-
Munkhjargal Dorjravdan, Katsuyasu Kouda, Tsolmon Boldoo, Naranzul Damb ...
原稿種別: Correction
2022 年 27 巻 p.
50
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/12/21
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
-
Yang Pu, Yinshuang Tang, Qiuling Shi, Hong Wang
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
49
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/12/17
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: To determine the relationship between pubertal timing and quality of life (QOL) in children and adolescents and to provide a basis for QOL intervention in pubertal children in the future to promote good adaptation and healthy physical and mental development of children.
Methods: The survey was conducted in one county using a stratified cluster sampling method. The five physiological change items of the Puberty Development Scale (PDS) were used to assess the timing of puberty in students. Compared to students of the same age and the same sex, students who scored higher than the mean + standard deviation (SD) of individual developmental scores were defined as an early pubertal timing group. A 39-item QOL Scale for Children in Puberty was used to assess the QOL of the respondents. Multiple linear regression models were fitted separately for boys and girls.
Results: Of the 7223 students, 3754 (51.97%) were boys and 3469 (48.03%) were girls. The prevalence of early pubertal periods was 16.07%. The total QOL score in the early pubertal timing group (137.16 ± 18.67) was significantly lower than in the normal (on time) group (142.02 ± 17.98) and the late group (142.76 ± 18.35) (F = 37.311, P < 0.001). A multiple linear regression model showed that early pubertal timing was a risk factor for QOL (P < 0.0014), compared with normal and late pubertal timing.
Conclusions: The early pubertal timing was associated with poorer QOL in children and adolescents. More attention should be paid to children with early pubertal timing in intervening children’s QOL during pubertal development. Future longitudinal studies are needed to confirm the association between pubertal timing and QOL.
抄録全体を表示
-
Xuefeng Lai, Jian Sun, Bingjie He, Daowei Li, Shengfeng Wang, Siyan Zh ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
48
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/12/16
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: Studies observing the relationship between pulmonary function and the risk of cognitive impairment in middle-aged and older adults was increasing, but the results were inconsistent. To date, evidence from longitudinal data is scarce and further research is urgently needed.
Methods: We used data from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. Participants were enrolled in 2011/2013 and followed up in 2013, 2015 and 2018. Pulmonary function was assessed via peak expiratory flow (PEF). Cognitive function, measured by episodic memory and mental status, was assessed through a face-to-face interview in each survey.
Results: A total of 8,274 participants (52.86% males; mean age, 56.44 years) were included. The scores of global cognition (12.46 versus 11.51, P < 0.001) of men were significantly higher than women at baseline, with a total of 5096 participants (61.59%) declining during the follow-up. Higher baseline PEF was associated with lower absolute decline in global cognition (OR per 1-SD difference 0.921; P = 0.031) and mental status (OR per 1-SD difference 0.9889; P = 0.002) during follow-up in men, and significant associations between higher baseline PEF and a lower absolute decline in the episodic memory were both found in men (OR per 1-SD difference 0.907; P = 0.006) and women (OR per 1-SD difference 0.915; P = 0.022). Second analysis showed that the significant associations between positive PEF variation and a lower rate of 4-year decline in global cognition, mental status and episodic memory were all only found in men. In subgroup analyses, higher PEF at baseline was significantly associated with a lower absolute decline of global cognition among male individuals >60 years. Significant associations between higher PEF at baseline and lower absolute decline in global cognition and episodic memory during follow-up were only found in never-smokers, while higher PEF was related to lower absolute decline in mental status among non-smoking and smoking males.
Conclusions: Pulmonary function correlates with cognitive functions in middle-aged and older people, especially males. Additional studies characterizing early and long-term PEF changes are needed.
抄録全体を表示
-
Xinyi Deng, Zhiyi Chen, Yang Zou, Ying He, Saijuan Chen, Qiuting Wang, ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
47
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/12/15
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
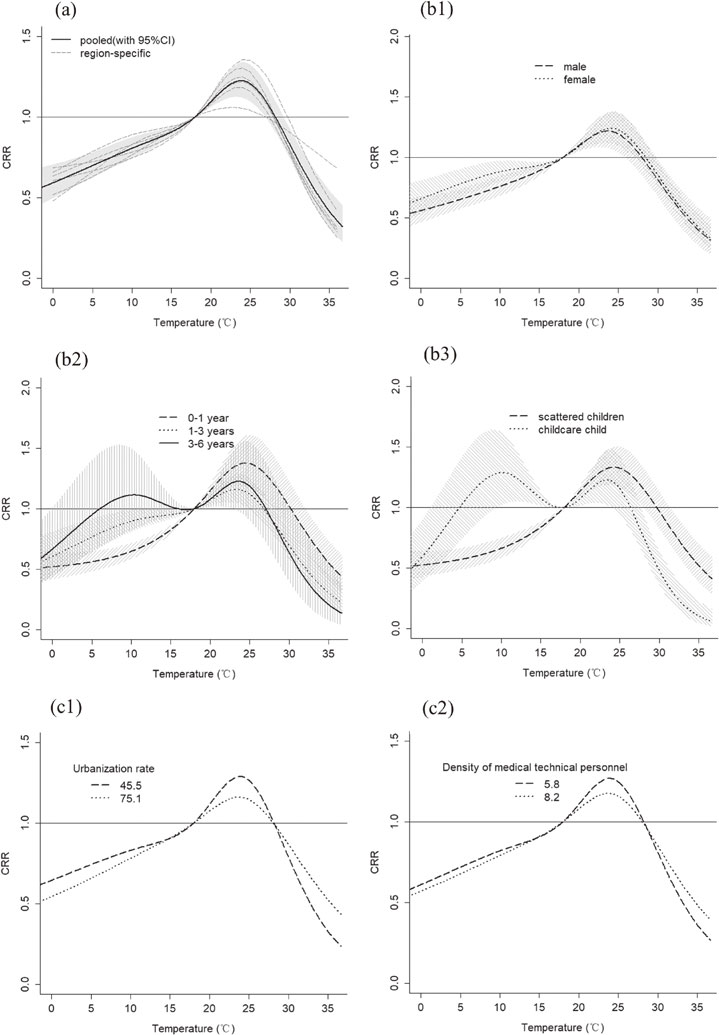
Background: Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) is a serious infectious disease which has become a public health problem. A multi-regional study was conducted in this study to explore the relationship between temperature and HFMD in different regions and the source of heterogeneity, and further detect the effect modifiers such as socio-economic factors, medical and health factors and meteorological factors.
Methods: The data on daily reported HFMD cases and meteorological data from 2010 to 2019 in Chongqing were collected. Thirty-eight districts and counties of Chongqing were divided into 6 regions. The distributed lag nonlinear model (DLNM) was applied to assess the effect of daily mean temperature on HFMD at region level with the pooled effect estimates from multivariate meta-regression model analysis. Stratified analyses by gender, age and children’s type were also conducted. Potential modifiers were considered in meta regression to explore the source of heterogeneity.
Results: There were nonlinear relationships with an inverted V-shape between temperature and HFMD. A maximum cumulative relative risk (CRR) of 1.22 (95% confidence interval (CI): 1.12–1.34) peaked at 23.8 °C, and the risk appeared immediately and lasted for the whole 14 days. Compared with other groups, warm temperature had a stronger effect on children aged 0–1 and scattered children, while cold temperature had a stronger effect on female, children aged 3–6 and childcare children with an M-shape. We found that socio-economic factors, medical health factors and meteorological factors were significantly associated with heterogeneity. Density of medical technical personnel, urbanization rate and density of health care institutions were the main modifiers for explaining heterogeneity of 26.10%, 24.90% and 24.86% respectively which were revealed by meta-analysis.
Conclusions: There was a significant nonlinear correlation between temperature and HFMD. Compared with other groups, children aged 0–1 and scattered children were more susceptible to warm temperature, while female, children aged 3–6 and childcare children were more susceptible to cold temperature. Socio-economic factors, medical health factors and meteorological factors may be the source of the heterogeneity. Therefore, local governments should consider different temperature–HFMD relationships between different regions and populations when formulating appropriate preventive measures.
抄録全体を表示
-
Midori Takada, Takahiro Tabuchi, Hiroyasu Iso
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
46
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/12/03
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
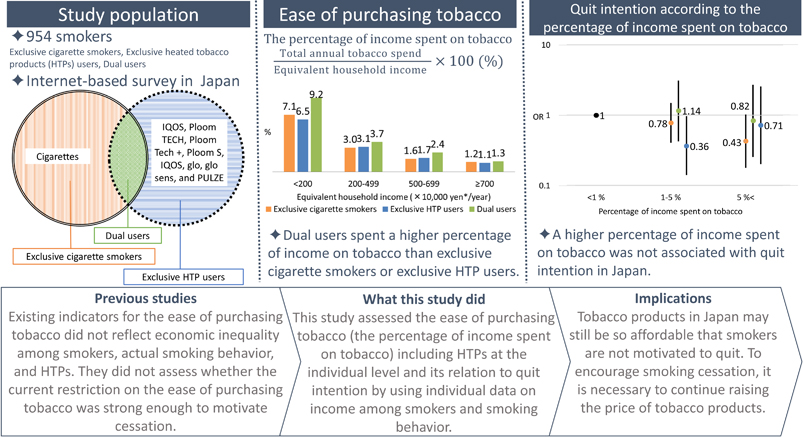
Background: Existing indicators for the ease of purchasing tobacco did not reflect the actual amount smoked and individual income, and did not assess heated tobacco products (HTPs). This study assessed the percentage of income spent on tobacco, including combustible cigarettes and/or HTPs, at the individual level and its relation to quit intention.
Methods: An internet-based self-reported questionnaire survey was conducted in 2020 as a part of the Japan Society and New Tobacco Internet Survey. A total of 954 smokers aged 15–72 years were analyzed. We calculated the percentage of income spent on tobacco according to income levels. A high percentage implies that tobacco is not easy to purchase. The odds ratios for quit intention according to three categories of percentage of income spent on tobacco (<1%, 1–5%, >5%) were calculated by multivariable logistic regression.
Results: The percentage of income spent on tobacco was higher as income level was lower, especially for dual cigarette and HTP users; the percentages in the lowest/highest income group were 7.1%/1.2% for exclusive combustible cigarette smokers; 6.5%/1.1% for exclusive HTPs users; and 9.2%/1.3% for dual users. The adjusted odds ratios (95% confidence intervals) of quit intention among the >5% of income spent on tobacco group compared with the <1% spent group were 0.43 (0.18–1.03) for exclusive combustible cigarette smokers, 0.71 (0.20–2.54) for exclusive HTPs users, and 0.11 (0.02–0.77) for dual users.
Conclusions: Higher tobacco expenditure was not associated with quit intention for all categories of tobacco product users, probably due to the low price of tobacco in Japan.
