-
編集者のコメント
In contrast to many successful cases of lipase-catalyzed dynamic kinetic resolution (DKR) of racemic secondary alcohols, only one successful DKR of a tertiary alcohol has been reported, and the reaction required 13 days. The challenges stem from low reactivity of lipase toward bulky tertiary alcohols and activity loss of lipase and racemization catalyst V-MPS4 over time. This paper addressed these issues by combining two approaches: creating a double mutant of Candida antarctica lipase A to improve its catalytic activity and using a hydrophobic polydimethylsiloxane thimble to separate the reaction sites of lipase and V-MPS4 in one flask.
-
編集者のコメント
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
Nitric oxide (NO) plays key roles in vasodilation as an endogenous signaling mediator, and photocontrollable NO-releasing compounds are expected to serve as novel phototherapeutic agents. This study explores structural modifications of PeT-driven NO releasers, focusing on the linker region between the light-harvesting antenna and the NO-releasing moiety. The authors demonstrate that while most substituents minimally affect NO release and vasodilation, dialkylamino groups impart pH-responsive behavior. These findings provide valuable insights into the design of next-generation NO releasers with enhanced spatiotemporal and stimulus-specific control. -
編集者のコメント
Resin glycosides, characteristic constituents of plants in the Convolvulaceae family, are well-known purgative components present in traditional medicinal crude drugs such as Pharbitidis Semen, Mexican Scammoniae Radix, Orizabae Tuber, and Jalapae Tuber. In addition to their purgative effects, many resin glycosides exhibit diverse biological activities. In this study, the authors analyzed the crude resin glycoside fraction from the leaves and stems of Ipomoea lacunosa L., identifying organic acids, monosaccharides, hydroxy fatty acids, and glycosidic acids, including a newly identified glycosidic acid. They report the isolation and structural elucidation of eight new and two known resin glycosides. Of the nine compounds evaluated for cytotoxicity against HL-60 human promyelocytic leukemia cells, four showed moderate activity.
-
編集者のコメント
This study introduces a dynamic dialysis method that integrates a parsimonious kinetic model to assess ammonia-driven doxorubicin release from clinically approved liposomal formulations. By enabling real-time release profiling without requiring liposome separation and strict sink conditions, the approach simplifies experimental design while capturing essential kinetics. The model successfully condenses drug partitioning behavior into a single permeability parameter and demonstrates broad applicability to both brand and generic liposomal drugs. These findings support the hypothesized tumor microenvironment mechanism and provide a practical framework for evaluating and optimizing drug release from nanoparticle-based formulations.
-
73 巻 (2025) 6 号 p. 568-573Photo-Enhanced Aqueous Solubilization of Azobenzene-Incorporated Lipids もっと読む編集者のコメント
Lipid hydrophobicity poses significant challenges for formulation and administration in pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. This study by Tomoshige et al. addresses this by demonstrating a novel photo-enhanced aqueous solubilization strategy for azobenzene-incorporated lipids. The synthesized azo-lipids exhibited reversible photoisomerization, leading to enhanced solubility upon UV irradiation. Notably, azobenzene-incorporated phosphatidylcholine analog showed a remarkable 496-fold increase in solubilization after UV irradiation. This improvement is attributed to efficient photoisomerization and molecular bending, which reduces intermolecular interactions. These findings offer a valuable approach for improving the handling and potential therapeutic administration of lipid-based compounds.
-
編集者のコメント
This study investigates the relationship between the chemical stability of itraconazole (ITZ) adsorbed on silica and its NMR relaxation. The authors applied time domain NMR to measure the NMR relaxation of hydrogen nuclei in ITZ before storage, excluding silica signals. Since NMR relaxation reflects molecular mobility, the measurement provides insight into the dynamic state of the adsorbed drug. ITZ was adsorbed onto silica powder. A positive correlation was found between the relaxation rate and the amount of degradant after storage, especially for Aerosil 200, suggesting its potential as a predictor of chemical stability.
-
73 巻 (2025) 5 号 p. 449-456Selection of Short 5′-UTR of Chemically Synthesized mRNA to Improve Translation Efficiency もっと読む編集者のコメント
mRNA is a promising platform for therapies such as cancer vaccines and protein replacement, with chemically synthesized mRNA offering added advantages. However, its short length poses sequence design challenges. This study achieved the successful adaptation of ribosome and polysome profiling methods, commonly used for long mRNAs, to optimize untranslated regions in short chemically synthesized mRNAs. The authors identified novel 9-nucleotide 5’-UTR sequences that enhance translation efficiency compared to conventional Kozak sequence. These findings offer a practical framework for enhancing chemically synthesized mRNA design and expand its potential in next-generation therapeutic applications.
