-
Editor's pick
This paper describes the development of the planar chiral [2.2]paracyclophane-based bisoxazoline (PCP-Box) ligands for Cu-catalyzed O-H insertion reactions of α-diazo esters. C2-symmetric PCP-Box ligands, in which the achiral oxazoline unit is located at the meta-position of the benzene spacer having a bulky substituent at the para-position, gave better levels of enantioselectivity in ethanolic O-H insertion than the spacer free PCP-Boxes with or without central chirality of the oxazoline rings. The former also showed good enantioselectivities in inter- and intramolecular aromatic O-H insertions.
-
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 9 Pages 873-879Manganese-Catalyzed Oxophosphorylation Reaction of Carbon–Carbon Double Bonds Using Molecular Oxygen in Air Read moreEditor's pick
A novel aerobic manganese-catalyzed oxophoshporylation reaction of carbon–carbon double bonds of styrene derivatives and vinyl ethers using diethyl H-phosphonates was developed. This direct transformation of alkenes to b-ketophosphonates readily proceeded at room temperature via the incorporation of molecular oxygen present in air (open flask). All of the experimental procedures in this reaction can be performed in air without cooling, heating, or high pressure. This methodology serves an alternative approach to produce β-ketophosphonates because of its simplicity and mildness.
-
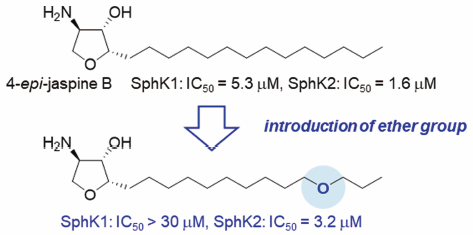
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 9 Pages 866-872Introduction of a Polar Functional Group to the Lipid Tail of 4-epi-Jaspine B Affects Sphingosine Kinase Isoform Selectivity Read moreEditor's pick
4-epi-Jaspine B derivatives containing a polar functional group in the lipid tail were designed and synthesized for the development of sphingosine kinase (SphK) inhibitors, which would be applicable to the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. A biological evaluation revealed that the replacement of one methylene at the lipid tail with ether oxygen affected the inhibitory activity of 4-epi-jaspine B, leading to the identification of a selective SphK2 inhibitor.
-
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 8 Pages 773-778Macrocyclic Compounds from Ansamycin Antibiotic Class as Inhibitors of PD1–PDL1 Protein–Protein Interaction Read moreEditor's pick
Antibody therapies that bind to PD1 protein and inhibit its binding with PDL1 protein have shown unprecedented clinical success in activating innate immune system to treat cancer. Here, the authors investigated activity of several macrocyclic compounds in inhibiting PD1-PDL1 interaction, leading to identification of Rifabutin, an approved macrocyclic antibiotic, as top active compound with remarkable IC50 value of ~25 µM. Computational docking followed by molecular dynamics simulations revealed Rifabutin making key interactions with PD1, occupying and blocking majority of the area on PD1 protein where PDL1 is known to bind.
-
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 8 Pages 794-804Ultra Cryo-Milling with Liquid Nitrogen and Dry Ice Beads: Characterization of Dry Ice as Milling Beads for Application to Various Drug Compounds Read moreEditor's pick
The authors developed a novel cryogenic milling technique in liquid nitrogen (LN2) using dry ice beads. The contamination issue related to fragments of eroded beads could be overcome due to their spontaneous removal. In this study, the transformation process from the pellets and the morphological change of dry ice beads during milling process in LN2 was monitored to assess their potential as milling media. The authors presented that dry ice could maintain its bead shape even under vigorous agitation in LN2. Further, they demonstrated that their milling performance was comparable to conventional technique using zirconia beads.
-
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 8 Pages 805-809Rapid Analysis of Cyclic Peptide Cyclosporine A by HPLC Using a Column Packed with Nonporous Particles Read moreEditor's pick
The authors developed a rapid and efficient analytical technique for cyclosporine A using HPLC. Under optimized conditions, cyclosporine A was separated with high resolution from other cyclic peptides within 3 min, because the mass transfer resistance in the stationary phase was reduced by the use of the small, nonporous particle columns. The results indicate that cyclosporine A is structurally rigid and undergoes poor water solvation even at high temperature. In the context of the rapid development of cyclic peptides with similar physicochemical characteristics to cyclosporine A, the developed method is useful for the development of cyclic peptide therapeutics.
