Eclampsia. By employing SWATH-based proteomics for comprehensive discovery and SRM-based target quantification using in silico peptide selection criteria for validation, the authors were able to identify a 3-protein combination biomarker (AFAM, FINC and SHBG) that can predict effectively during gestational weeks 14-24 whether pregnant women would subsequently develop Pre-Eclampsia.
-
編集者のコメント
Cisplatin is an effective anti-cancer drug. A serious major side effect of cisplatin is an acute kidney injury. The authors demonstrated that panduratin A, a bioactive flavonoid, ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibition of cell apoptosis. The renoprotective effect of panduratin A is mediated by reducing oxidative stress and inhibiting ERK1/2 and caspase 3 activations. The protective effect of panduratin A did not impair the anti-cancer activity of cisplatin in cancer cells. Panduratin A might be a good candidate agent to alleviate cisplatin’s nephrotoxicity.
-
編集者のコメント
Influenza causes nosocomial outbreaks in healthcare settings. Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) for healthcare workers is one of the effective strategies for preventing outbreaks of influenza. However, PEP adherence in healthcare workers is rarely analysed. This retrospective questionnaire-based study showed that the adherence to PEP among healthcare workers was low, especially among physicians, and that the primary factor for preventing PEP adherence was misguided self-decision that continuation of PEP was unnecessary. This study emphasized that medication education should be provided to ensure treatment compliance and maximize the therapeutic benefits of PEP when PEP is administered.
-
編集者のコメント
The article by Nomura et al. suggested a novel mechanism of radiation-induced DNA damage repair contributing to radioresistance in melanoma. Authors have shown that the transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8) channel is involved in radiation-induced DNA damage response, cell death, and cell cycle regulation. Furthermore, TRPM8 channel inhibitor enhanced tumor growth-inhibitory effect by gamma-ray in vivo. These findings proposed that the TRPM8 channel contributes to the resistance of the growth-inhibitory effect of radiation in melanoma and could be a novel molecular target to improve the efficiency of radiation therapy for melanoma.
-
編集者のコメント
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ɤ (PPARɤ) agonists, such as pioglitazone, are anti-diabetic drugs, but they cause PPARɤ-related adverse effects such as body weight gain, cardiac hypertrophy, and bone loss. The authors found that a novel PPARɤ modulator, KY-903, has similar anti-diabetic effects without PPARɤ-related adverse effects in diabetic mice, possibly due to increases in adiponectin without adipogenesis. KY-903 also has anti-obesity effects with slight bone loss in obese rats, possibly by PPARɤ antagonism against endogenous or diet-derived PPARɤ ligands. These findings are useful for research on PPARɤ, and KY-903 is a potential candidate of anti-diabetic and/or anti-obesity drugs.
-
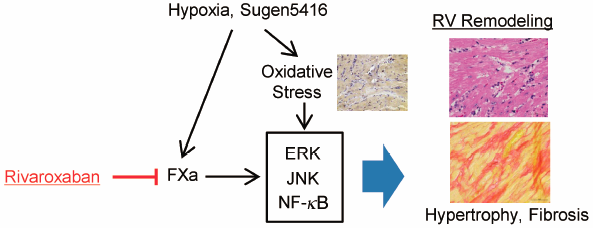
44 巻 (2021) 5 号 p. 669-677Rivaroxaban Attenuates Right Ventricular Remodeling in Rats with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension もっと読む編集者のコメント
The authors investigated the effects of rivaroxaban on right ventricular (RV) remodeling in a rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), created with Sugen5416 and chronic hypoxia (SuHx). The Fulton index, RV systolic pressure, and RV Tei index increased by SuHx were significantly decreased when treated with rivaroxaban. Rivaroxaban has the potential of improving RV remodeling in PAH model rats through the suppression of multiple signaling pathways, including ERK, JNK, and NF-kB, associated with protease-activated receptor-2. These findings suggest the additive effects that rivaroxaban may have on the RV remodeling in PAH.
-
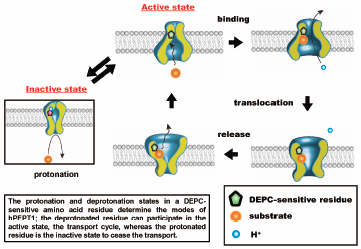
編集者のコメント
The authors indicated that the protonation of the histidine residue at the extracellular site in human oligopeptide transporter (hPEPT1) results in a decrease in the efflux activity, which is distinct from the sites of proton coupling for transport operation and substrate binding. Furthermore, they found that the decrease in extracellular pH reduced the turnover rate of transporters; in other words, the number of available transporters in the cycle was reduced. The protonation/deprotonation state of histidine determines the transport activity; the deprotonated histidine residue can participate in the transport cycle, whereas the protonated histidine residue can cease the transport.
-
編集者のコメント
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the most frequent arrhythmias in patients with hypertension. The authors found that an L/N-type calcium channel blocker cilnidipine exerts anti-AF effects in the remodeled atria of Dahl salt-sensitive rats more potently than amlodipine. Since plasma catecholamine levels is lower in the cilnidipine-treated animals than those in amlodipine-treated ones, blockade of N-type calcium channels presumably contributes to the superior cardioprotective effect of cilnidipine. These findings provide important information for considering treatment of hypertension complicating AF.
-
44 巻 (2021) 4 号 p. 522-527Dietary Fructooligosaccharides Reduce Mercury Levels in the Brain of Mice Exposed to Methylmercury もっと読む編集者のコメント
Fructooligosaccharides (FOS), typical nondigestible oligosaccharides, change the composition and/or activity of microbiota in the large intestine. Intestinal microbiota has important roles in the decomposition and fecal excretion of methylmercury (MeHg). Fecal Hg excretion was markedly higher in FOS-fed mice than in controls after oral administration of MeHg, but urinary Hg excretion was not. FOS-fed mice had lower total Hg levels in all tissues (including the brain) than controls. The possible mechanism on function of FOS is accelerated MeHg demethylation by intestinal bacteria and reduced MeHg absorption in the large intestine.
-
編集者のコメント
Psoriasis is an inflammatory skin disease characterized by red scaly papules or plaques. It has been suggested that activation of immune cells such as T cells and abnormal differentiation and proliferation of keratinocytes are involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. IL-2-inducible T cell kinase (ITK) is a tyrosine kinase expressed in T cells that regulates T cell activation. Authors showed that topical application of BMS-509744, a selective ITK inhibitor, ameliorates psoriasis-like inflammation in the skin of mice. This study suggests that ITK inhibition in skin lesion is a promising candidate treatment for psoriasis.
-
44 巻 (2021) 4 号 p. 544-549Increase in Blood Pressure by Local Injection of Ketamine into the Amygdala in Rats もっと読む編集者のコメント
Ketamine is known as a dissociative anesthetic that suppresses the cerebral cortex and activates the limbic system, and is unique as an anesthetic, since it induces blood pressure increase. Author examined the effect of ketamine, applied directly to the amygdala, on blood pressure. The results showed that the blood pressure was increased by ketamine injection into the basolateral and central nuclei of the amygdala, endopiriform nucleus and piriform cortex. Elucidation of the mechanism of ketamine-induced blood pressure increase will lead to understanding of the mechanism of side effects of ketamine, and will contribute to its appropriate use.