-
43 巻 (2020) 10 号 p. 1583-1590Effect of Cinacalcet on the Redox Status of Albumin in Secondary Hyperparathyroidism Patients Receiving Hemodialysis もっと読む編集者のコメント
Cinacalcet is a calcimimetic that permits impaired endothelial functions to be recovered via inhibiting parathyroid hormone (PTH) production in SHPT patients receiving hemodialysis. However, the underlying mechanism for its action remains unknown. The article by Imafuku et al. reported cinacalcet improves the redox status of human serum albumin (HSA) by inhibiting PTH production and partially by its radical scavenging action and increaed the anti-oxidant defense system in the blood circulation of SHPT patients. Such an anti-oxidative action of cinacalcet may, in part, explain the reduced risk for cardiovascular and all-cause mortality during cinacalcet treatment.
-
43 巻 (2020) 9 号 p. 1293-1300Current Understanding of the Intestinal Absorption of Nucleobases and Analogs もっと読む編集者のコメント
Knowledge of the intestinal absorption of nucleobases and analogs has accumulated, as is generally the case, mainly from studies using non-primate experimental animals. However, the recent identification of sodium-dependent nucleobase transporter 1, which plays a major role in their absorption in such animals, has led to exposing the fact that this important transporter is genetically missing in humans. To help to embark on efforts now needed to elucidate the mechanism of intestinal absorption of nucleobases and analogs in humans, which could be totally different from that in non-primate experimental animals, this article presents a comprehensive review on relevant knowledge and issues.
-
編集者のコメント
Vascular dementia (VD) is a common neurodegenerative disease, in the progress of which neuroinflammation and beta-amyloid (Aβ) deposition act as vital elements. In this study, lots of Aβ and nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome were found in VD rats’ brains induced by bilateral common carotid artery occlusion. A traditional Chinese medicine-Shechuangzi (osthole) extracted from the fruit of Cnidium monnieri (L.) possesses multiple pharmacological characteristics. This study has been proved the effect of osthole on VD rat evidenced by improving the behavior function, inhibiting the activation of microglia and reducing NLRP3 content, as well as decreasing the Aβ formation.
-
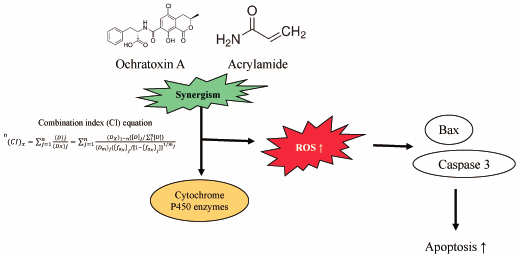
43 巻 (2020) 9 号 p. 1346-1355Synergistic Interaction of Ochratoxin A and Acrylamide Toxins in Human Kidney and Liver Cells もっと読む編集者のコメント
The toxicity of each ochratoxin A and acrylamide is known but there is uncertainty about the cumulative toxicity of two compounds. In this research, Pyo et al. demonstrated that there is a synergistic relationship between ochratoxin A and acrylamide that raises oxidative stress, reduces antioxidant enzymes and causes apoptosis, exacerbating liver and kidney toxicity. These findings indicate that the risk could be increased further by the food-borne toxicant 's interaction with the toxicant produced during processing.
-
編集者のコメント
Crocetin is a major bioactive component in saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and it has favorable cardiovascular protective effects. This study investigated the regulative effects of crocetin on L-type Ca2+ current (ICa-L), contractility, and the Ca2+ transients in rat ventricular cardiomyocytes using patch-clamp technique and Ion Optix system. The results indicated that crocetin inhibited ICa-L, intracellular Ca2+ concentration and contractility of cardiomyocytes. Crocetin (600 μg/ml) reduced cell shortening and the crest value of the ephemeral Ca2+ by 28.6 ± 2.31%, 31.87 ± 2.57%, respectively. These findings reveal that crocetin could be a potential calcium blocker for the treatment of cardiovascular disease.