-
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 8 Pages 810-817Synthesis and Evaluation of Fuligocandin B Derivatives with Activity for Overcoming TRAIL Resistance Read moreEditor's pick
Fuligocandin B isolated from the slime mold Fuligo candida induced apoptosis in TRAIL resistance cancer cells by increasing death receptor 5 (DR5) thorough binding to valosin-containing protein (VCP). Heterocyclic derivatives of fuligocandin B were synthesized and evaluated. Amine derivative designed based on docking simulation showed potent cytotoxicity against TRAIL resistance human gastric adenocarcinoma (AGS) cells. The figure represents picture of Fuligo candida, structure of 7’-amino fuligocandin B and image of increasing DR5 which goes to bind to TRAIL on the cell surface.
-
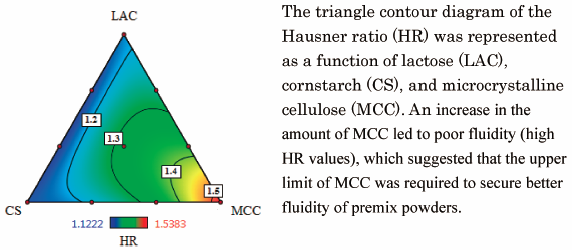
Editor's pick
The triangle contour diagram of the Hausner ratio (HR) was represented as a function of lactose (LAC), cornstarch (CS), and microcrystalline cellulose (MCC). The HR is given as the ratio of tapped density to bulk density of powders, and the value is often used as an index of powder fluidity. Although the fluidity of most formulations was acceptable, an increase in the amount of MCC led to poor fluidity (high HR values), which suggested that the upper limit of MCC was required to secure better fluidity of premix powders.
-
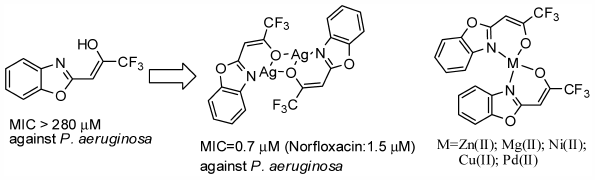
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 7 Pages 732-740Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of 2-Trifluoroacetonylbenzoxazole Ligands and Their Metal Complexes Read moreEditor's pick
New Zn(II), Mg(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), Pd(II), and Ag(I) complexes of 2-trifluoroacetonylbenzoxazole ligand have been synthesized. Their structures were determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analyses. Some metal complexes have more antibacterial effects in comparison with the free ligand. Noticeably, the Ag(I) complex 2h exhibited low MIC value of 0.7 μM against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which was even superior to Norfloxacin with that of 1.5 μM. 2h is bacteriostatic, exerts the cell surface damage observed by scanning electron microscopy and is less likely to develop resistance. 2h has been found to display effective antimicrobial activity against a series of bacteria.
-
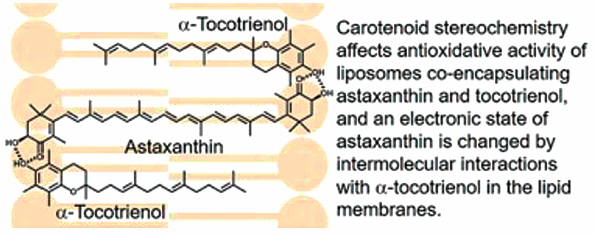
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 7 Pages 714-720Carotenoid Stereochemistry Affects Antioxidative Activity of Liposomes Co-encapsulating Astaxanthin and Tocotrienol Read moreEditor's pick
The antioxidative activity of liposomes co-encapsulating stereoisomer 3S,3’S-astaxanthin (Asx-S) and α-tocotrienol (α-T3) was higher than the calculated additive activity, which results from intermolecular interactions between both antioxidants. The optimal Asx-S/α-T3 ratio for antioxidation was 1:2. Consequently, the Asx stereochemistry affects the intermolecular interaction of Asx/T3, and it was suggested that the intermolecular interaction caused a change in the electronic state of the Asx-S polyene moiety by the presence of double bond in the α-T3 triene moiety.
