-
編集者のコメント
Allergic contact dermatitis is a common dermatitis and is induced by contact with allergens. The authors found that methionine suppressed this dermatitis in some strains of mice. They also found that the strength of the effect depended on the suppression of liver betaine homocysteine methyltransferase (Bhmt) expression by the dermatitis. Although the mechanism has not been elucidated, the authors propose that while dermatitis suppresses liver Bhmt expression in some strains of mice, the fact that the metabolic state of the liver affects the suppression of dermatitis suggests that there is at least a skin-liver interaction, especially a dermatitis-liver interaction.
-
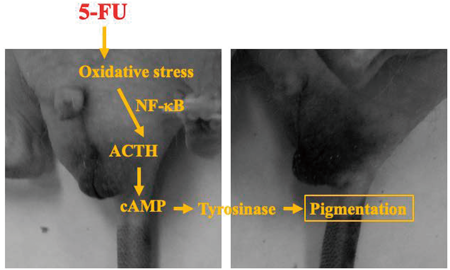
46 巻 (2023) 7 号 p. 955-963ACTH/cAMP-Mediated Skin Pigmentation Caused by 5-Fluorouracil Administration もっと読む編集者のコメント
This study aimed to investigate the mechanism underlying the skin pigmentation caused by anticancer drugs using 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), a widely used anticancer drug known to cause this complication. Authors believe our study makes a significant contribution to the literature because anticancer drug-induced skin pigmentation remarkably affects the quality of life of cancer patients, has no established treatment, and has an unknown mechanism. This result provides new insight into the role of the ACTH/cAMP/tyrosinase pathway in 5-FU-mediated skin pigmentation and may help manage this complication.
-
編集者のコメント
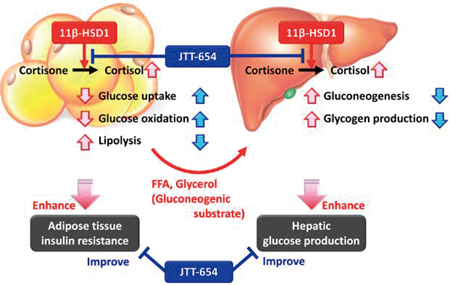
11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11β-HSD1) is the only enzyme that converts inactive glucocorticoids to active forms and plays an important role in regulating glucocorticoid action in target tissues. Excess glucocorticoids cause insulin resistance in the liver and adipose tissue. Several 11β-HSD1 inhibitors have been reported, but all have been evaluated in obese diabetes models. In the present study, the authors investigated the pharmacological properties of JTT-654, a selective 11β-HSD1 inhibitor, in cortisone-treated rats and non-obese Goto-Kakizaki rats with type 2 diabetes, because many Asians, including Japanese, have non-obese type 2 diabetes. Information gained from detailed analysis of the mechanism of action of JTT-654 may provide a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of non-obese type 2 diabetic patients.
-
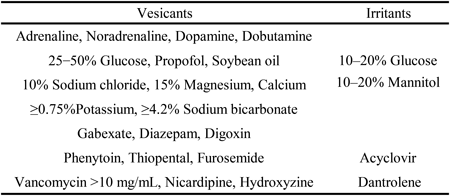
46 巻 (2023) 6 号 p. 746-755Extravasation of Noncytotoxic Agents: Skin Injury and Risk Classification もっと読む編集者のコメント
A typical manifestation of iatrogenic injury associated with intravenous injection is extravascular leakage. The severity of injury and treatment for extravascular leakage of cytotoxic agents is well known, however there is insufficient information on non-cytotoxic agents. The authors reviewed human and animal studies of extravascular injury induced by non-cytotoxic agents and classified them based on the severity of injury. The classification of non-cytotoxic agents in the extravasation is useful information in clinical practice to provide appropriate warning of the risk of injury and to prevent worsening of injury.
-
編集者のコメント
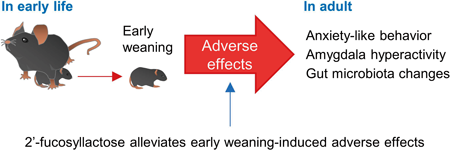
Recently, evidence is accumulating on functional communication between the central nervous system (CNS) and the gut microbiota. Given this, early prebiotic treatment may assist the development of the CNS through the gut microbiota. In this study, Araki et al. found that 2'-fucosyllactose (2´-FL), a human milk oligosaccharide, altered the fecal microbiota and reduced anxiety-like behavior and amygdala hyperactivity observed in mice exposed to early weaning stress. These findings suggest that prebiotic treatment with 2´-FL may alleviate the adverse effects of early life stress in the CNS such as anxiety and amygdala hyperactivity.