-
編集者のコメント
Niemann-Pick diseases are classified into types A/B and C and early definitive diagnosis of them is important for better prognosis of the diseases. The authors developed a novel diagnostic screening strategy for Niemann-Pick diseases using a combination of serum concentrations of N-Palmitoyl-O-phosphocholine-serine and sphingosylphosphocholine based on analyses by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. In this study, a rapid method and a validated analysis were developed. The former was useful for screening and the latter were useful for differentiation of Niemann–Pick diseases. This strategy may be useful for screening of Niemann-Pick diseases in clinical practice.
-
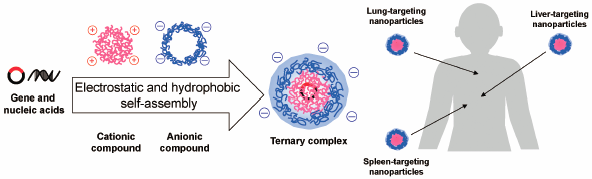
43 巻 (2020) 8 号 p. 1147-1153Development of Multi-functional Nanoparticles for Clinical Application to Gene and Nucleic Acid Medicines もっと読む編集者のコメント
The clinical application of gene/nucleic acid medicines is highly dependent on the development of effective and reliable drug delivery systems. Dr. Sasaki successfully developed several ternary complexes as novel gene delivery carriers, which were constructed by gene/nucleic acid medicine, the cationic polymer, and the anionic polymer. This ternary complex consists of biodegradable materials found in foods and medical products that are already in clinical use and can deliver gene/nucleic acid medicines to specific organs (liver, spleen, lung, and cancer cells etc.) without toxicity. The ternary complexes are expected to apply to clinical practice.
-
編集者のコメント
The sodium salt of isosteviol (STVNa) is a beyerane diterpene synthesized through acid hydrolysis of stevioside. STVNa improves multiple types of tissue injuries. However, it is not known how Isosteviol sodium affects high-fat and high cholesterol diet (HFD)-induced kidney. The current study suggested that STVNa inhibited HFD-induced kidney injury evident by reducing the increased levels of serum CRE. Specifically, STVNa attenuated HFD-induced kidney injury by inhibiting inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. These findings indicate that STVNa may have a therapeutic potential for metabolic syndrome associated kidney dysfunction by inhibiting inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis.
-
編集者のコメント
Increasing the immunostimulatory activity of unmethylated cytosine-phosphate-guanine oligodeoxynucleotide (CpG ODN) is an important issue for its clinical application as immunoadjuvant. In this study, the authors combined two approaches, i.e., nanostructured DNA formation and mannose modification, for efficient delivery of CpG ODN to mannose receptor-positive immune cells. Mannosylated CpG ODN (Man-CpG ODN) loaded onto polypod-like structured nucleic acid (polypodna) induced a greater tumor necrosis factor-α release than Man-CpG ODN or CpG ODN/polypodna from the cells. Thus, this study provides a new and promising approach to increasing the therapeutic potency of CpG ODN.
-
43 巻 (2020) 8 号 p. 1248-1252Trends of Antifungal Use Based on Sales Data in Japan from 2006 to 2015 もっと読む編集者のコメント
The detailed epidemiology of invasive mycoses and superficial mycoses has not been clarified in Japan. This is the first study to clarify the trends of antifungal use in Japan. The authors found that total antifungal use decreased over time. Notably, the trend of antifungal use for invasive mycoses was significantly increased by 19.9% whereas the trend of antifungal use for superficial mycoses significantly decreased by 49.8%. In Japan, the increase in the number of immunocompromised patients might be associated with an increase in the frequency of antifungal use for invasive mycoses.
