
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Ken-ichi Kusakabe2024 Volume 72 Issue 7 Pages 600-601
Published: July 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDownload PDF (204K) Full view HTML
-
Naoyuki Suzuki, Takuya Hatta, Mana Ito, Ken-ichi Kusakabe2024 Volume 72 Issue 7 Pages 602-609
Published: July 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAmyloid-β (Aβ) plaques and neurofibrillary tangles containing phosphorylated tau protein are major hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Drug discovery efforts to target Aβ and tau have been the primary focus for several decades. Recently, substantial breakthroughs have been achieved in the clinical development of Aβ antibodies; aducanumab was approved under conditional accelerated pathway by Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the U.S. as the first disease-modifying agent for treating AD, and lecanemab has been granted traditional full approved in the U.S. and Japan. In addition, donanemab met the primary endpoint in a phase 3 study. On the other hand, tau-targeting therapies have failed to show clinical benefit although that increased tau levels show a strong correlation with cognitive impairment relative to Aβ depositions. Currently, tau immunotherapies, such as anti-tau antibodies and tau vaccines, have shown functional benefits in clinical trials. Also, clinical trials for combination therapy of Aβ and tau antibodies to see their potential are being investigated. In this review, we provide updates on the results of clinical trials of anti-Aβ antibodies and anti-tau therapeutics and suggest future directions for these therapeutics.
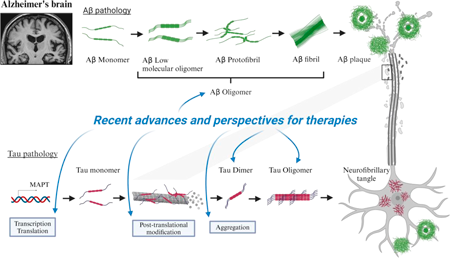 View full abstractDownload PDF (1039K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1039K) Full view HTML -
Takuya Oguma, Kohei Jino2024 Volume 72 Issue 7 Pages 610-617
Published: July 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAgitation and psychosis are key behavioral and psychological symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). For family and caregivers of patients, such symptoms are critical factors of distress and increased burden, but medication to treat them is limited. In most cases, drugs for other neuropsychiatric diseases have been used to manage these symptoms in an off-label manner. Due to the complex pathological background of AD and limited clinical data, obtaining proof of concept for the treatment of these symptoms is challenging. However, in 2023, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved brexpiprazole as the first and only drug to treat agitation in AD. Several other compounds have been evaluated in clinical situations. This review highlights recent pipelines being developed for agitation and psychosis for patients living with AD.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (522K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (522K) Full view HTML -
Takuya Yamane, Takeshi Yoshioka, Yusuke Shimo2024 Volume 72 Issue 7 Pages 618-629
Published: July 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAlzheimer’s disease (AD) is a common form of dementia. Although the causal mechanisms of AD are not fully understood, intracerebral accumulation of amyloid beta (Aβ) and tau aggregates seems to play an important role in disease development. Therefore, numerous experimental and clinical studies targeting the Aβ and tau proteins have been performed. However, these treatments have not achieved good clinical results. Additionally, recent findings have indicated that immune abnormalities contribute to the pathogenesis of AD. Several immune- and microglia-related genes have been identified as putative causative genes for the disease. Microglia, which are resident immune cells in the central nervous system (CNS), are key players that maintain brain homeostasis by communicating with other cells, such as astrocytes and immune cells, in or around the CNS. Furthermore, dysfunction of microglia and the immune system of the CNS could lead to chronic neuroinflammation and impairment of protective neuroimmune responses, which have been associated with the pathogenesis of AD and other forms of dementia. In this review, we assemble information regarding genetic evidence, imaging and biofluid biomarkers, and the pathophysiology of AD, especially highlighting bilateral (protective or detrimental) microglial functions, thus connecting neuroimmune dysfunction and AD. We also introduce candidate drugs to target neuroimmune dysfunction in AD. Finally, we discuss future therapeutic precision medicine approaches for AD, which could be achieved by identifying and targeting signals critical for AD pathogenesis through analyses of interactions between genetic risk factors, as well as identifying and modulating disease-relevant immune cell populations.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (854K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (854K) Full view HTML -
Yasunobu Yamashita, Yukihiro Itoh, Yuri Takada, Takayoshi Suzuki2024 Volume 72 Issue 7 Pages 630-637