-
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 7 Pages 708-713Protective Effect of Taohong Siwu Decoction on Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Induced by Incomplete Medical Abortion in Rats during Early Pregnancy Read moreEditor's pick
Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) induced by incomplete abortion, which is a common gynecological disease. Taohong Siwu decoction (TSD) has been developed to treat AUB for hundreds of years. In this study, it demonstrated that TSD significantly shortened the duration and reduced the quantity of uterine bleeding. These results suggested that TSD promoted endometrial repair and had a protective effect on uteri. The mechanism may be concerned with up-regulation of the levels of E2 and ERα expression.
-
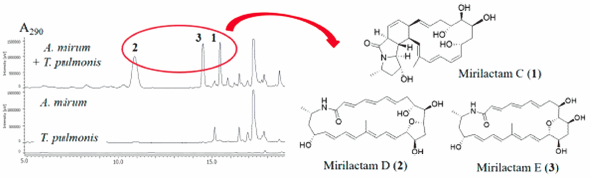
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 6 Pages 660-667Mirilactams C–E, Novel Polycyclic Macrolactams Isolated from Combined-Culture of Actinosynnema mirum NBRC 14064 and Mycolic Acid-Containing Bacterium Read moreEditor's pick
Actinobacteria are the rich source of natural products while the large parts of biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) are silent under the standard culture conditions. The authors previously demonstrated that co-culture with mycolic acid-containing bacterium (MACB) effectively activates the silent BGCs in actinobacteria. In this study, the authors investigated the actinobacterium which produces a polyene macrolactam, mirilactam A. The authors tested co-culture of the mirilactam A producer strain with MACB, and successfully obtained three novel polycyclic macrolactams, mirilactams C-E, by activating silent biosynthetic genes responsible for the epoxidation and cyclization of the polyene mirilactam A.
-
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 6 Pages 642-650Identification of Two Phenanthrene Derivatives from Australasian Allied Species in Genus Dendrobium Read moreEditor's pick
The genus Dendrobium (Orchidaceae) is comprised of more than 1,000 species and divided into two major groups, Asian and Australasian clades. There are many ethnobotanical important species in this genus and various phenanthrenes and bibenzyl derivatives have been isolated from Dendrobium in previous studies. Secondary metabolites produced by species of the Australasian clade have not been studied well, even though several species of this group have also been used as traditional herbal remedies. The authors provide an overview of secondary metabolites of Dendrobium by combined non-target metabolomics and multivariate analysis, and identified characteristic compounds from several closely related Australasian species.
-
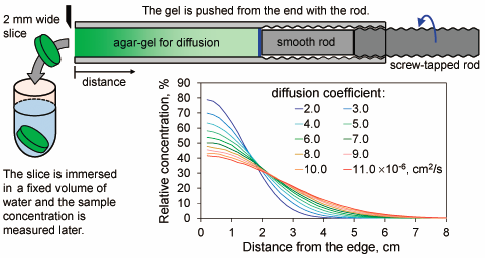
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 6 Pages 632-636Estimating the Diffusion Coefficients of Sugars Using Diffusion Experiments in Agar-Gel and Computer Simulations Read moreEditor's pick
This article describes the estimation of the diffusion coefficients of sugars and a related compound. A simple and handy experimental system with agar-gel was built and used to observe diffusion of small molecules. The correlation formulas derived from computer simulations of the experimental diffusion system were then applied to estimate diffusion coefficients. The values obtained for these coefficients agree reasonably well with those published in the literature. This finding supports the efficacy of the approach for estimating diffusion coefficients, leading to the elucidation of the diffusion coefficients of galactose, trehalose and glycerol.
-
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 6 Pages 624-631Stable and Selective Antiparallel Type Triplex DNA Formation by Targeting a GC Base Pair with the TFO Containing One N2-Phenyl-2′-deoxyguanosine Read moreEditor's pick
The antiparallel triplex DNA is formed by the interaction between purine-rich triplex forming oligonucleotides (TFOs) and the homo-purine region within a duplex DNA. The formation of such a structure with the genome DNA promises to control the gene expression in a living cell. In this paper, in an attempt to enhance the stability of the triplex DNAs, the authors have designed and synthesized the N2-arylated deoxyguanosine derivatives. The TFOs containing N2-phenyl-2′-deoxyguanosine (PhdG) showed a stable and selective triplex DNA formation with the GC base pair as compared to the natural dG/GC triplet.