-
編集者のコメント
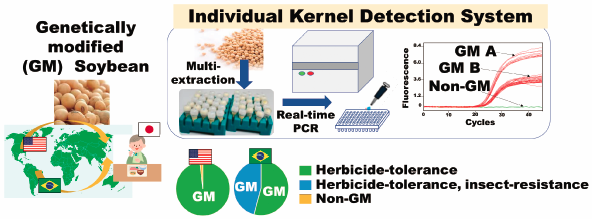
Today, majority of soybeans in Japan comes from foreign countries, where genetically modified (GM) soybeans are cultivated. The details of GM soybean actually consumed for food in Japan have been unknown. The article by Soga et al. reported a quantitative GM soybean kernel detection system and that the most of imported soybean in the non-identity-preserved soybean samples examined were herbicide-tolerant and insect-resistant GM soybean events that were authorized in Japan. These data would provide useful information on risk analysis concerning regulations on GM soybean for food use.
-
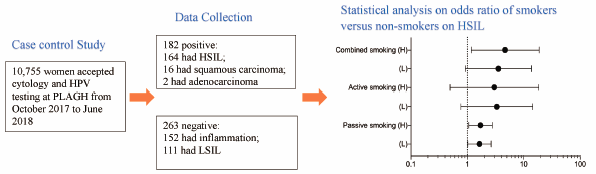
43 巻 (2020) 7 号 p. 1061-1066Evidence of Passive Smoking as a Risk Factor of High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion: A Case-Control Study もっと読む編集者のコメント
The association between risk factors and occurrence or development of cervical intraepithelial lesions, such as persistent infection with high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV), multiple sexual partners and smoking have been discussed. However, the effect of passive smoking on the disease is unclear. In this case-control study, Du et al. found that passive smoking was a significant independent risk factor on the occurrence of HSIL and showed a positive correlated dose-response relationship. HPV infection interacting with passive smoking led to an even higher disease risk. Adolescent exposure to passive smoking persistent for more than 20 years would also increase the HSIL risk.
-
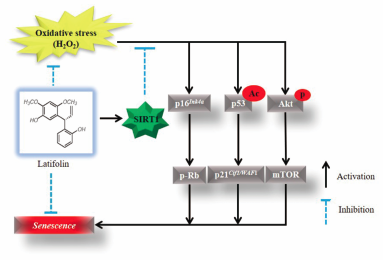
43 巻 (2020) 7 号 p. 1104-1110Latifolin Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Senescence via Upregulation of SIRT1 in Human Dermal Fibroblasts もっと読む編集者のコメント
Aging is the most important risk factor for various diseases such as cancer, osteoarthritis, dementia, atherosclerosis, and infection. Therefore, the researchers has attempted to find phytochemicals for ameliorating aging-related diseased. Latifolin, isolated from Dalbergia odorifera T. Chen, has been reported to exhibit anti-inflammatory and anti-carcinogenic activities. In present study, the authors investigated the anti-aging effect of latifolin in human dermal fibroblasts. Modulation of SIRT1 may be involved in latifolin protective effect against H2O2-induced oxidant injury. These results suggest that latifolin supplementation might be a possible route for improving aging and age-related diseases.
-
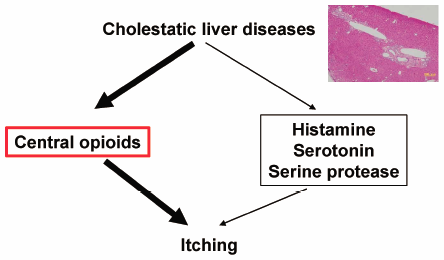
43 巻 (2020) 7 号 p. 1111-1117Pharmacological Characterization of a Novel Mouse Model of Cholestatic Pruritus もっと読む編集者のコメント
Patients with cholestatic liver diseases, such as primary biliary cirrhosis, usually suffer from pruritus. However, the pathogenesis of cholestatic pruritus is unclear, and there is no current effective treatment for it. In order to find a treatment for the condition, an appropriate mouse model should be developed. Andoh et al. established a surgically-induced mouse model of cholestatic pruritus and evaluated anti-pruritic effects of several drugs using this mouse model. In results, they suggested that partial obstruction of bile secretion in mice induced anti-histamine-resistant itching and that central opioid system is involved in cholestatic itching.