-
編集者のコメント
It is believed that 15-lipoxygenase plays a role in tissue damage under conditions of low oxygen levels through lipid-derived radical chain reactions. The authors of this study discovered that when a higher content of linoleate than oxygen content was stood with 15-lipoxygenase in the presence of hydrogen polysulfides, which are believed to be endogenous bioactive substance in cells, the conjugated diene moiety of the oxidized linoleate derivatives was isomerized from E/Z form to E/E form. Based on these findings, authors proposed a hypothesis that hydrogen polysulfides scavenge lipid-derived radicals, generating thiyl radicals, which then isomerized the conjugated diene moiety.
-
編集者のコメント
Lactic acid bacteria (LABs) are well known as beneficial microorganisms to maintain human health. Although LABs are recognized as probiotics, these bacteria produce many kinds of bioactive compounds. The mechanisms how LABs produce these bioactive substances are not well known. Additionally, unlike the cases of E. coli and yeast, there are not enough commercially available tools for a genetic approach of LABs. Therefore, in the present study, the authors have constructed a new plasmid as an efficient genetic engineering tool for random insertional mutagenesis in LABs using a combination of transposon Tn10 and the temperature-sensitive replication system.
-
編集者のコメント
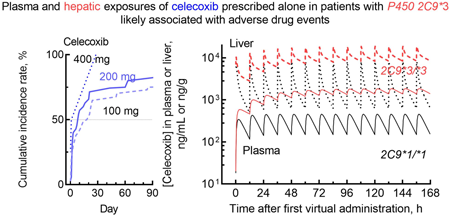
Although the potential for cytochrome P450 2C9 (CYP2C9) to cause drug interactions, there are few cases of information related to the influence of CYP2C9 polymorphism on drug labeling recommendations in Japan. Among the various factors related to adverse events in the database associated with the prescription of celecoxib or diclofenac alone, variations in the in vivo intrinsic clearance of the drug may exist. Virtual hepatic and plasma exposures estimated by pharmacokinetic modeling in patients harboring impaired CYP2C9*3 could represent a causal factor for adverse events induced by celecoxib or diclofenac in a manner similar to that for drug interactions.
-
46 巻 (2023) 5 号 p. 700-706Regional Disparity in First-in-Class Anticancer Drug Development in the US, EU, and Japan もっと読む編集者のコメント
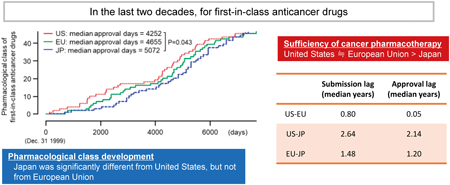
Recent improvement of pharmacotherapy on cancer is remarkable, however cancer is still one of the most devastating diseases for patients and their caregivers. The authors compared the development and approval status of first-in-class (FIC) anticancer drugs between the US, EU, and Japan, and found that approval in Japan lagged substantially behind compared to the other regions (more than 1 year vs the EU and more than 2 years vs the US). Considering the high impact of anticancer drugs on society worldwide, we should work together to reduce drug lag among regions using an improved international cooperative framework.
-
46 巻 (2023) 5 号 p. 707-712Effect of Ointment Base on the Skin Wound-Healing Deficits in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rat もっと読む編集者のコメント
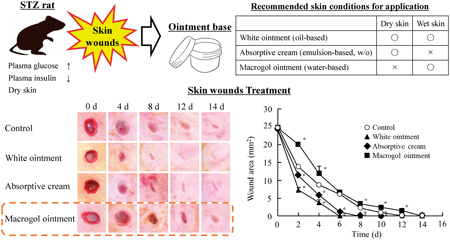
The authors investigated weather difference ointment bases (absorbent cream, white-, and macrogol-ointment) affect the skin wound healing rate in normal and diabetic models (streptozotocin-induced rat, STZ rat). The wound healing rate was similar in the normal rat treated with three-bases. In contrast of this result, the wound healing in STZ rats treated with macrogol-ointment was delayed in comparison with other two-bases. These results indicate that the wound healing in STZ rats is affected by the properties of ointment base, and the selection of appropriate ointment base according to the skin condition may be important for the wound healing in patients with diabetes.