抄録全体を表示
-
Miyako Kimura, Kazushige Ide, Koryu Sato, Eunji Bang, Toshiyuki Ojima, ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
45
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/11/09
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Background: People’s preventive behavior is crucial for reducing the infection and transmission of a novel coronavirus, especially in aging societies. Moreover, since behavioral restrictions may lead to high risks of secondary health impacts among older people, health-promoting behaviors, including proper nutrition intake and regular exercise, should also be encouraged. Although various studies have reported the positive association between social participation and health among older people, whether their social participation relates to preventive and health-promoting behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic was uncertain. This study examined the relationships between social participation before the COVID-19 pandemic and preventive and health-promoting behaviors during the pandemic among older people in Japan.
Methods: We obtained longitudinal data from the Japan Gerontological Evaluation Study (JAGES), which conducted baseline and follow-up surveys from November 2019 to January 2020 (pre-pandemic) and from November 2020 to February 2021 (during the pandemic) in ten municipalities. In total, 10,523 responses were analyzed. Preventive and health-promoting behaviors were measured by nine actions (e.g., wash/disinfect hands, wear masks, do exercise), and the total of these actions was divided into two (highly implemented ≥7 or not highly implemented <7). Social participation was assessed by nine activities (e.g., participating in volunteering, sports clubs, had paid work). Adjusted for covariates, we examined the relationships between each social participation and preventive and health-promoting behavior by the logistic regression analysis or the Poisson regression analysis.
Results: Older people who participated in social activities pre-pandemic showed a tendency to implement preventive and health-promoting behaviors during the pandemic. Especially, participations in “sports” and “Kayoi-no-ba” were positively related to “do exercise.” Only “had paid work” was negatively related to highly implemented preventive and health-promoting behaviors.
Conclusions: There were the positive relationships between social participation and preventive and health-promoting behavior. This study also indicated that older people who did not participate in social activities or had paid work before the COVID-19 pandemic may have higher risks of infection and secondary health impacts. Taking into account such old people’s lifestyles as well as their workplace conditions, promoting appropriate behaviors need to be considered.
抄録全体を表示
-
Qing Li, Hiroko Ochiai, Toshiya Ochiai, Norimasa Takayama, Shigeyoshi ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
44
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/11/02
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Background: We previously found that a forest bathing (shinrin-yoku) program significantly reduced the scores for depression, anxiety, anger, fatigue, and confusion and increased the score for vigor in the profile of mood states (POMS) test and showed a potential preventive effect on the depressive status in both males and females. In the present study, we investigated the effects of a forest bathing program on the level of serotonin in serum, depressive symptoms and subjective sleep quality in middle-aged males.
Methods: Twenty healthy male subjects aged 57.3 ± 8.4 years were selected after obtaining informed consent. These subjects took day trips to a forest park, the birthplace of forest bathing in Japan named Akasawa Shizen Kyuyourin, Agematsu, Nagano Prefecture (situated in central Japan), and to an urban area of Nagano Prefecture as a control in June 2019. On both trips, they walked 2.5 km for 2 hours each in the morning and afternoon on Saturday and Sunday, respectively. Blood was sampled in the afternoon before and after each trip. Concentrations of serotonin and lactic acid in serum were measured. The POMS test and a questionnaire for subjective sleep quality were conducted before and after the trips. Ambient temperature and humidity were monitoring during the trips. The Ethics Committees of the Nippon Medical School and Nagano Prefectural Kiso Hospital approved this study.
Results: The forest bathing program significantly increased level of serotonin in serum, and significantly increased the score for vigor and decreased the score for fatigue in the POMS test. The forest bathing program also improved the sleepiness on rising and feeling refreshed (recovery from fatigue) in the Oguri-Shirakawa-Azumi sleep inventory MA version (OSA-MA).
Conclusions: Taken together, the present study suggests that forest bathing may have potential preventive effects on depression (depressive status).
抄録全体を表示
-
Qing Li
原稿種別: Review Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
43
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/11/01
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Humans have enjoyed forest environments for ages because of the quiet atmosphere, beautiful scenery, mild climate, pleasant aromas, and fresh, clean air. In Japan, since 2004, serial studies have been conducted to investigate the effects of forest environments (Forest bathing/Shinrin-yoku) on human health. My research team has established a new medical science called Forest Medicine. The Forest Medicine is a new interdisciplinary science, belonging to the categories of alternative medicine, environmental medicine and preventive medicine, which studies the effects of forest environments (Forest bathing/Shinrin-yoku) on human health. It has been reported that Forest bathing/Shinrin-yoku has the following beneficial effects on human health:
1 Shinrin-yoku increases human natural killer (NK) activity, the number of NK cells, and the intracellular levels of anti-cancer proteins, suggesting a preventive effect on cancers.
2 Shinrin-yoku reduces blood pressure and heart rate showing preventive effect on hypertension and heart diseases.
3 Shinrin-yoku reduces stress hormones, such as urinary adrenaline and noradrenaline and salivary/serum cortisol contributing to stress management.
4 Shinrin-yoku increases the activity of parasympathetic nerves and reduces the activity of sympathetic nerves to stabilize the balance of autonomic nervous system.
5 Shinrin-yoku improve sleep.
6 Shinrin-yoku increases the levels of serum adiponectin and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate.
7 In the Profile of Mood States (POMS) test, Shinrin-yoku reduces the scores for anxiety, depression, anger, fatigue, and confusion, and increases the score for vigor, showing preventive effects on depression.
8 Shinrin-yoku may apply to rehabilitation medicine
9 Shinrin-yoku in city parks also has benefits on human health.
10 Shinrin-yoku may have preventive effect on COVID-19 by boosting immune function and by reducing mental stress.
Taken together, these findings suggest that Shinrin-yoku may have potential preventive effects on non-communicable diseases.
抄録全体を表示
-
Jumpei Sato, Naohiro Mitsutake, Masaru Kitsuregawa, Tomoki Ishikawa, K ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
42
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/10/29
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Background: Driven by the rapid aging of the population, Japan introduced public long-term care insurance to reinforce healthcare services for the elderly in 2000. Precisely predicting future demand for long-term care services helps authorities to plan and manage their healthcare resources and citizens to prevent their health status deterioration.
Methods: This paper presents our novel study for developing an effective model to predict individual-level future long-term care demand using previous healthcare insurance claims data. We designed two discriminative models and subsequently trained and validated the models using three learning algorithms with medical and long-term care insurance claims and enrollment records, which were provided by 170 regional public insurers in Gifu, Japan.
Results: The prediction model based on multiclass classification and gradient-boosting decision tree achieved practically high accuracy (weighted average of Precision, 0.872; Recall, 0.878; and F-measure, 0.873) for up to 12 months after the previous claims. The top important feature variables were indicators of current health status (e.g., current eligibility levels and age), risk factors to worsen future healthcare status (e.g., dementia), and preventive care services for improving future healthcare status (e.g., training and rehabilitation).
Conclusions: The intensive validation tests have indicated that the developed prediction method holds high robustness, even though it yields relatively lower accuracy for specific patient groups with health conditions that are hard to distinguish.
抄録全体を表示
-
Nlandu Roger Ngatu, Kazuto Tayama, Kanae Kanda, Tomohiro Hirao
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
41
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/10/21
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: COVID-19 pandemic is tremendously impacted by socioeconomic and health determinants worldwide. This study aimed to determine factors associated with COVID-19 fatality among member states and partner countries of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD).
Methods: An ecological study was conducted using COVID-19 data of 48 countries for the period between 31 December 2019–31 December 2021. The outcome variables were COVID-19 case fatality rate (CFR) and years of life lost to COVID-19 (YLLs). Countries’ sociodemographics and COVID-19-related data were extracted from OECD website, Our World in Data, John Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center, Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) and WHO.
Results: In the first year of the pandemic (December 2019–January 2021), highest CFR was observed in Mexico, 8.51%, followed by China, 5.17% and Bulgaria, 4.12%), and highest YLLs was observed in Mexico, 2,055 per 100,000. At regional level, highest CFR was observed in North & central America, 4.25 (3.71) %, followed by South America (2.5 (0.1) %); whereas highest YLLs was observed in South America region 1457.5 (274.8) per 100,000, followed by North & central America, 1207.3 (908.1) per 100,000. As of 31 December 2021, Mexico (7.52%) and Bulgaria (4.78%) had highest CFR; on the other hand, highest YLLs was observed in England, 26.5 per 1,000, followed by the United States, 25.9 per 1,000. At regional level, highest CFR (3.37(3.19) %) and YLLs (16.7 (13) per 1,000) were both observed in North & central America. Globally, the analysis of the 2-year cumulative data showed inverse correlation between CFR and nurse per 10,000 (R = −0.48; p < 0.05) and GDP per capita (R = −0.54; p < 0.001), whereas positive correlation was observed between YLLs and elderly population rate (R = 0.66; p < 0.05) and overweight/obese population rates (R = 0.55; p < 0.05).
Conclusion: This study provides insights on COVID-19 burden among OECD states and partner countries. GDP per capita, overweight/obesity and the rate of elderly population emerged as major social and health determinants of COVID-19 related burden and fatality. Findings suggest that a robust economy and interventions designed to promote healthy longevity and prevent weight gain in at-risk individuals might reduce COVID-19 burden and fatality among OECD states and partner countries.
抄録全体を表示
-
Yoshiyasu Ito, Jun Kako, Kohei Kajiwara, Yasutaka Kimura, Takahiro Kak ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
40
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/10/15
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: The effect of the prolonged coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic on the mental health of nursing students is unclear. This study assesses the prevalence of anxiety, depression, and insomnia among nursing students in Japan during the pandemic and determines the risk factors associated with such symptoms.
Methods: An online survey-based cross-sectional study was conducted from August 16 to October 16, 2021. Participants were first- to fourth-year nursing students enrolled in undergraduate programs at the eight universities in Japan. Anxiety, depression, and insomnia were assessed using the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7, Patient Health Questionnaire-9, and Insomnia Severity Index-7, respectively. We calculated descriptive statistics for each measurement item and performed univariate and logistic regression analyses to evaluate the potential risk factors.
Results: We received responses from 1,222 of 3,056 nursing students (response rate: 40.0%). After 25 participants were excluded due to missing outcome values, 1,197 students (valid response rate: 98.0%) were included in the analysis. The prevalence of anxiety, depression, and insomnia was 4.8%, 12.4%, and 18.0%, respectively. The risk of anxiety was lower among participants who did not have any relatives or friends who had been infected with SARS-CoV-2 than among those who did (aOR 0.36, 95% CI 0.14–0.94). The risk of depression was higher among participants whose financial status had worsened during the pandemic than among those whose financial status had not changed (aOR 3.44; 95% CI 1.98–5.96). Common factors that increased the risk of anxiety, depression, and insomnia were life satisfaction and fear of COVID-19.