-
編集者のコメント
Large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKCa) channels possess significant physiological functions in various types of cells. The stoichiometry between BKa and newly identified ɤ1 subunits (BKɤ1) remains unclear. Here, the authors utilized a single molecule fluorescence imaging with a total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) microscope to directly count the number of GFP-tagged BKɤ1 within a single BKCa channel complex in HEK293 expression system. Counting of GFP bleaching steps revealed that a BKCa channel contains mainly four BKɤ1 per channel. These results suggest that BKɤ1 forms a BKCa channel complex with BKa in a 1:1 stoichiometry in a human cell line.
-
43 巻 (2020) 6 号 p. 932-937Ziyuglycoside II Inhibits Rotavirus Induced Diarrhea Possibly via TLR4/NF-κB Pathways もっと読む編集者のコメント
In the present study, Ziyuglycoside II inhibits rotavirus (RV) induced diarrhea via toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) signaling pathway. Ziyuglycoside II inhibited the proliferation of MA104 cells infected with RV via suppressing RV duplication. The combination of Ziyuglycoside II and Ribavirin protected against RV-induced diarrhea through regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Moreover, the combined treatment suppressed the level of pro-inflammation cytokines and overexpressed anti-inflammation cytokine. Moreover, the combined therapy improved the lesion changes and inhibited the cell apoptosis in vivo. Thus Ziyuglycoside II may function as protective role in RV-induced diarrhea.
-
43 巻 (2020) 6 号 p. 959-967Characterization and Immunological Activities of Polysaccharides from Polygonatum sibiricum もっと読む編集者のコメント
Polygonatum sibiricum first appeared in ancient Chinese medicine books around 1000 years ago and is used to tonify the spleen and nourish the lungs. The authors present here a kind of natural polysaccharides (PSP) extracted from Polygonatum sibiricum were purified, characterized and assayed both in vitro and in vivo for its immunomodulatory activity and mechanism. It is of interest to note that PSP not only regulated the immune function of normal mice, but participated in the protection against immunosuppression in cyclophosphamide-treated mice, highlighting its potential as an immunostimulant.
-
43 巻 (2020) 6 号 p. 968-975Potential Mechanisms Underlying the Hepatic–Protective Effects of Danshensu on Iron Overload Mice もっと読む編集者のコメント
Danshensu (3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-(2R)-lactic acid) is one of the water-soluble active ingredients of Salvia miltiorrhizae, a traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. This study investigated the protective effects of Danshensu on the acute liver injury induced by iron overload in mice. The results indicated that the underlying mechanisms at least partly involve anti-oxidation, anti-inflammation, anti-apoptosis, and decreasing hepatic iron deposition possibly through down-regulating the expression of iron uptake related proteins, such as DMT1, TfR, and L-type Ca2+ CP α1C. Therefore, they conclude Danshensu could be a promising prophylactic or therapeutic agent for iron overload diseases.
-
43 巻 (2020) 6 号 p. 1007-1015Detection of Abacavir-Induced Structural Alterations in Human Leukocyte Antigen-B*57 : 01 Using Phage Display もっと読む編集者のコメント
The interaction of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) with specific drugs induces structural alteration in HLA and delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions, which cause severe cutaneous toxicity. Shirayanagi et al. selected specific phage antibodies able to recognize HLA-B*57:01 and evaluated structural alterations in HLA-B*57:01 complexes induced by abacavir. The affinity of selected phage antibodies increased because of structural alterations in HLA-B*57:01 following exposure to abacavir, indicating that specific phage antibodies can identify drug-mediated structural changes in HLA complexes. These results suggest that phage display technology is a useful method for detecting structural changes in HLA complexes.
-
編集者のコメント
Efficiency and animal welfare are important factors in the development of new drugs. Considering this, Nakamura et al. propose a new way of predicting human PK for mAbs that is more efficient than conventional methods. By collecting mAb PK data on linear elimination and analyzing a two-compartment model, they revealed that half-life during elimination is the main contributor to plasma clearance. Based on this feature, they developed a novel method that uses easy-to-obtain parameters from humans and non-human primates to predict human PK. Called the half-life method, it can improve animal welfare and potentially accelerate the drug development process.