-
編集者のコメント
The addition of cellulose nanofiber (CNF) to mini-tablet (MT) formulations during direct compression has attracted increasing attention as a means to achieve both MT strength and disintegration. However, the large variation in the weight and drug content of the resulting MT remained a challenge. Therefore, this study analyzed the physical properties of CNF-containing MT of different particle sizes and evaluated the effect of the particle size on MT manufacturing. Thus, using smaller CNF particle sizes enabled the manufacturing of an orally disintegrating MT with adequate hardness and disintegration properties while also minimizing variations in MT weight and drug content.
-
73 巻 (2025) 5 号 p. 478-483Teleocidin Analogs Isolated from Streptomyces eurocidicus as Membrane-Vesicle-Regulated Natural Products もっと読む編集者のコメント
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
This study presents an innovative approach to natural product discovery by using bacterial membrane vesicles (MVs) to activate silent biosynthetic gene clusters. By applying MVs derived from Burkholderia multivorans to Streptomyces eurocidicus, the authors isolated five teleocidin analogs, including two novel congeners. Notably, this study reveals a two-step regulatory role of MVs in teleocidin biosynthesis: enhancing core metabolite production while suppressing downstream acetylation. The work offers a powerful framework for unlocking silent metabolites and offers new insights into the biosynthetic regulation and structural diversity of teleocidin analogs. -
編集者のコメント
Neurotoxic steroidal alkaloid veratridine is structurally characterized by its highly functionalized hexacyclic structure and serves as a formidable synthetic challenge. In this manuscript, the authors describe the synthesis of the 6/6/5-membered ABC-ring system of veratridine. Starting from 1,5-pentanediol, the AB-ring was constructed by the intramolecular Diels-Alder reaction based on the literature method. After the dihydroxylation of the C3-C4 double bond on the AB-ring and site-selective acylation of the C3-hydroxy group, the C-ring was formed through the C8-vinylation, chemo and stereoselective (allyl)2Zn-mediated C9-allylation, and ring-closing metathesis. The ABC-ring system would play a key intermediate in further synthetic studies of veratridine.
-
編集者のコメント
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
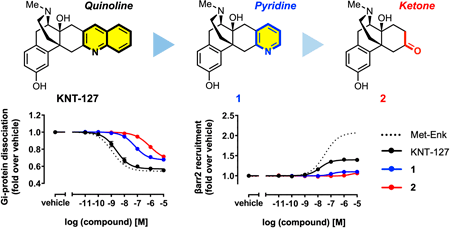
The δ-opioid receptor (DOR) has emerged as a promising target for treating chronic pain and stress-related disorders. This study investigates the structure–signal relationship of KNT-127 derivatives bearing systematic modifications to the quinoline moiety. Functional assays, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulations reveal that specific substituents on the quinoline ring, which is fused to the morphinan scaffold, attenuate β-arrestin recruitment and modulate signaling bias. These findings provide structural insights into DOR ligand bias and expand the message–address concept, to guide the rational development of safer, functionally selective DOR agonists. -
73 巻 (2025) 4 号 p. 355-368Design, Synthesis, and Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activity of Amodiaquine Analogs もっと読む編集者のコメント
The pandemic of COVID-19 caused by the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 remains a serious global concern. In this paper, we present new anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs based on the chemical structure of amodiaquine, which is known as an antimalarial drug. Some amodiaquine analogues functionalized with dialkylamino-pendant aminophenol moieties have been identified as having effective anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity and low toxicity. These drugs could be useful for designing and synthesizing low-molecular-weight antiviral agents to fight against not only SARS-CoV-2 but also other viral infections.
-
編集者のコメント
4ʹ-Modified nucleosides have been used as antiviral drugs and raw materials to produce oligonucleotide therapeutics. Thus, a new synthetic method for the 4ʹ-modified nucleosides is significant. In this manuscript, the authors reported a concise approach to prepare 4ʹ-modified thymidines from oxime imidates of thymidine. This strategy involves the generation of 4ʹ-carbon radicals via 1,5-hydrogen atom transfer (1,5-HAT) of iminyl radicals, the intermolecular 1,4-addition to electron-deficient olefines, and the hydrolysis of the imidate intermediates under acidic conditions. Moreover, using basic hydrolysis instead of acidic one allowed to isolate a 4ʹ-modified thymidine in a diastereoselective form.
-
編集者のコメント
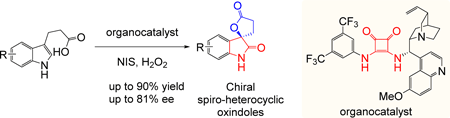
The disubstituted oxindoles comprising spiro-fused oxindoles have garnered significant attention as privileged scaffolds found in natural products, and pharmaceuticals. The authors demonstrated the first study accomplishing stereoselective oxidative cyclization from indole propionic acids using a squaramide organocatalyst, N-iodosuccinimide, and hydrogen peroxide under metal-free and mild reaction conditions. The asymmetric oxidative lactonization afforded the spiro-fused 2-oxindoles in moderate-to-good yields and enantioselectivities (up to 90% yield, 81% ee). The resulting spiro-fused 2-oxindoles offer a valuable pathway for the synthesis of natural products and medicinal compounds.