Conclusion: Mental health-related symptoms among nursing students in Japan have not necessarily worsened with the spread of COVID-19 but were exacerbated by the intensity of changes in daily living and fear, which are psychosocial effects associated with the pandemic.
抄録全体を表示
-
Jun Bai, Lijuan Li, Yanhong Li, Liansheng Zhang
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
39
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/10/15
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Background: Tibetans have lived at very high altitudes for thousands of years, and have a distinctive suite of physiological traits that enable them to tolerate environmental hypoxia. Expanding awareness and knowledge of the differences in hematology, hypoxia-associated genes, immune system of people living at different altitudes and from different ethnic groups may provide evidence for the prevention of mountain sickness.
Method: Ninety-five Han people at mid-altitude, ninety-five Tibetan people at high-altitude and ninety-eight Han people at high-altitude were recruited. Red blood cell parameters, immune cells, the contents of cytokines, hypoxia-associated gene single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were measured.
Results: The values of Hematocrit (HCT), Mean cell volume (MCV) and Mean cell hemoglobin (MCH) in red blood cell, immune cell CD19+ B cell number, the levels of cytokines Erb-B2 receptor tyrosine kinase 3 (ErbB3) and Tumor necrosis factor receptor II (TNF-RII) and the levels of hypoxia-associated factors Hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), Hypoxia inducible factor-2α (HIF-2α) and HIF prolyl 4-hydroxylase 2 (PHD2) were decreased, while the frequencies of SNPs in twenty-six Endothelial PAS domain protein 1 (EPAS1) and Egl-9 family hypoxia inducible factor 1 (EGLN1) were increased in Tibetan people at high-altitude compared with that of Han peoples at high-altitude. Furthermore, compared with mid-altitude individuals, high-altitude individuals showed lower blood cell parameters including Hemoglobin concentration (HGB), HCT, MCV and MCH, higher Mean cell hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), lower immune cells including CD19+ B cells, CD4+ T cells and CD4/CD8 ratio, higher immune cells containing CD8+ T cells and CD16/56NK cells, decreased Growth regulated oncogene alpha (GROa), Macrophage inflammatory protein 1 beta (MIP-1b), Interleukin-8 (IL-8), and increased Thrombomodulin, downregulated hypoxia-associated factors including HIF1α, HIF2α and PHD2, and higher frequency of EGLN1 rs2275279.
Conclusions: These results indicated that biological adaption to hypoxia at high altitude might have been mediated by changes in immune cells, cytokines, and hypoxia-associated genes during the evolutionary history of Tibetan populations. Furthermore, different responses to high altitude were observed in different ethnic groups, which may provide a useful knowledge to improve the protection of high-altitude populations from mountain sickness.
抄録全体を表示
-
Zemin Cai, Wei Hu, Ruotong Wu, Shukai Zheng, Kusheng Wu
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
38
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/10/06
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and their metabolites have severe impact on human health, but few studies focus on their nephrotoxicity. This study was conceived to explore hub genes that may be involved in two hydroxylated polybrominated diphenyl ethers toxicities on impairment of adrenocortical secretory function.
Methods: Gene dataset was obtained from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). Principal component analysis and correlation analysis were used to classify the samples. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened using the limma package in RStudio (version 4.1.0). Gene Ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) and Reactome enrichment analyses of DEGs were conducted. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was established using STRING network, and genes were filtered by Cytoscape (version 3.8.2). Finally, the hub genes were integrated by plug-in CytoHubba and RobustRankAggreg, and were preliminarily verified by the Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD).
Results: GSE8588 dataset was selected in this study. About 190 upregulated and 224 downregulated DEGs in 2-OH-BDE47 group, and 244 upregulated and 276 downregulated DEGs in 2-OH-BDE85 group. Functional enrichment analyses in the GO, KEGG and Reactome indicated the potential involvement of DEGs in endocrine metabolism, oxidative stress mechanisms, regulation of abnormal cell proliferation, apoptosis, DNA damage and repair. 2-OH-BDE85 is more cytotoxic in a dose-dependent manner than 2-OH-BDE47. A total of 98 hub genes were filtered, and 91 nodes and 359 edges composed the PPI network. Besides, 9 direct-acting genes were filtered for the intersection of hub genes by CTD.
Conclusions: OH-PBDEs may induce H295R adrenocortical cancer cells in the disorder of endocrine metabolism, regulation of abnormal cell proliferation, DNA damage and repair. The screened hub genes may play an important role in this dysfunction.
抄録全体を表示
-
Masayuki Shima, Narumi Tokuda, Hideki Hasunuma, Yoshiko Kobayashi, Hir ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
37
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/09/28
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: Epidural analgesia relives pain during labor. However, the long-term effects on neurodevelopment in children remain unclear. We explored associations between exposure to epidural analgesia during labor and childhood neurodevelopment during the first 3 years of life, in the Japan Environment and Children’s Study (JECS), a large-scale birth cohort study.
Methods: Pregnant women were recruited between January 2011 and March 2014, and 100,304 live births of singleton children born at full-term by vaginal delivery, and without congenital diseases were analyzed. Data on mothers and children were collected using a self-administered questionnaires and medical record transcripts. The children’s neurodevelopment was repeatedly assessed for five domains (communication, gross motor, fine motor, problem solving, and personal-social), using the Ages and Stages Questionnaires, Third Edition, at six time points from age 6 to 36 months. After adjusting for potential confounders, the associations between exposure to epidural analgesia during labor and children’s neurodevelopment at each time point were assessed.
Results: Of the 42,172 children with valid data at all six time points, 938 (2.4%) were born to mothers who received epidural analgesia during labor. Maternal exposure to epidural analgesia was associated with neurodevelopmental delays during the first 3 years after birth. Delay risks in gross and fine motor domains were the greatest at 18 months (adjusted odds ratio (aOR) [95% confidence interval (CI)]: 1.40 [1.06, 1.84] and 1.54 [1.17, 2.03], respectively), subsequently decreasing. Delay risks in communication and problem-solving domains were significantly high at 6 and 24 months, and remained significant at 36 months (aOR [95% CI]: 1.40 [1.04, 1.90] and 1.28 [1.01, 1.61], respectively). Exposure to epidural analgesia was also associated with the incidence of problem solving and personal-social delays from 18 to 24 months old. Neurodevelopmental delay risks, except for communication, were dominant in children born to mothers aged ≥30 years at delivery.
Conclusions: This study showed that maternal exposure to epidural analgesia during labor was associated with neurodevelopmental delays in children during the first 3 years after birth.
抄録全体を表示
-
Ananya Roy, Md Ashraful Alam, Yoonhee Kim, Masahiro Hashizume
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
36
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/09/28
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: Previous studies have reported that high ambient temperature is associated with increased risk of suicide; however, the association has not been extensively investigated with drug overdose which is the most common method of unsuccessful suicidal behavior in Japan. Therefore, this study aims to examine the short-term association between daily mean temperature and the incidence of self-harm attempts by drug overdose in Tokyo, Japan.
Methods: We collected the emergency ambulance dispatch data and daily meteorological data in Tokyo from 2010 to 2014. A quasi-Poisson regression model incorporating a distributed lag non-linear function was applied to estimate the non-linear and delayed association between temperature and drug overdose, adjusting for relative humidity, seasonal and long-term trends, and days of the week. Sex, age and location-specific associations of ambient temperature with drug overdose was also estimated.
Results: 12,937 drug overdose cases were recorded during the study period, 73.9% of which were female. We observed a non-linear association between temperature and drug overdose, with the highest risk observed at 21 °C. The highest relative risk (RR) was 1.30 (95% Confidence Interval (CI): 1.10–1.67) compared with the risk at the first percentile of daily mean temperature (2.9 °C) over 0–4 days lag period. In subgroup analyses, the RR of a drug overdose at 21 °C was 1.36 (95% CI: 1.02–1.81) for females and 1.07 (95% CI: 0.66–1.75) for males. Also, we observed that the risk was highest among those aged ≥65 years (RR = 2.54; 95% CI: 0.94–6.90), followed by those aged 15–34 years (RR = 1.25; 95% CI: 0.89–1.77) and those aged 35–64 years (RR = 1.15; 95% CI: 0.78–1.68). There was no evidence for the difference in RRs between urban (23 special wards) and sub-urban areas in Tokyo.
Conclusions: An increase in daily mean temperature was associated with increased drug overdose risk. This study indicated the positive non-linear association between temperature and incomplete attempts by drug overdose. The findings of this study may add further evidence of the association of temperature on suicidal behavior and suggests increasing more research and investigation of other modifying factors.
抄録全体を表示
-
Kouji H. Harada, Sani Rachman Soleman, Jeremy Sea Meng Ang, Antoine P. ...
原稿種別: Commentary
2022 年 27 巻 p.
35
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/09/02
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
On 24 February 2022, Russian military forces invaded Ukraine. The fighting has already caused unimaginable conditions and millions of people were forced to flee their homes. For decades, conflicts have been linked to environmental pollution, exposure to radioactivity and heavy metals as well as infectious diseases. The invasion may cause specific environmental risks, like the release of radioactive substances from nuclear power plants and contaminated soils. Because international collaboration is one of the most effective ways to address environmental problems, it is critical to establish scientific bodies within a global framework to identify concrete actions and tangible measures to provide immediate assistance to citizens. This commentary discusses the above issues from lessons learned from the past wars and the way forward in the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
抄録全体を表示
-
Noora Seilo, Susanna Paldanius, Reija Autio, Kristina Kunttu, Minna Ka ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
34
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/08/19
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: General health checks are an established component of preventive health care in many countries. Declining participation rates have raised concerns in health care providers. Understanding the reasons for attendance and non-attendance is necessary to improve the preventive health care system. The aim of this study was to examine health- and study-related factors associated with university entrants’ health check attendance.
Methods: Since 2009, an electronic health questionnaire (eHQ) has been conducted yearly to all Finnish university entrants by the Finnish Student Health Service (FSHS) to screen students for a general health check. The questionnaire comprises 26 questions about health, health habits and studying. The study population consisted of the 3346 entrants from the 2011–2012 academic year who were referred to a health check based on their eHQ responses. The eHQ data were linked with health check attendance information. Multivariable logistic regression was used to study the associations between the questionnaire responses and non-attendance of the health check.
Results: Male sex (OR 1.6, 95% CI % 1.4–1.9) and low engagement with studies (OR 1.5, 95% CI 1.2–2.0) were the variables most strongly associated with non-attendance. Having low state of mind was negatively associated with health check non-attendance thus enhanced the health-check attendance (OR 0.6, 95% CI 0.5–0.8).
Conclusions: The results suggest that providing health checks in student health care may serve as a way of reaching students with health concerns. However, motivating males and smokers to attend general health checks continue to be a challenge also in a university student population. That low engagement with studies associates with health check non-attendance points to need to improve collaboration between universities and student health care.