Published: July 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAlzheimer’s disease (AD) is the leading cause of senile dementia, and the rapid increase in the frequency of AD cases has been attributed to population aging. However, current drugs have difficulty adequately suppressing symptoms and there is still a medical need for symptomatic agents. On the other hand, it has recently become clear that epigenetic dysfunctions are deeply involved in the development of cognitive impairments. Therefore, epigenetics-related proteins have attracted much attention as drug targets for AD. Early-developed epigenetic inhibitors were inappropriate for AD treatment because of their limited potential for oral administration, blood-brain barrier penetration, high target selectivity, and sufficient dose-limiting toxicity which are essential properties for small molecule drugs targeting chronic neurodegenerative diseases such as AD. In recent years, drug discovery studies have been actively performed to overcome such problems and several novel inhibitors targeting the epigenetics-related proteins are of interest as promising AD therapeutic agents. Here, we review the small molecule inhibitors of histone deacetylase (HDAC), lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) or bromodomains and extra-terminal domain (BET) protein, that enable memory function improvement in AD model mice.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (935K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (935K) Full view HTML
-
Tetsuya Iida, Yukihiro Itoh, Yukari Takahashi, Yuka Miyake, Farzad Zam ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 7 Pages 638-647
Published: July 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialLysine demethylase 5 (KDM5) proteins are involved in various neurological disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, and KDM5 inhibition is expected to be a therapeutic strategy for these diseases. However, the pharmacological effects of conventional KDM5 inhibitors are insufficient, as they only target the catalytic functionality of KDM5. To identify compounds that exhibit more potent pharmacological activity, we focused on proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs), which degrade target proteins and thus inhibit their entire functionality. We designed and synthesized novel KDM5 PROTAC candidates based on previously identified KDM5 inhibitors. The results of cellular assays revealed that two compounds, 20b and 23b, exhibited significant neurite outgrowth-promoting activity through the degradation of KDM5A in neuroblastoma neuro 2a cells. These results suggest that KDM5 PROTACs are promising drug candidates for the treatment of neurological disorders.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1260K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1260K) Full view HTML
-
Takashi Kamei, Jun Miyazaki, Ryoga Hori, Hiroaki Saito, Tatsuo Takahas ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 7 Pages 648-657
Published: July 06, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 06, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialButin and butein are significant bioactive flavanones derived from plants, existing as tautomers of each other. However, their physicochemical attributes, such as their spectral profiles under varying experimental conditions in aqueous solutions and established chromatographic methods for distinguishing between them, remain undetermined. In this study, we determined the basic properties of butin and butein using conventional spectroscopic, reversed-phase, and chiral HPLC analyses. The spectra of the synthesized butin and butein were analyzed using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer in several solvents with different polarities as well as in aqueous solutions at various pH values. Furthermore, the behavior of the measured spectra was reproduced by calculations to reveal the effects of the solvent and pH on the spectra of butin and butein in organic and aqueous solutions. Subsequently, we assessed the structural stability of butin and butein using reversed-phase HPLC, which revealed that butein is unstable compared with butin in a general culture medium. The synthesized butin was effectively separated into R- and S-isomers with positive and negative Cotton effects, respectively, via HPLC using a chiral column. These findings will aid in uncovering the individual properties of both butin and butein that may have been concealed by their tautomerism and enable the synthesis of S-butin, which is typically challenging and time-consuming to isolate.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1042K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1042K) Full view HTML -
Genichiro Tsuji, Takashi Misawa, Yosuke Demizu2024 Volume 72 Issue 7 Pages 658-663
Published: July 11, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 11, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn recent years, there has been a growing focus on the development of medium-sized drugs based on peptides or nucleic acids owing to their potential therapeutic benefits. As some of these medium-sized drugs exert their therapeutic effects by adopting specific secondary structures, evaluating their conformational states is crucial to ensure the efficacy, quality, and safety of the drug products. It is important to assess the structural integrity of biomolecular therapeutics to guarantee their intended pharmacological activity and maintain the required standards for drug development and manufacturing. One widely utilized technique for quality evaluation is secondary structural analysis using circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. Given the higher production and quality control costs associated with medium-sized drugs compared with small-molecule drugs, developing analytical techniques that enable CD analysis with reduced sample volumes is highly desirable. Herein, we focused on a microsampling disk-type cell as a potential solution for reducing the required sample volume. We investigated whether CD spectral analysis using a microsampling disk could provide equivalent spectra compared with the standard cell (sample volume: approx. 300 µL). Our findings demonstrated that the microsampling disk (sample volume: 2–10 µL) could be successfully applied to CD spectral analysis of peptide and nucleic acid drugs, paving the way for more efficient and cost-effective quality evaluation processes.