-
46 巻 (2023) 5 号 p. 713-717Rapid Screening Detection of Genetically Modified Papaya by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification もっと読む編集者のコメント
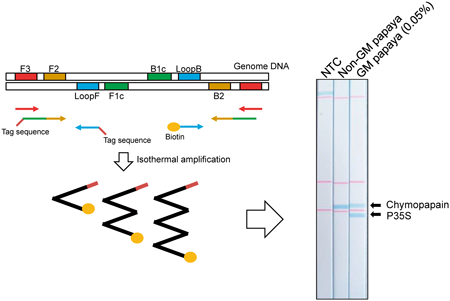
A loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)-mediated screening detection method for genetically modified (GM) papaya was developed using a Genie II real-time fluorometer. The authors also designed a primer set for the detection of the papaya endogenous reference sequence, chymopapain, and the species-specificity was confirmed. To enhance the simplicity, the authors attempted to develop a lateral flow DNA chromatography to detect LAMP products, and a duplex detection was successfully applied. This simple and quick method for the screening of GM papaya will be useful for the prevention of environmental contamination of unauthorized GM crops.
-
編集者のコメント
The author found that bio-ventures established in the 1990s and 2000s played a crucial role in creating new drugs approved by the FDA from 2017 to 2022 in regions outside of Japan. In contrast, in Japan, all approved drugs were created by old incumbent pharmaceutical companies, highlighting the urgent need to foster drug discovery start-ups in Japan. A case study of the Japanese company that created the largest number of FDA-approved drugs suggests that focused investment in modality technology development, strengthening collaboration with academia in biology, and the reutilizing small-molecule drug discovery capabilities are essential for improving drug discovery productivity.
-
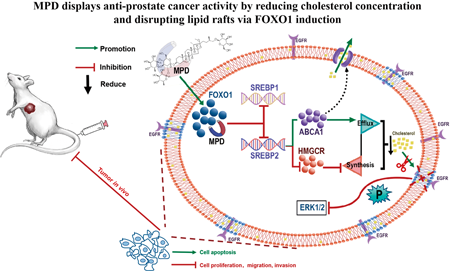
編集者のコメント
High cholesterol concentration can promote the growth of prostate cancer. Methyl protodioscin (MPD), a furostanol saponin found in the rhizomes of Dioscoreaceae, has lipid-lowering and broad anticancer properties. In this research, MPD decreased expression of SREBP1 and SREBP2 by inducing FOXO1, lead to the induction of the expression of cholesterol export pump ABCA1 and reduction of the expression of the rate-limiting enzyme of cholesterol synthesis HMGCR. Reduced cholesterol caused to disrupted lipid rafts and MAPK pathway on it, contributing to MPD anti-prostate cancer activity. Consequently, MPD may be used as an active drug for treatment in prostate cancer.
-
編集者のコメント
The authors described prescription trends of the antidiabetic agents used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Japan from 2012 to 2020 using administrative claims data. Noteworthy, this study examined the prescription trends in every line for T2DM treatment, including the combinations of antidiabetic agents, and showed that sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors were rapidly introduced into T2DM treatment from several perspectives. Such a descriptive study revealed how T2DM treatment changed in accordance with cumulated evidence and can provide interesting information on public health.
-
編集者のコメント
The polyphenol derivative 3,4-dihydroxybenzalacetone (DBL) is the primary antioxidative component of the medicinal folk mushroom Chaga. The authors investigated whether the antioxidative effect of DBL could propagate to recipient cells using extracellular vesicles (EVs)-enriched fractions prepared by sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation from conditioned medium of SH-SY5Y cells exposed to hydrogen peroxide after pre-exposing DBL. The results obtained from cell-based tests including the radical scavenging and the fluorescent Paul Karl Horan-labeled EVs uptake assays suggest that cell-to-cell communication via bioactive substances, such as EVs propagate the hydrogen peroxide-induced radical scavenging effect, whereas pre-conditioning with DBL inhibits it.