抄録全体を表示
-
Fuyu Miyake, Chimed-Ochir Odgerel, Ayako Hino, Kazunori Ikegami, Tomoh ...
原稿種別: Review Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
33
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/08/11
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Background: Previous studies have reported an increase in loneliness since the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), but there are few data on the relationship between job stress and loneliness. This study aimed to assess the relationship between job stress and loneliness among desk workers, with a focus on the impact of remote working.
Methods: This study was part of the Collaborative Online Research on the Novel-coronavirus and Work (CORoNaWork) project in Japan. We extracted data from 13,468 workers who indicated that they were doing desk work. Loneliness was assessed using a single question and job stress was valuated using the Job Content Questionnaire (JCQ). Multiple logistic regression was performed.
Results: Participants who worked remotely 4 or more days per week were marginally more likely to report feeling lonely compared with those who did not work remotely (adjusted odds ratio = 1.23, 95% CI: 0.99–5.84, P = 0.066). Remote working did not explain the interaction between JCQ scale scores and loneliness. Among remote workers, the level of support provided by co-workers and supervisors was strongly associated with feelings of loneliness as well as non-remote workers (co-worker support: AOR = 4.06, 95% CI: 2.82–5.84, P < 0.001; supervisor support: AOR = 2.49, 95% CI: 1.79–3.47, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: To reduce loneliness and the risk of associated mental health problems, high-frequency remote workers should interact with supervisors and co-workers using the information and communication technology developed for this purpose.
抄録全体を表示
-
Takashi Shimazaki, Hiroto Okoshi, Takashi Yamauchi, Koji Takenaka, Mac ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
32
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/07/28
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
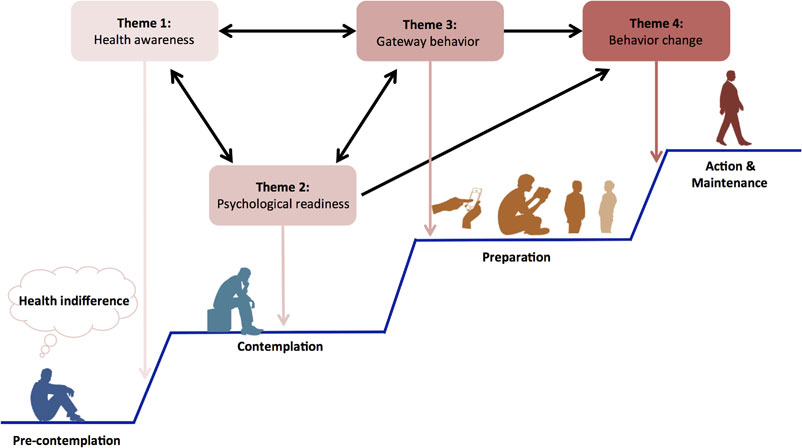
Background: In Japan and elsewhere, there is major concern over individuals who are uninterested in health and reluctant to change their health behaviors. While previous studies have investigated cognitive and behavioral characteristics in this population, there is limited evidence on whether they recognize the significance of health, nor is it clear how to motivate necessary behavior changes. This study identified specific characteristics of positive psychological and behavioral change in individuals who were uninterested in health, then constructed a model for their behavior change process, as advised via professional health expertise in the Japanese context.
Methods: This qualitative survey study was conducted among 86 health professionals (public health nurses, registered dieticians, and city/prefectural employees). These participants reported their demographic characteristics (gender, age, job, and length of service) and entered free descriptions concerning perceived cognitive and behavior changes in individuals who were uninterested in health. Finally, we thematically analyzed the contents on psychological/behavioral change and constructed a thematic map.
Results: We obtained 409 relative descriptive codes and four main themes, including (1) Health awareness: Recognize the significance of health via personal experience and/or illness among family/friends; (2) Psychological readiness: Preparative psychological state toward health behavior; (3) Gateway behavior: Precursory behavior leading to health behavior; and (4) Health behavior: Traditional healthy lifestyle behavior, with 45 subthemes. We constructed the abovementioned thematic map according to the Transtheoretical Model. Herein, health awareness may catalyze changes in health behavior, while changes in both psychological readiness (e.g., new interest in health behaviors and attitude toward appearance) and gateway behaviors (e.g., new points of discussion and information gathering) may arise before changes in health behavior.
Conclusions: This study clarified positive cognitive and behavior changes in individuals who were uninterested in health and elucidated their behavior change process. As behavior changes in such individuals tend to be rigid, they are often left behind by health care systems and programs. In this regard, we identified pertinent cognitive and behavioral characteristics during the behavior change process and constructed a relevant model. These findings should be useful in developing interventions that can motivate the desire for behavior change.
抄録全体を表示
-
Huanhuan Jia, Shang Gao, Panpan Shang, Peng Cao, Jianxing Yu, Xihe Yu
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
31
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/07/14
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Background: The shortage of health care workforce is a common problem all over the world and one of the main reasons for the shortage is the high turnover rate. Based on the characteristics of medical work, this study explored the relationship among public service motivation (PSM), work stress, task performance and turnover intention.
Methods: Medical personnel in public hospitals were selected by stratified random sampling in Jilin province of China and validated scales from previous studies were applied to measure the variables. Besides, a structural equation model of turnover intention was constructed to demonstrate the relationship.
Results: A total of 3191 valid questionnaires were collected. The results showed that the score of turnover intention was 2.02 ± 1.13. There are significant differences in turnover intention among medical staff of different genders and departments. At the same time, PSM had direct and negative effects on the turnover intention (β = −0.292, P < 0.001), work stress had direct and positive effects on the turnover intention (β = 0.479, P < 0.001), whereas task performance had no significant effect on turnover intention (β = 0.044, P < 0.142). The results showed an acceptable fit model.
Conclusion: The greater the PSM, the lower the turnover intention, and the higher the work stress, the higher the turnover intention. In addition, work stress and task performance play a mediating role between PSM and turnover intention. This paper provides theoretical support for the measures to reduce the turnover intention of medical staff.
抄録全体を表示
-
Aya Sugiyama, Fumie Okada, Kanon Abe, Hirohito Imada, Serge Ouoba, Bun ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
30
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/07/07
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: This longitudinal study aimed to determine chronological changes in the seroprevalence of prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, including asymptomatic infections in Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan.
Methods: A stratified random sample of 7,500 residents from five cities of Hiroshima Prefecture was selected to participate in a three-round survey from late 2020 to early 2021, before the introduction of the COVID-19 vaccine. The seroprevalence of anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies was calculated if at least two of four commercially available immunoassays were positive. Then, the ratio between seroprevalence and the prevalence of confirmed COVID-19 cases in Hiroshima was calculated and compared to the results from other prefectures where the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare conducted a survey by using the same reagents at almost the same period.
Results: The numbers of participants in the first, second, and third rounds of the survey were 3025, 2396, and 2351, respectively and their anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies seroprevalences were 0.03% (95% confidence interval: 0.00–0.10%), 0.08% (0.00–0.20%), and 0.30% (0.08–0.52%), respectively. The ratio between the seroprevalence and the prevalence of confirmed COVID-19 cases in Hiroshima was 1.2, which was smaller than that in similar studies in other prefectures.
Conclusions: The seroprevalence of anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in Hiroshima increased tenfold in a half year. The difference between seroprevalence and the prevalence of confirmed COVID-19 cases in Hiroshima was smaller than that in other prefectures, suggesting that asymptomatic patients were more actively detected in Hiroshima.
抄録全体を表示
-
Koji Mori, Takahiro Mori, Tomohisa Nagata, Hajime Ando, Ayako Hino, Se ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
29
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/07/01
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Background: Vaccination is considered the most effective control measure against COVID-19. Vaccine hesitancy and equitable vaccine allocation are important challenges to disseminating developed vaccines. To promote COVID-19 vaccination coverage, the government of Japan established the workplace vaccination program. However, while it appears that the program was effective in overcoming vaccine hesitancy, the program may have hindered the equitable allocation of vaccines because it mainly focused on employees of large companies. We investigated the relationship between company size and COVID-19 vaccination completion status of employees and the impact of the workplace vaccination program on this relationship.
Methods: We conducted an internet-based prospective cohort study from December 2020 (baseline) to December 2021. The data were collected using a self-administered questionnaire survey. Briefly, 27,036 workers completed the questionnaire at baseline and 18,560 at follow-up. After excluding ineligible respondents, we finally analyzed the data from 15,829 participants. At baseline, the participants were asked about the size of the company they worked for, and at follow-up they were asked about the month in which they received their second COVID-19 vaccine dose and the availability of a company-arranged vaccination opportunity.
Results: In each month throughout the observation period, the odds of having received a second COVID-19 vaccine dose were significantly lower for small-company employees than for large-company employees in the sex- and age-adjusted model. This difference decreased after adjusting for socioeconomic factors, and there was no significant difference after adjusting for the availability of a company-arranged vaccination opportunity.
Conclusions: The workplace vaccination program implemented in Japan to control the COVID-19 pandemic may have been effective in overcoming vaccine hesitancy in workers; however, it may have caused an inequitable allocation of vaccines between companies of different sizes. Because people who worked for small companies were less likely to be vaccinated, it will be necessary to enhance support of vaccination for this population in the event of future infectious disease outbreaks.
Trial registration: Not applicable.
抄録全体を表示
-
Bita Eslami, Sadaf Alipour, Ramesh Omranipour, Kazem Naddafi, Mohammad ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
28
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/07/01
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: Air pollution is one of the major public health challenges in many parts of the world possibly has an association with breast cancer. However, the mechanism is still unclear. This study aimed to find an association between exposure to six criteria ambient air pollutants (PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, O3, and CO) and mammographic breast density (MBD), as one of the strongest predictors for developing breast cancer, in women living in Tehran, Iran.
Methods: Participants were selected from women attending two university hospitals for screening mammography from 2019 to 2021. Breast density was rated by two expert radiologists. Individual exposures to 3-year ambient air pollution levels at the residence were estimated.
Results: The final analysis in 791 eligible women showed that low and high breast density was detected in 34.8 and 62.2 of participants, respectively. Logistic regression analysis after considering all possible confounding factors represented that an increase in each unit of NO2 (ppb) exposure was associated with an increased risk of breast density with an OR equal to 1.04 (95CI: 1.01 to 1.07). Furthermore, CO level was associated with a decreasing breast density (OR = 0.40, 95CI = 0.19 to 0.86). None of the other pollutants were associated with breast density.
Conclusion: Higher MBD was associated with an increased level of NO2, as a marker of traffic-related air pollution. Furthermore, CO concentration was associated with a lower MBD, while other criteria air pollutants were not related to MBD. Further studies are needed to evaluate the association between ambient air pollutants with MBD.
抄録全体を表示
-
You Kyoung Shin, Soonho Kwon, Yu Shan Hsieh, A Young Han, Geun Hee Seo ...
原稿種別: Short Communication
2022 年 27 巻 p.