-
73 巻 (2025) 4 号 p. 412-418Development of Fluorescent Estrogen Receptor Ligands with pH Sensor Functionality もっと読む編集者のコメント
Estrogen receptors (ERs) and their ligands regulate a variety of physiological processes, and altered ER signaling is associated with serious disorders. Estrogens also binds to other receptors, and so fluorescent estrogen ligands would be useful for various functional studies and for development of drug candidates. In this manuscript, the authors describe fluorescent estrogen receptor ligands, and they also function as pH-dependent OFF-ON-OFF type fluorescent sensors, enabling the detection of specific ranges of pH. This pH-dependent fluorescence would be potentially useful for visualization of the ligand-bound receptor, and microenvironmental changes around the receptor protein could potentially be visualized; for example, during endocytosis, the pH is gradually changes.
-
73 巻 (2025) 3 号 p. 213-226Evaluation of Time-Dependent Deformation Behavior of Pharmaceutical Excipients in the Tableting Process もっと読む編集者のコメント
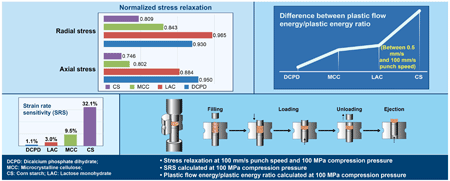
In this manuscript, the authors investigate the time-dependent deformation behavior of powdered or granular materials during tableting using a compaction simulator. Four pharmaceutical excipients with different compression characteristics were analyzed using a trapezoidal punch displacement profile, where only the punch speed during loading was varied. By evaluating strain rate sensitivity, mechanical energy, and stress relaxation, differences in deformation behavior between the materials were identified. The results suggest that an accurate understanding of the time-dependent deformation characteristics of raw materials is important to support appropriate scale-up of the tableting process.
-
編集者のコメント
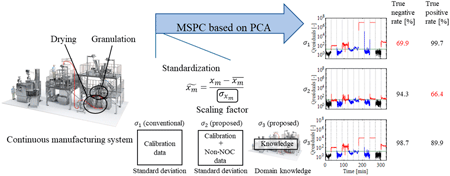
Multivariate statistical process control (MSPC) has attracted considerable attention as a monitoring method for pharmaceutical continuous manufacturing. However, there are few examples of its application in pharmaceutical manufacturing, and previous studies have shown high false positive rates. In this study, the authors proposed a method to improve the accuracy of anomaly detection using MSPC by determining the appropriate scaling factor used for standardization and applied it to the granulation and drying processes in pharmaceutical continuous manufacturing. The proposed method reduces the false positive rate compared to conventional methods and can detect changes in process parameters and raw materials.
-
編集者のコメント
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
The δ-opioid receptor (DOR) is a promising therapeutic target with reduced side effects compared to μ-opioid receptor agonists. However, some DOR agonists, such as SNC80, have been reported to induce convulsions, potentially involving β-arrestin signaling. This study investigates the first structure–signal relationship of KNT-127, a morphinan-based DOR agonist, and demonstrates that the morphinan skeleton reduces β-arrestin recruitment, while the quinoline moiety modulates the bias between G protein and β-arrestin pathways. These findings expand the classical message–address concept and offer valuable insights into the rational design of functionally selective DOR agonists with improved safety profiles. -
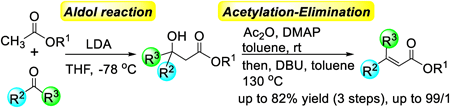
73 巻 (2025) 3 号 p. 264-267Concise and Highly Stereoselective Synthesis of β,β-Disubstituted α,β-Unsaturated Esters もっと読む編集者のコメント
β,β-Disubstituted α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds, which are characterized by two distinct substituents at the β-position, are found in various bioactive molecules. In this paper, the authors report a concise and highly stereoselective synthesis method for β,β-disubstituted α,β-unsaturated esters. This synthesis method comprises three well-known reactions: the aldol reaction of acetic ester derivatives with ketones, the acetylation of tert-alcohols, and an elimination reaction utilizing DBU. Two important findings, i.e., that the acetylation of bulky tert-alcohol proceeded efficiently using Ac2O and DMAP without DBU as a base, and that the formation of isomerized byproducts in the elimination reaction was suppressed by removing excess DMAP, enabled the synthesis of various β,β-disubstituted α,β-unsaturated esters.
-
編集者のコメント
The alnumycin-class antibiotics constitute a polyketide-derived benzoisochromanequinone core hybridized with a structurally rearranged D-ribose. In this article, the authors reported the stereoselective synthesis and absolute configuration of prealnumycin, the aglycon of alnumycin. The key transformation involves the highly diastereoselective introduction of an n-propyl group onto a tricyclic lactone via nucleophilic addition, followed by silane reduction. Subsequent regioselective arene oxidation to naphthoquinone, acidic deprotection, and dehydration afford prealnumycin in eight steps. The findings from this synthesis provide insights into the total synthesis of this class of natural products.