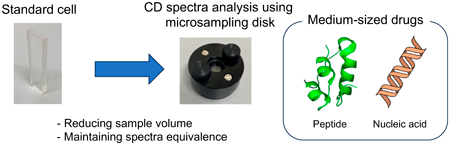 View full abstractDownload PDF (2338K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2338K) Full view HTML
-
Naohiro Oshima, Maiko Tahara, Tsuyoshi Kawakami, Akiko Yagami, Takumi ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 7 Pages 664-668
Published: July 11, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 11, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialHenna is a plant-based dye obtained from the powdered leaf of the pigmented plant Lawsonia inermis, and has often been used for grey hair dyeing, treatment, and body painting. As a henna product, the leaves of Indigofera tinctoria and Cassia auriculata can be blended to produce different colour variations. Although allergy from henna products attributed to p-phenylenediamine, which is added to enhance the dye, is reported occasionally, raw material plants of henna products could also contribute to the allergy. In this study, we reported that raw material plants of commercial henna products distributed in Japan can be estimated by LC-high resolution MS (LC-HRMS) and multivariate analysis. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) score plot clearly separated 17 samples into three groups [I; henna, II; blended henna primarily comprising Indigofera tinctoria, III; Cassia auriculata]. This grouping was consistent with the ingredient lists of products except that one sample listed as henna was classified as Group III, indicating that its ingredient label may differ from the actual formulation. The ingredients characteristic to Groups I, II, and III by PCA were lawsone (1), indirubin (2), and rutin (3), respectively, which were reported to be contained in each plant as ingredients. Therefore, henna products can be considered to have been manufactured from these plants. This study is the first to estimate raw material plants used in commercial plant-based dye by LC-HRMS and multivariate analysis.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (836K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (836K) Full view HTML
-
Xiongwei Deng, Qiang Li, Haitao Yuan, Hejun Hu, Shaoyong Fan2024 Volume 72 Issue 7 Pages 669-675
Published: July 13, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 13, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTendon injury is a prevalent orthopedic disease that currently lacks effective treatment. Galangin (GLN) is a vital flavonoid found abundantly in galangal and is known for its natural activity. This study aimed to investigate the GLN-mediated molecular mechanism of tendon-derived stem cells (TDSCs) in tendon repair. The TDSCs were characterized using alkaline phosphatase staining, alizarin red S staining, oil red O staining, and flow cytometry. The effect of GLN treatment on collagen deposition was evaluated using Sirius red staining and quantitative (q)PCR, while a Western bot was used to assess protein levels and analyze pathways. Results showed that GLN treatment not only increased the collagen deposition but also elevated the mRNA expression and protein levels of multiple tendon markers like collagen type I alpha 1 (COL1A1), decorin (DCN) and tenomodulin (TNMD) in TDSCs. Moreover, GLN was also found to upregulate the protein levels of transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) and p-Smad3 to activate the TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway, while GLN mediated collagen deposition in TDSCs was reversed by LY3200882, a TGF-β receptor inhibitor. The study concluded that GLN-mediated TDSCs enhanced tendon repair by activating the TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway, suggesting a novel therapeutic option in treating tendon repair.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (4483K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (4483K) Full view HTML
-
Takashi Ono, Kotaro Okada, Misaki Kaga, Hidekatsu Eto, Shungo Kumada, ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 7 Pages 676-680
Published: July 17, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 17, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe purpose of this study was to continuously monitor the pseudopolymorphic transition from anhydrate to monohydrate by measuring the NMR relaxation using time-domain NMR (TD-NMR). Taking advantage of the simplicity of the low-field NMR instrument configuration, which is an advantage of TD-NMR, the NMR instrument was connected to a humidity controller to monitor the pseudopolymorphic transition. First, ezetimibe (EZT) monohydrate was prepared from its anhydrate using a saturated salt solution method, and T1 relaxation of EZT monohydrate and anhydrate was measured without a humidity controller. The T1 relaxation results confirmed that EZT anhydrate and monohydrate could be distinguished using T1 relaxation measurement. Next, continuous monitoring was conducted by TD-NMR and connected to a humidity controller. Anhydrous EZT was placed in an NMR glass tube and the T1 relaxation measurement was repeated while maintaining the humidity on the side entering the NMR tube at 80% relative humidity. The T1 relaxation became gradually faster from the initial to middle monitoring phases. The final T1 relaxation was then recovered fully and these T1 relaxation times were the same as the T1 relaxation of EZT monohydrate. This study successfully monitored the pseudopolymorphic transition from EZT anhydrate to monohydrate via NMR relaxation.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (864K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (864K) Full view HTML
-
Tianao Zhang, Min Yu, Yong Fan, Lingyang Wang, Lu Yuan, Yong Sun2024 Volume 72 Issue 7 Pages 681-688