27
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/06/24
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Background: Ulcerative colitis (UC) is related to stress, but few studies have evaluated the influence of stress on factors affecting colon contractility in rats with UC. Also, there have been no studies investigating beneficial effects of linalyl acetate (LA), the major component of lavender essential oil, in repeatedly stressed-ulcerative colitis rats. Therefore, we investigated the differences in factors affecting colon contractility of UC rats with or without repeated restraint stress (RRS) and the effects of LA on these parameters in repeatedly stressed-UC rats.
Methods: Rats were assigned to following groups: control, RRS, UC, RRS+UC, and RRS+UC treated with LA or sulfasalazine. To induce UC, rats were administered 2% dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) water on days 1–5, followed by tap water on days 6–15 and DSS water on days 16–20. RRS was induced by immobilizing rats for 2 hr/day on days 1–20. LA or sulfasalazine were daily administered on days 16–20.
Results: Disease activity index (DAI) was markedly increased in RRS+UC. Serum interleukin-6 levels and acetylcholine-induced colon contraction were higher in RRS+UC than in control, RRS and UC. Colon nitrite levels also significantly increased in RRS+UC compared to the control and RRS. Blood pressure (BP) was higher in RRS+UC than in the control and UC. Both LA and sulfasalazine was effective in decreasing DAI, colon nitrite levels, acetylcholine-induced colon contraction in RRS+UC. Sulfasalazine significantly reduced serum IL-6 levels in RRS+UC with decreasing tendency in RRS+UC treated by LA. Only LA significantly reduced BP in RRS+UC.
Conclusions: Our findings emphasize the importance of stress management in UC patients. Also, LA may be beneficially used in repeatedly stressed-UC patients with high BP.
抄録全体を表示
-
Takafumi Abe, Jun Kitayuguchi, Noritoshi Fukushima, Masamitsu Kamada, ...
原稿種別: Short Communication
2022 年 27 巻 p.
26
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/06/18
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: Physical inactivity during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic may have hindered the development of fundamental movement skills in preschoolers. This serial cross-sectional study compared fundamental movement skills by age group before and during the COVID-19 pandemic (2019–2020), among Japanese preschoolers aged 3–5 years.
Methods: Of the 22 preschools within Unnan City, Shimane Prefecture, Japan, 21 (95.5%) and 17 (77.3%) participated in the 2019 and 2020 surveys, respectively. We analyzed 608 and 517 preschoolers in both surveys. Fundamental movement skills were objectively assessed with a 25 m run, standing long jump, and softball throw, based on the Japanese physical activity guidelines for preschoolers. Mann–Whitney U tests were used to compare the fundamental movement skills data between periods.
Results: For the 25 m run, participants aged 5 years were faster before than during the pandemic (p = 0.018), while participants aged 3 and 4 years showed no significant differences. Participants aged 3–5 years showed no significant differences before and during the pandemic for the standing long jump (p ≥ 0.072). For the softball throw, all grades scored higher before than during the pandemic (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: These findings suggest that the COVID-19 pandemic impeded the development of fundamental motor skills, especially for object control skills. This highlights the need for interventions aimed at developing fundamental motor skills in preschoolers during and after the pandemic.
抄録全体を表示
-
Jun Ueyama, Yuki Ito, Risa Hamada, Naoko Oya, Sayaka Kato, Taro Matsuk ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
25
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/06/14
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Background: Pyrethroid (PYR) insecticides are widely used for controlling various pests. There are two types that differ in terms of usage: agricultural-purpose PYR (agriculture-PYR) and hygiene purpose PYR (hygiene-PYRs). Few studies exist on the exposure to these chemicals in small children. In this study, we conducted biomonitoring of urinary pyrethroid metabolites in 1.5-year-old children throughout the year.
Methods: Study subjects were 1075 children participating in an Aichi regional sub-cohort of the Japan Environment and Children’s Study as of 18-month health check-up. The concentrations of four specific hygiene-PYR metabolites including 2,3,5,6-tetrafluoro-1,4-benzenedimethanol (HOCH2-FB-Al), and five common metabolites of hygiene- and agriculture-PYRs including 3-phenoxybenzoic acid (3PBA) and cis- and trans-3-(2,2-dichlorovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (DCCA), were measured in urine samples extracted from soiled diapers using a triple quadrupole gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer.
Results: The highest detection frequencies were for 3PBA, followed by DCCA, 1R-trans-chrysanthemum dicarboxylic acid, and HOCH2-FB-Al. Among the six metabolites, urinary concentrations were seasonally varied. However, this variation was not observed in the most studied PYR metabolite, 3PBA. Spearman’s correlation analysis demonstrated a significant positive correlation between FB-Al and DCCA (r = 0.56) and HOCH2-FB-Al and 4-methoxymethyl-2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzyl alcohol (r = 0.60).
Conclusions: This biomonitoring survey found widespread and seasonally specific exposure to multiple hygiene- and agriculture-PYRs in 1.5-year-old Japanese children.
抄録全体を表示
-
Sumitaka Kobayashi, Fumihiro Sata, Reiko Kishi
原稿種別: Review Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
24
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/06/09
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: There are only limited numbers of reviews on the association of maternal-child genetic polymorphisms and environmental and lifestyle-related chemical exposure during pregnancy with adverse fetal growth. Thus, this article aims to review: (1) the effect of associations between the above highlighted factors on adverse fetal growth and (2) recent birth cohort studies regarding environmental health risks.
Methods: Based on a search of the PubMed database through August 2021, 68 epidemiological studies on gene-environment interactions, focusing on the association between environmental and lifestyle-related chemical exposure and adverse fetal growth was identified. Moreover, we also reviewed recent worldwide birth cohort studies regarding environmental health risks.
Results: Thirty studies examined gene-smoking associations with adverse fetal growth. Sixteen maternal genes significantly modified the association between maternal smoking and adverse fetal growth. Two genes significantly related with this association were detected in infants. Moreover, the maternal genes that significantly interacted with maternal smoking during pregnancy were cytochrome P450 1A1 (CYP1A1), X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 3 (XRCC3), interleukin 6 (IL6), interleukin 1 beta (IL1B), human leukocyte antigen (HLA) DQ alpha 1 (HLA-DQA1), HLA DQ beta 1 (HLA-DQB1), and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Fetal genes that had significant interactions with maternal smoking during pregnancy were glutathione S-transferase theta 1 (GSTT1) and fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO). Thirty-eight studies examined the association between chemical exposures and adverse fetal growth. In 62 of the 68 epidemiological studies (91.2%), a significant association was found with adverse fetal growth. Across the studies, there was a wide variation in the analytical methods used, especially with respect to the genetic polymorphisms of interest, environmental and lifestyle-related chemicals examined, and the study design used to estimate the gene-environment interactions. It was also found that a consistently increasing number of European and worldwide large-scale birth cohort studies on environmental health risks have been conducted since approximately 1996.
Conclusion: There is some evidence to suggest the importance of gene-environment interactions on adverse fetal growth. The current knowledge on gene-environment interactions will help guide future studies on the combined effects of maternal-child genetic polymorphisms and exposure to environmental and lifestyle-related chemicals during pregnancy.
抄録全体を表示
-
Ahmed Arafa, Yoshihiro Kokubo, Rena Kashima, Masayuki Teramoto, Yukie ...
原稿種別: Review Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
23
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/06/09
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
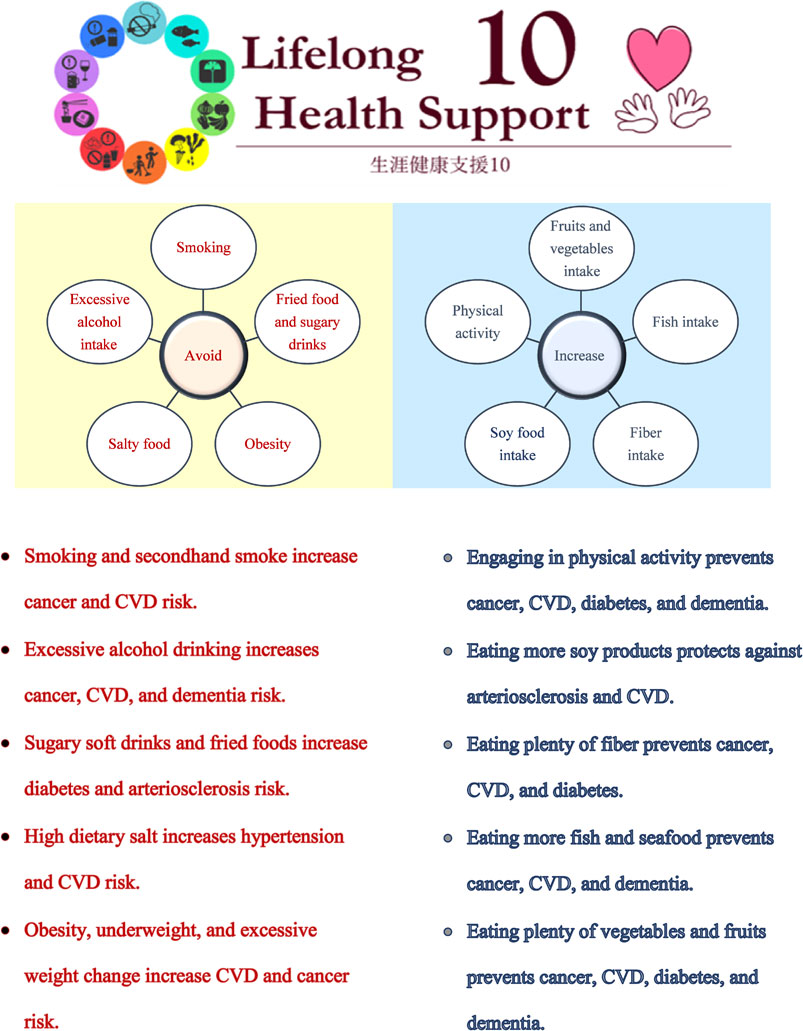
Background: Although the age-adjusted incidence and mortality of cancer and cardiovascular disease (CVD) have been decreasing steadily in Japan, both diseases remain major contributors to morbidity and mortality along with the aging society. Herein, we aim to provide a prescription of 10 health tips for long and healthy life named the “Lifelong Health Support 10 (LHS10).”
Method: The LHS10 was developed by the preventive medicine specialists at the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center in Suita, where it has been used for health guidance to prevent CVD, cancer, and cognitive decline in addition to their major risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, and obesity. It consisted of the lifestyle modification recommendations of the 2014 Japanese Society of Hypertension guidelines and the 2017 Japan Atherosclerosis Society Guidelines for preventing atherosclerotic CVD. Further, it came in line with other international lifestyle modification guidelines. In this narrative review, we summarized the results of several Japanese epidemiological studies investigating the association between the LHS10 items and the risk of cancer, CVD, and other chronic diseases including dementia, diabetes, and chronic kidney disease.