-
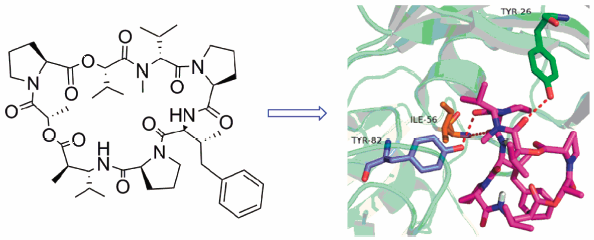
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 6 Pages 602-607Modeling Analysis of Potential Target of Dolastatin 16 by Computational Virtual Screening Read moreEditor's pick
Dolastatin 16 is a cyclic depsipeptide isolated from cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula, however, its bioactivity has been a historical question. In this study, FKBP1A was predicted as a potential target of dolastatin 16 via PharmMapper as well as verified using chemical-protein interactome (CPI) and molecular docking. The lowest binding energy of dolastatin 16-FKBP1A complex was -7.4 kcal/mol. The ligand dolastatin 16 formed three hydrogen bonds and seven hydrophobic interactions within the active site residues. And the pharmacophore model was shown feasibly matching with the molecular feature of dolastatin 16.
-
Editor's pick
Photographs of tropical and subtropical plants of Madagascar, Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia and Okinawa, Japan by courtesy of the authors. And some chemical structures of new compounds isolated from these plants are shown. Upper left: Macaranga tanarius and a prenylflavanone, Upper middle: Senna siamea, Upper right: Croton tonkinensis and an ent-Kaurane diterpene, Middle left: Rhinacanthus nasutus, Central middle: Baobab; Adansonia grandidieri, Middle right: Impatiens balsamina, Lower left: Artemisia roxburghiana and X-ray crystallography of a guaianolide, Lower middle: Justicia gendarusa, Lower right: Croton cascarilloides and a plausible biosynthetic pathway of new skeletons.
-
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 5 Pages 575-580Structural Development of Cell-Penetrating Peptides Containing Cationic Proline Derivatives Read moreEditor's pick
The authors designed and synthesized a series of cell-penetrating peptides containing cationic proline derivatives (ProGu) that exhibited responsive changes in their secondary structures to the cellular environment. Effects of the peptide length and steric arrangement of the side chain in cationic proline derivatives [Pro4SGu and Pro4RGu] on their secondary structures and cell membrane permeability were investigated. Moreover, peptides 3 and 8 exhibited efficient intracellular delivery of plasmid DNA. These results indicate that the peptides containing cationic proline derivatives could be a useful tool to deliver the hydrophilic biomolecules into the cells.
-
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 5 Pages 562-567Palladium-Catalyzed External-CO-Free Carbonylation of Aryl Bromides Using 2,4,6-Trichlorophenyl Formate Read moreEditor's pick
A practical Pd-catalyzed carbonylation of (hetero)aryl bromides using a crystalline carbon monoxide (CO) surrogate, 2,4,6-trichlorophenyl formate (TCPF), was developed. This reaction proceeds without the slow addition technique that was previously required and with a low catalyst loading (1 mol%) on a gram scale. The utility of this Pd-catalyzed external-CO-free carbonylation using TCPF was demonstrated in the synthesis of a histone deacetylase inhibitor.
-
Volume 66 (2018) Issue 5 Pages 548-553Scale-Up of Lubricant Mixing Process by Using V-Type Blender Based on Discrete Element Method Read moreEditor's pick
In this study, scale-up experiments of the lubricant mixing processes were conducted for V-type blenders under the same condition of fill level and Froude number. Three scales of V-type blender were used for the scale-up experiment. However, the physical properties of them were not corresponded either mixing time or number of revolution. Thus, the DEM simulations of three scales of V-type blender mixing were conducted to find the scale-up factor. As a result, it was found that a scale-up simulation based on the travel distance of particles is valid for lubricant mixing scale-up processes.