Published: July 17, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 17, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialClarithromycin (CLA) is the preferred drug for treating respiratory infections in pediatric patients, but it has the drawbacks of extreme bitterness and poor water solubility. The purpose of this study was to improve solubility and mask the extreme bitterness of CLA. We use Hot Melt Extrusion (HME) to convert CLA and Eudragit® E100 into Solid Dispersion (SD). Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and Powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) were used to identify the crystalline form of the prepared SDs, which showed that the crystalline CLA was converted to an amorphous form. At the same time, an increase in dissolution rate was observed, which is one of the properties of SD. The results showed that the prepared SD significantly increased the dissolution rate of crystalline CLA. Subsequently, the SD of CLA was prepared into a dry suspension with excellent suspending properties and a taste-masking effect. The bitterness bubble chart and taste radar chart showed that the SD achieved the bitter taste masking of CLA. Principal components analysis (PCA) of the data generated by the electronic tongue showed that the bitter taste of CLA was significantly suppressed using the polymer Eudragit® E100. Subsequently, a dry suspension was prepared from the SD of CLA. In conclusion, this work illustrated the importance of HME for preparing amorphous SD of CLA, which can solve the problems of bitterness-masking and poor solubility. It is also significant for the development of compliant pediatric formulations.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (4992K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (4992K) Full view HTML
-
Koichiro Ota, Naoya Kashima, Haruhiko Fukaya, Shinnosuke Okazaki, Hiro ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 7 Pages 689-692
Published: July 23, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 23, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialHere, we report the first synthesis of oxyphyllin A/belchinoid A, a 7,9-seco-8,12-dinor-guaiane sesquiterpene whose isolation was reported independently by two groups in 2023. This synthesis utilizes a key sequential sulfone-mediated intermolecular alkylation/5-endo-tet cyclization reaction to establish the C1, C4, C5 stereocenters. Subsequent transformations, including regio- and stereoselective hydride addition-based desulfonylation via a π–allyl palladium complex and the Wittig reaction with a stable phosphonium ylide, facilitated the synthesis of oxyphyllin A/belchinoid A.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (813K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (813K) Full view HTML
-
Mitsuaki Yamashita, Akari Nakanishi, Chiehming Chang, Kosei Tsurushima ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 7 Pages 693-699
Published: July 23, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 23, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThis study evaluated the ability of isolated or semisynthesized trichothecene sesquiterpenes to prevent cancer emergence and proliferation and inhibit signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) phosphorylation through in vitro assays. Trichothecinol A (TTC-A), which bears a hydroxy group at C3, exhibited greater cancer prevention, antiproliferation, and STAT3 phosphorylation inhibition effects than trichothecin (TTC), which lacks a hydroxy group at C3. Furthermore, trichothecinol B (TTC-B), which is a reduced derivative of TTC and has similar cytotoxic effect, showed substantially weaker chemoprotection and STAT3 phosphorylation inhibition effects than TTC. These results clearly indicate that the hydroxy group at C3 and carbonyl group at C8 are crucial for inducing both potent chemoprevention and STAT3 phosphorylation inhibition.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (784K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (784K) Full view HTML -
Yumi Sekigawa, Shinichi Asada, Yurie Ichikawa, Kazuaki Tsubokawa, Shoh ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 7 Pages 700-710
Published: July 26, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: July 26, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialWe report two methods for the preparation of peptide thioesters containing Tyr(SO3H) residue(s), without use of a protecting group for the sulfate moiety. The first was based on direct thioesterification using carbodiimide on a fully protected peptide acid, prepared on a 2-chlorotrityl (Clt) resin with fluoren-9-ylmethoxycarbonyl (Fmoc)-based solid-phase peptide synthesis (Fmoc-SPPS). Subsequent deprotection of the protecting groups with trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) (0 °C, 4 h) yielded peptide thioesters containing Tyr(SO3H) residue(s). Peptide thioesters containing one to three Tyr(SO3H) residue(s), prepared by this method, were used as building blocks for the synthesis of the Nα-Fmoc-protected N-terminal part of P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 (PSGL-1) (Fmoc-PSGL-1(43–74)) via silver-ion mediated thioester segment condensation. The other method was based on the thioesterification of peptide azide, derived from a peptide hydrazide prepared on a NH2NH-Clt-resin with Fmoc-SPPS. Peptide thioester containing two Tyr(SO3H) residues, prepared via this alternative method, was used as a building block for the one-pot synthesis of the N-terminal extracellular portion of CC-chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5(9–26)) by native chemical ligation (NCL). The two methods for the preparation of peptide thioesters containing Tyr(SO3H) residue(s) described herein are applicable to the synthesis of various types of sulfopeptides.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (954K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (954K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|