Results: The LHS10 included avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke exposure, engaging in physical activity, refraining from excessive alcohol drinking, reducing fried foods and sugary soft drinks, cutting salt in food, consuming more vegetables, fruits, fish, soy foods, and fibers, and maintaining proper body weight. All items of the LHS10 were shown to reduce the risk of cancer, CVD, and other chronic diseases.
Conclusions: The LHS10 can be a helpful tool for health guidance.
抄録全体を表示
-
Keiko Kinumaki, Hironori Imano, Yukiko Takao, Yoshinobu Okuno, Yasuko ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
22
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/05/28
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
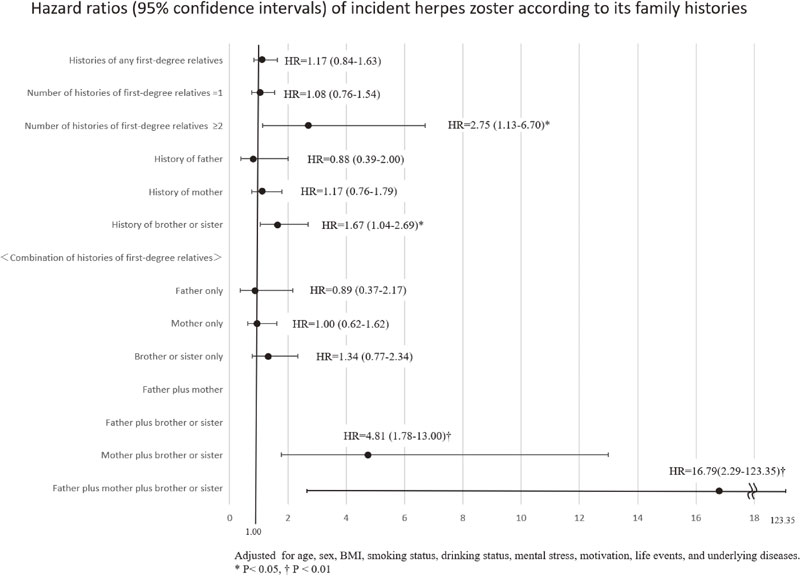
Background: We investigated whether family histories of herpes zoster (HZ) are associated with the risk of incident HZ in a Japanese population.
Methods: A total of 12,522 Japanese residents aged ≥50 years in Shozu County participated in the baseline survey between December 2008 and November 2009 (the participation rate = 72.3%). They were interviewed at baseline by research physicians regarding the registrants’ history of HZ. A self-administered questionnaire survey was conducted to evaluate the potential confounding factors. 10,530 participants without a history of HZ were followed up to ascertain the incidence of HZ during 3-years follow-up until the end of November 2012 with Japanese nationals. We estimated hazard ratios (HRs) of incident HZ according to first-degree family histories using the Cox proportional hazard regression after adjusting for age, sex, and other potential confounding factors.
Results: Compared to no HZ history of each family member, a history of brother or sister was associated with a higher risk of incident HZ while histories of father and mother were not. The multivariable HR (95%CI) of incident HZ for a history of brother or sister was 1.67 (1.04–2.69). When comparing to no family histories of all first-degree relatives, the multivariable HRs (95%CIs) were 1.34 (0.77–2.34) for a history of brother or sister alone, but 4.81 (1.78–13.00) for a history of mother plus brother or sister. As for the number of family histories, the multivariable HRs (95%CIs) were 1.08 (0.76–1.54) for one relative (father, mother, or brother or sister) and 2.75 (1.13–6.70) for two or more relatives.
Conclusion: Family histories of mother plus brother or sister and two or more first-degree relatives were associated with a higher risk of incident HZ.
抄録全体を表示
-
Bing Lin, Jiaxiu Liu, Yingjie Ma, Xiaoni Zhong
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
21
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/05/27
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Background: Men who have sex with men (MSM), as a marginal population, has been largely ignored by health service projects. We assessed the utilization of HIV testing and counselling services and its influencing factors based on Andersen’s Behavioral Model, so as to provide a theoretical basis for future infectious disease prevention and control strategies and health services policy formulation for these population.
Method: This was a cross-sectional study. A sample survey was conducted in Western China, and an anonymous self-administered questionnaire survey was conducted among MSM. Based on Andersen’s Behavioral Model, the questionnaire divided the influencing factors into predisposing factor, enabling factor and need factor. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to explore the factors influencing the utilization of HIV testing and counselling.
Results: There were 3184 valid questionnaires. In the survey of HIV health services, 82.85% MSM had HIV testing and 64.98% MSM had HIV counselling, respectively. Among the predisposing factor, age 25 years old and over was a facilitator of HIV testing and counselling, and ethnicity was a factor associated with HIV testing. Among the enabling factor, MSM living in urban were more likely to have access to testing and counselling services, and income was also linked to HIV testing. Among the need factor, a high level of HIV knowledge could promote testing and counselling, and a history of sexually transmitted diseases (STD) was a facilitator of testing.
Conclusions: HIV testing is widespread in Western China and higher than counselling service. MSM with high-risk characteristics should be identified as a priority in the future public health services.
抄録全体を表示
-
Machi Suka, Takashi Shimazaki, Takashi Yamauchi, Hiroyuki Yanagisawa
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
20
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/05/21
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: Pretesting is the key to understanding how the intended audience will react to the message. Resistant reactions affect message processing or can lead to undesirable boomerang effects. The objective of this study was to develop a rating scale for measuring active (reactance) and passive (disengagement) resistance to persuasive health messages.
Methods: Six candidate items (3 items for disengagement and 3 items for reactance) were generated based on literature review. A web-based survey was conducted among Japanese adults aged 25–64 years to verify the reliability and validity of the 6-item resistance scale. Participants were asked to rate one of the advance care planning (ACP) promotion messages. All scale items were scored on a 1-to-5 point Likert scale and they were averaged to produce the resistance score.
Results: Explanatory factor analysis revealed a two-factor solution that agreed with the disengagement and reactance domains, respectively. Correlation coefficients between each set of items ranged between 0.30–0.69. Cronbach alpha (0.86) indicated satisfactory internal consistency of the set of items. Confirmatory factor analysis showed a good fit of the two-factor model with CFI = 0.998, SRMR = 0.011, and RMSEA = 0.041. The resistance score showed a moderate positive correlation with negative emotional responses (displeasure γ = 0.55, anger γ = 0.53) and was significantly inversely related to the persuasiveness score (γ = −0.50). Multivariable logistic regression analysis showed that the odds ratio for ACP intention per 1-point increase in the resistance score was 0.47 (95% confidence interval 0.40–0.56) with adjustment for the persuasiveness score.
Conclusion: The 6-item resistance scale exhibited adequate reliability and validity for measuring audience resistance when applied to the ACP promotion messages in Japanese people. The scale will be useful for pretesting health messages to make them more acceptable to the intended audience.
Trial registration: Not applicable; this is not a report of intervention trial.
抄録全体を表示
-
Wensu Zhou, Wenjuan Wang, Chaonan Fan, Fenfen Zhou, Li Ling
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
19
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/05/03
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: Research on the relationship between residential altitude and hypertension incidence has been inconclusive. Evidence at low altitudes (i.e., <1,500 m) is scarce, let alone in older adults, a population segment with the highest hypertension prevalence. Thus, the objective of this study is to determine whether hypertension risk may be affected by altitude in older adults living at low altitudes.
Methods: This prospective cohort study collected data from the Chinese Longitudinal Healthy Longevity Survey (CLHLS). We selected 6,548 older adults (≥65 years) without hypertension at baseline (2008) and assessed events by the follow-up surveys done in 2011, 2014, and 2018 waves. The mean altitude of 613 residential units (county or district) in which the participants resided was extracted from the Digital Elevation Model (DEM) of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and was accurate to within 30 m. The Cox regression model with penalized splines examined the linear or nonlinear link between altitude and hypertension. A random-effects Cox regression model was used to explore the linear association between altitude and hypertension.
Results: The overall rate of incident hypertension was 8.6 per 100-person years. The median altitude was 130.0 m (interquartile range [IQR] = 315.5 m). We observed that the exposure–response association between altitude and hypertension incidence was not linear. The shape of the exposure–response curve showed that three change points existed. Hypertension risk increased from the lowest to the first change point (247.1 m) and slightly fluctuated until the last change point (633.9 m). The risk decreased above the last change point. According to the categories stratified by the change points, altitude was only significantly associated with hypertension risk (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.003; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.002–1.005) under the first change point (247.1 m) after adjusting for related covariates.
Conclusion: Our study found that the association between altitude and hypertension risk might not be linear. We hope the further study can be conducted to confirm the generality of our findings.
抄録全体を表示
-
Kimiko Tomioka, Midori Shima, Keigo Saeki
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
18
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/05/03
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: Community health activities by public health nurses (PHNs) are known to improve lifestyle habits of local residents, and may encourage the practice of infectious disease prevention behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic. We investigated the association between prefecture-level COVID-19 incidence rate and the number of PHNs per population in Japan, by the COVID-19 variant type.
Methods: Our data were based on government surveys where prefectural-level data are accessible to the public. The outcome variable was the COVID-19 incidence rate (i.e., the cumulative number of COVID-19 cases per 100,000 population for each variant type in 47 prefectures). The explanatory variable was the number of PHNs per 100,000 population by prefecture. Covariates included socioeconomic factors, regional characteristics, healthcare resources, and health behaviors. The generalized estimating equations of the multivariable Poisson regression models were used to estimate adjusted incidence rate ratio (IRR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for the COVID-19 cases. We performed stratified analyses by variant type (i.e., wild type, alpha variant, and delta variant).
Results: A total of 1,705,224 confirmed COVID-19 cases (1351.6 per 100,000 population) in Japan were reported as of September 30, 2021. The number of PHNs per 100,000 population in Japan was 41.9. Multivariable Poisson regression models showed that a lower number of PHNs per population was associated with higher IRR of COVID-19. Among all COVID-19 cases, compared to the highest quintile group of the number of PHNs per population, the adjusted IRR of the lowest quintile group was consistently significant in the models adjusting for socioeconomic factors (IRR: 3.76, 95% CI: 2.55–5.54), regional characteristics (1.73, 1.28–2.34), healthcare resources (3.88, 2.45–6.16), and health behaviors (2.17, 1.39–3.37). These significant associations were unaffected by the variant type of COVID-19.
Conclusion: We found that the COVID-19 incidence rate was higher in prefectures with fewer PHNs per population, regardless of the COVID-19 variant type. By increasing the number of PHNs, it may be possible to contain the spread of COVID-19 in Japan and provide an effective human resource to combat emerging infectious diseases in the future.
抄録全体を表示
-
Daisuke Hori, Yuichi Oi, Shotaro Doki, Tsukasa Takahashi, Tomohiko Ike ...