-
46 巻 (2023) 4 号 p. 630-635Apigenin Alleviates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Apoptosis in INS-1 β-Cells もっと読む編集者のコメント
Protection against impaired insulin secretion and β-cell apoptosis is an important strategy to prevent the progression of type 2 diabetes. The authors have reported the effects of apigenin, a dietary trihydroxyflavone, on pancreatic β-cell functions, underlying its anti-diabetic effects. The study demonstrated that apigenin exerts insulinotropic and anti-apoptotic effects in the β-cell line INS-1D. The anti-apoptotic effect of apigenin was further supported by reduced expression of apoptotic signaling proteins and pro-apoptotic protein. The results suggest and provide a basis for the development of apigenin as a potential therapeutic for type 2 diabetes through promoting β-cell survival and function.
-
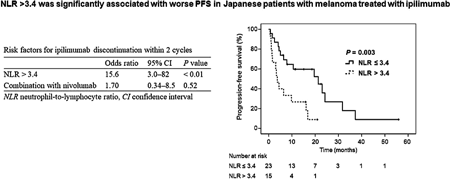
編集者のコメント
Studies have reported an association between elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and poor prognosis in patients with melanoma treated with ipilimumab. However, it remains unclear whether NLR is useful in Japanese. Authors retrospectively examined 38 patients, and found that baseline NLR>3.4 was an independent risk factor for ipilimumab discontinuation that was significantly associated with shorter progression-free survival. Because the NLR cut-off value in this study was lower than values in American and European studies, it possibly differs by race. Hence, it should be extrapolated to Japanese patients with caution.
-
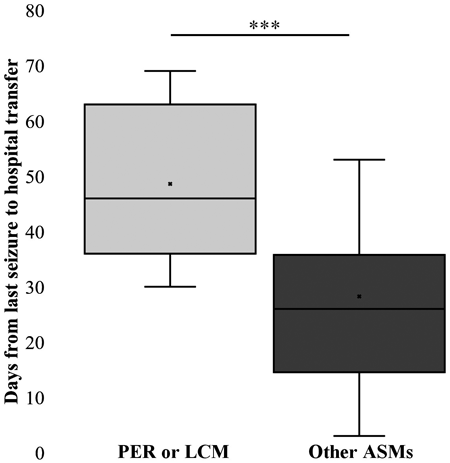
編集者のコメント
This investigation of the impact of antiseizure medications (ASMs) on hospital transfer was undertaken because chronic-care hospitals have refused to accept several post-stroke epilepsy patients using novel ASMs from acute-care hospitals. Patients with stroke receiving novel ASMs, i.e., perampanel and lacosamide, had longer times to hospital transfer than patients receiving other ASMs. Furthermore, a weak correlation was found between the cost of a patient's daily medications and the number of days to hospital transfer. These results indicate that considering the availability and cost of ASMs in the transfer destination hospital is important when choosing medications for patients requiring hospital transfer.
-
編集者のコメント
The authors found that amentoflavone, apigenin, kaempferol, and chrysin enhanced the activity and expression of neprilysin, one of the major Aβ-degrading enzymes, by screening a polyphenol library, and that chemical structures involving a double bond between positions 2 and 3 in the C ring of flavones were important for neprilysin enhancement. Moreover, natural compounds, such as quercetin, were not effective per se, but were changed to effective compounds by adding a lipophilic moiety. These findings provide a basis for the development of novel small molecules as disease-modifying drugs for Alzheimer’s disease.
-
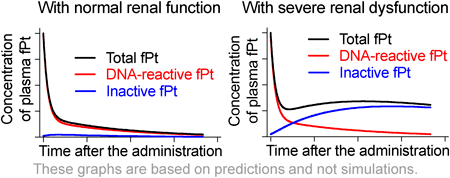
編集者のコメント
Oxaliplatin is a platinum (Pt)-based chemotherapeutic drug that is widely used to treat gastrointestinal and pancreatic cancers. The authors hypothesized that the DNA-binding capacity is one of the properties of reactive Pt species and aimed to evaluate the contribution of the kidney to the plasma levels of DNA-reactive Pt in an animal model and a hemodialysis patient. The results of this study showed that severe renal dysfunction has a limited effect on the plasma levels of DNA-reactive Pt after oxaliplatin administration.