原稿種別: Letter to the Editor
2022 年 27 巻 p.
17
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/04/16
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Background: Ibaraki’s Amabie-chan is a COVID-19 infection control system unique to Ibaraki prefecture, Japan. It requires residents to register each time they visit events, commercial facilities, and restaurants. The number of registrations has been limited, and its function alerting about people positive for COVID-19 infection seems not to be working. Nevertheless, registration with the system might have some impact on the user’s behavior. In the current preliminary survey, the possible impact of Ibaraki’s Amabie-chan on infection prevention behavior and fear of COVID-19 was investigated.
Methods: A cross-sectional, web-based, anonymous, and self-administered survey was conducted at two workplaces in Tsukuba Science City, Ibaraki, Japan. The first survey was conducted at one of the workplaces in November 2020, and the second survey, at the other workplace in February 2021. Variables of interest were sex, age group, marital status, employment status, Ibaraki’s Amabie-chan use, COVID-19 Contact-Confirming Application use, ten items of infection prevention behaviors, and fear of COVID-19. Hierarchical linear regression analysis was performed.
Results: In both surveys, use of Ibaraki’s Amabie-chan was significantly associated with COCOA use and with “physical condition management such as body temperature measurement.” No association was found with other infection prevention behaviors or with fear of COVID-19.
Conclusions: Our findings did not provide sufficient evidence for the effectiveness of Ibaraki’s Amabie-chan in regard to users’ infection control behavior. Further detailed study is needed to investigate the effectiveness in terms of infection prevention and the cost-effectiveness of Ibaraki’s Amabie-chan.
抄録全体を表示
-
Kimiko Tomioka, Midori Shima, Keigo Saeki
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
16
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/03/31
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: The relationship between leisure activities (LA) in old age and prevention of disability has not been fully investigated, and age and gender differences of these relationships are unknown. This study aimed to investigate whether physical and cognitive LA predicted incident disability among community-dwelling older adults by age and gender.
Methods: We prospectively observed 8,275 residents aged 65 or above without disability at baseline for 3 years. Incident disability was defined as a new certification of the public long-term care insurance system. LA were classified into two types: physical LA and cognitive LA. The frequency of LA was categorized into frequent (i.e., once a week or more), moderate (i.e., monthly or yearly), and non-engagement. Covariates included age, gender, family number, education, perceived economic situation, body mass index, chronic medical conditions, alcohol consumption, smoking status, regular dental visits, depression, cognitive functioning, and social participation. Multivariable Poisson regression models were used to estimate adjusted cumulative incidence ratio (CIR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for incident disability. We performed stratified analyses by age groups (i.e., the young-old aged 65–74 and the old-old aged 75–97) and gender (i.e., men and women).
Results: The 3-year cumulative incidence of disability was 7.5%. After adjustment for covariates and mutual adjustment for both types of LA, a significant dose-response relationship between more frequent LA and lower risk of incident disability was found in young-old physical LA (P-trend < 0.001), in old-old cognitive LA (P-trend = 0.012), in male cognitive LA (P-trend = 0.006), and in female physical LA (P-trend = 0.030). Compared with people without LA, adjusted CIR (95% CI) of frequent LA was 0.47 (0.30–0.74) in young-old physical, 0.75 (0.58–0.96) in old-old cognitive, 0.65 (0.46–0.89) in male cognitive, and 0.70 (0.52–0.95) in female physical. Regarding the effect modification according to age and gender, only interaction between age and physical LA significantly prevented incident disability (P for interaction = 0.019).
Conclusion: We found age differences in the association of physical LA with incident disability among community-dwelling older adults. An effective measure to prevent long-term care in the community would be to recommend frequent physical LA for the young-old.
抄録全体を表示
-
Daniel Tzu-Hsuan Chen
原稿種別: Commentary
2022 年 27 巻 p.
15
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/03/31
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Tobacco intersects with the COVID-19 pandemic not only in terms of health consequences, but also environmental change and planetary health. Tobacco use exacerbates inequalities, causes catastrophic environmental degradation and climate change and adds burdens to COVID-19-related mortality, which are major challenges to recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the pandemic has provided a chance to combat tobacco use and accelerate efforts to alleviate these challenges in response. The MPOWER measures introduced by the World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) can play a crucial role in COVID-19 recovery to fight tobacco use and contribute to sustainable and equitable development. To accelerate recovery, it is critical to call for actions for governments and policy-makers to strengthen synergies and coordinate policy actions emphasising tobacco control and cessation across equity, public health, and climate actions as global authorities pledge to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and net zero emissions targets as part of the Climate Change Conference 2021 (COP26).
抄録全体を表示
-
Miyako Kimura, Kazushige Ide, Kazuki Kimura, Toshiyuki Ojima
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
14
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/03/26
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: Happiness may help to prevent negative physiological outcomes in response to life events; however, factors contributing to happiness during the COVID-19 pandemic have not been longitudinally investigated. This study explored the predictors of happiness in mothers of young children in Japan using comparable data that were obtained before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: We conducted the baseline survey in February 2020, and 4 months later, we also conducted the follow-up survey. Throughout all 47 prefectures in Japan, 4,700 (100 respondents/prefecture) mothers of infants and/or preschoolers (0–6 years) participated in the baseline online survey; 2,489 of these also participated in the follow-up survey.
Results: We performed hierarchical multiple regression analysis and our final model indicated that maternal happiness during COVID-19 pandemic was positively related to employment status (homemaker, β = 0.052, p = 0.014), levels of available social support (average, β = 0.052, p = 0.012, high, β = 0.055, p = 0.010) and happiness score before the pandemic (β = 0.467, p < 0.001), and satisfaction toward the measures against the COVID-19 at partners’ workplace (average, β = 0.129, p < 0.001; high, β = 0.279, p < 0.001), preventive behavior against COVID-19 (average, β = 0.055, p = 0.002; high, β = 0.045, p = 0.015) and positive attitudes/thinking (β = 0.087, p < 0.001) during the pandemic. In contrast, poor mental health (K6 ≥5, β = −0.042, p = 0.011) before the pandemic and negative changes during the pandemic (≥3, β = −0.085, p < 0.001) were negatively related to maternal happiness during the pandemic. Our final model explained 44.9% of the variance in mothers’ happiness during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusions: Satisfaction toward the measures against the COVID-19 at partners’ workplace, preventive behavior, and positive attitudes/thinking were especially important for maternal happiness during the COVID-19 pandemic. Future study is needed to consider measures against infectious diseases in the workplace that are desirable for the well-being of parents with young children, taking into account the gender perspective.
抄録全体を表示
-
Qinxue Chang, Keyun Wang, Honglu Zhang, Changping Li, Yong Wang, Huaiq ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
13
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/03/19
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: Although previous studies have shown that meteorological factors such as temperature are related to the incidence of bacillary dysentery (BD), researches about the non-linear and interaction effect among meteorological variables remain limited. The objective of this study was to analyze the effects of temperature and other meteorological variables on BD in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, which is a high-risk area for BD distribution.
Methods: Our study was based on the daily-scale data of BD cases and meteorological variables from 2014 to 2019, using generalized additive model (GAM) to explore the relationship between meteorological variables and BD cases and distributed lag non-linear model (DLNM) to analyze the lag and cumulative effects. The interaction effects and stratified analysis were developed by the GAM.
Results: A total of 147,001 cases were reported from 2014 to 2019. The relationship between temperature and BD was approximately liner above 0 °C, but the turning point of total temperature effect was 10 °C. Results of DLNM indicated that the effect of high temperature was significant on lag 5d and lag 6d, and the lag effect showed that each 5 °C rise caused a 3% [Relative risk (RR) = 1.03, 95% Confidence interval (CI): 1.02–1.05] increase in BD cases. The cumulative BD cases delayed by 7 days increased by 31% for each 5 °C rise in temperature above 10 °C (RR = 1.31, 95% CI: 1.30–1.33). The interaction effects and stratified analysis manifested that the incidence of BD was highest in hot and humid climates.
Conclusions: This study suggests that temperature can significantly affect the incidence of BD, and its effect can be enhanced by humidity and precipitation, which means that the hot and humid environment positively increases the incidence of BD.
抄録全体を表示
-
Caitlin P. Bailey, Angelo F. Elmi, Mary T. Hoban, Christine Kukich, Me ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
12
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/03/19
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Background: Campus environments are associated with undergraduate weight. However, few studies have examined campus type and geographic location in relation to student weight. This article aimed to identify college/university students with elevated BMIs by campus type and region.
Methods: Linear mixed effects regression models were fit to data from the American College Health Association-National College Health Assessment II. Analyses tested associations between campus type/region and student self-reported BMI.
Results: The sample included 404,987 students from 445 schools with mean BMI 24.9 ± 5.8. Across all school types/regions, BMI confidence intervals included overweight values. Two-year and public school students had higher BMIs compared to four-year and private school students, respectively. Students in the Midwest had higher BMIs compared to students in the Northeast. In the South only, Minority Serving Institution (MSI) students had higher BMIs compared to non-MSI students.
Conclusion: Healthy weight maintenance programs should be made available to undergraduate students.
抄録全体を表示
-
Wen-Hsuan Hou, Jia-Ling Wu, Chin-Li Lu, Lilis Sulistyorini, Muhammad A ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
11
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/03/12
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: Associations of acute glycemic complications with season and ambient temperature have been reported in general population with diabetes. However, little is known about the risks of acute glycemic complications in relation to season and ambient temperature in pregnant women, who are likely to be even more vulnerable. This work aimed to investigate the associations of season and ambient temperature with pregnancies complicated with hyperglycemia emergency or severe hypoglycemia.
Methods: Two separate case-control studies were nested within 150,153 pregnancies by women with type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes between 2009 and 2014 in Taiwan. Hyperglycemia emergency (mainly diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state) and severe hypoglycemia occurred in 77 and 153 diabetic pregnancies (cases), respectively. Ten control pregnancies were randomly selected for each case by matching each case pregnancy on type of diabetes (i.e., T1DM, T2DM, or GDM), maternal age on the date of acute glycemic complication occurrence (i.e., index date), and “length of gestation at risk” (i.e., period between conception and index date). Meteorological parameters were retrieved from 542 meteorological monitoring stations across Taiwan during 2008–2014. Conditional logistic regression analysis with generalized estimation equation was separately performed to estimate the covariate adjusted odds ratios (ORs) of each of the two acute glycemic complications in association with season and ambient temperature within 30 days prior to the index date.
Results: Compared to summer, winter season was associated with a significantly elevated risk of severe hypoglycemia with an OR of 1.74 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.08–2.79). The OR of hyperglycemic emergency was also elevated in winter season at OR of 1.88, but the significance is only marginal (95% CI 0.97–3.64, p = 0.0598). Subgroup analyses further noted that such seasonal variation was also observed in pregnancies with pre-pregnancy type 1 diabetes and gestational diabetes. On the other hand, ambient temperature was not significantly associated with the two acute glycemic complications.
Conclusions: A moderately but significantly elevated risk of severe hypoglycemia was found in pregnant women with diabetes during winter season, and such increased risk was more evident in pregnancies with T1DM.
抄録全体を表示
-
Ahmed Arafa, Yoshihiro Kokubo, Keiko Shimamoto, Rena Kashima, Emi Wata ...
原稿種別: Short Communication
2022 年 27 巻 p.
10
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/03/04
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: A protective role for physical activity against the development of atrial fibrillation (AF) has been suggested. Stair climbing is a readily available form of physical activity that many people practice. Herein, we investigated the association between stair climbing and the risk of AF in a Japanese population.
Methods: In this prospective cohort study, we used data of 6,575 people registered in the Suita Study, aged 30–84 years, and had no history of AF. The frequency of stair climbing was assessed by a baseline questionnaire, while AF was diagnosed during the follow-up using a 12-lead ECG, health records, check-ups, and death certificates. We used the Cox regression to calculate the hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals of AF incidence for climbing stairs in 20–39%, 40–59%, and ≥60% compared with <20% of the time.
Results: Within 91,389 person-years of follow-up, 295 participants developed AF. The incidence of AF was distributed across the stair climbing groups <20%, 20–39%, 40–59%, and ≥60% as follows: 3.57, 3.27, 3.46, and 2.63/1,000 person-years, respectively. Stair climbing ≥60% of the time was associated with a reduced risk of AF after adjustment for age and sex 0.69 (0.49, 0.96). Further adjustment for lifestyle and medical history did not affect the results 0.69 (0.49, 0.98).
Conclusion: Frequent stair climbing could protect from AF. From a preventive point of view, stair climbing could be a simple way to reduce AF risk at the population level.
抄録全体を表示
-
Ahmed Arafa, Rena Kashima, Yoshihiro Kokubo
原稿種別: Letter to the Editor
2022 年 27 巻 p.
9
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/03/04
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
-
Akari Takaya Uno, Ken-ichi Mukaisho, Masahito Hitosugi
原稿種別: Letter to the Editor
2022 年 27 巻 p.
8
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/03/04
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Background: A Japanese woman in her early twenties had committed suicide, jumped from a 25-meter high bridge into a lake. She had been suffering from severe dysmenorrhea and general fatigue monthly.
Results: A forensic autopsy revealed indications of a bicorporeal uterus, obstructed hemi-vagina, and ipsilateral renal agenesis, which lead to a diagnosis of obstructed hemi-vagina and ipsilateral renal anomaly (OHVIRA) syndrome. On the right side of the uterus, an enclosed cavity composed of black clots was observed. Histological findings suggested that her endometrium was in the early proliferative phase, implying that she was in the menstrual phase just before her death. She may have been suffering from severe lower abdominal pain from the increased pressure of the closed uterus cavity.
Conclusions: This case indicates that dysmenorrhea from undiagnosed OHVIRA syndrome can possibly lead to a suicide attempt. In Japan, because suicide was the leading cause of death for people aged 15 to 39 in 2019, preventive measures for suicide should be promoted. The present case also suggests that intervention for dysmenorrhea may prevent this in adolescent woman.
抄録全体を表示
-
Lisa Yamasaki, Shuhei Nomura
原稿種別: Letter to the Editor
2022 年 27 巻 p.
7
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/03/04
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
The Tokyo 2020 Olympic and Paralympic Games provided a significant opportunity to consider global warming as an issue to be seriously addressed to run the safe and fair games in the era of climate change. As the global temperature continuously rises and extreme hot-weather events increase in frequency and intensity, the future summer Olympic and Paralympic games will need to deal with the heat by applying thorough and appropriate countermeasures. In the recent decades, many mitigation measures to protect athletes from heat have been rapidly discussed by the sports community, including countermeasures to hold games at times and places with moderate temperature and climatic risk assessments with Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) during the games. However, the excessive heat conditions in the Tokyo 2020 Games affected not only athletes, but also all people concerned the events. While deliberate considerations by organizers had been given to mitigate extraordinary heat, the evaluations of these measures and epidemiological analyses of risk factors of patients must be further enhanced to develop efficient measures for the future. Therefore, we discussed the underlying climate-related problems of the summer Olympic and Paralympic Games in view of what we had experienced in the Tokyo 2020 Games. Facing with emerging global warming, future intervention against heat in the summer Olympic and Paralympic games will need to integrate systematic disease surveillance and evaluation of intervention with an effective combination with the approaches previously conducted. The Tokyo 2020 Games is a wake-up call to accelerate the public health measures towards the creeping global warming.
抄録全体を表示
-
Sharifullah Alemi, Keiko Nakamura, Kaoruko Seino, Shafiqullah Hemat
原稿種別: Short Communication
2022 年 27 巻 p.
6
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/02/23
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: To protect the health and safety of healthcare workers (HCWs), it is essential to ensure the provision of sustainable water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) services and standard precautions in healthcare facilities (HCF). The objectives of this short communication were 1) to assess the availability of WASH services and standard precautions in HCFs in seven provinces in Afghanistan before the COVID-19 pandemic, and 2) to elucidate the relevance of these patterns with the number of reported HCW infections from COVID-19 in the mentioned provinces.
Methods: We analyzed secondary data from the 2018-19 Afghanistan Service Provision Assessment survey, which included 142 public and private HCFs in seven major provinces in Afghanistan. Data on COVID-19 cases were obtained from the Afghanistan Ministry of Public Health Data Warehouse. Weighted prevalence of WASH services and standard precautions were calculated using frequencies and percentages. ArcGIS maps were used to visualize the distribution of COVID-19 cases, and scatter plots were created to visualize the relevance of WASH services and standard precautions to COVID-19 cases in provinces.
Results: Of the 142 facilities surveyed, about 97% had improved water sources, and over 94% had improved toilet for clients. Overall, HCFs had limited availability of hygiene services and standard precautions, which was lower in private than public facilities. More than half of the facilities had safe final disposal and appropriate storage of sharps and medical waste. Of the seven provinces, Herat province had the highest cumulative COVID-19 case rate among HCWs per 100,000 population and reported lower availability of WASH services and standard precautions in HCFs compared to other provinces.
Conclusion: Our findings show disparities in the availability of WASH services and standard precautions in public and private facilities. Private facilities had a lower availability of hygiene services and standard precautions than public facilities. Provinces with higher availability of WASH services and standard precautions in HCFs had a lower cumulative COVID-19 case rate among HCWs per 100,000 population. Pre-pandemic preparation of adequate WASH services and standard precautions in HCFs could be potentially important in combating infectious disease emergence.
抄録全体を表示
-
Wei Wang, Xiaofeng Chen, Chunping Li, Rui Zhao, Jinlong Zhang, Hong Qi ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
5
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/02/19
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: This study aimed to evaluate the correlation between long non-coding RNA (lncRNA)-related single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and susceptibility to silicosis.
Methods: First, RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) data were comprehensively analyzed in the peripheral blood lymphocytes of eight participants (four silicosis cases and four healthy controls) exposed to silica dust to identify differentially expressed lncRNAs (DE-lncRNAs). The functional SNPs in the identified DE-lncRNAs were then identified using several databases. Finally, the association between functional SNPs and susceptibility to silicosis was evaluated by a two-stage case-control study. The SNPs of 155 silicosis cases and 141 healthy silica-exposed controls were screened by genome-wide association study (GWAS), and the candidate SNPs of 194 silicosis cases and 235 healthy silica-exposed controls were validated by genotyping using the improved Mutiligase Detection Reaction (iMLDR) system.
Results: A total of 76 DE-lncRNAs were identified by RNA-seq data analysis (cut-offs: fold change > 2 or fold change < 0.5, P < 0.05), while 127 functional SNPs among those 76 DE-lncRNAs were identified through multiple public databases. Furthermore, five SNPs were found to be significantly correlated with the risk of silicosis by GWAS screening (P < 0.05), while the results of GWAS and iMLDR validation indicated that the variant A allele of rs1814521 was associated with a reduced risk of silicosis (OR = 0.76, 95% CI = 0.62–0.94, P = 0.011).
Conclusion: The presence of the SNP rs1814521 in the lncRNA ADGRG3 is associated with susceptibility to silicosis. Moreover, ADGRG3 was found to be lowly expressed in silicosis cases. The underlying biological mechanisms by which lncRNA ADGRG3 and rs1814521 regulate the development of silicosis need further study.
抄録全体を表示
-
Junko Kameyama, Yumi Hashizume, Yuko Takamura, Shoko Nomura, Tomoki Go ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
4
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/02/19
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Background: Global aging continues to progress. The shortage of human resources involved in long-term care (LTC) is a serious problem worldwide. It is necessary to promote the stable employment of foreign care workers. The purpose of this study was to identify which factors, including well-being, work engagement, and original items, contribute to foreign care workers’ intent to continue working.
Methods: We conducted an anonymous self-administered questionnaire survey of 259 foreign LTC workers at LTC facilities in Japan. The questionnaire survey items included the Japanese version of the Subjective Well-being Scale (J-SWBS), the Japanese version of the Utrecht Work Engagement Scale (J-UWES), and original items related to educational needs and issues. We used multiple regression analysis to predict variability from correlations among variables. And after that, we conducted a path analysis using structural equation modeling (SEM), and added that the explanatory variables (IV) were well-being, work engagement, and the original item component, and that the outcome variable (DV) was intention to continue working. We set a hypothetical model based on structural equations, corrected by path analysis, and examined its suitability.
Results: The number of returned questionnaires for 259 foreign care workers was 147 (response rate 56.7%), and the number of analyzable questionnaires was 129 (valid response rate 49.8%). For intention to continue working, the results of structural equation modeling showed direct effects for satisfaction with low back pain measure guidance (β = .255), satisfaction with the national examination guidance method (β = .217), well-being (β = .046), and work engagement (β = .026). In work-engagement, there was a direct effect of happiness (β = .715), willingness to learn good care (β = 4.849), and confidence in my ability (β = 2.902,), whilst in well-being, satisfaction with low back pain measure guidance (β = 1.582) and confidence in my ability (β = 1.999) were found to have direct effects.
Conclusions: To increase the intent of foreign care workers to continue working, appropriate guidance should be given related to the development of lumbago. In addition, to provide a place and scene where they can learn good care, having a relationship in practice where foreign care workers can feel that their abilities are being utilized, and developing and maintaining educational support that motivates them to learn good care may be effective.
抄録全体を表示
-
Shanshan Sun, Qiujing Li, Zhenkun Zhang, Sili Xiong, Yujie Zhang, Qian ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
3
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/02/19
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Background: SMARCA2 (SWI/SNF Related, Matrix Associated, Actin Dependent Regulator of Chromatin, Subfamily A, Member 2) is an important ATPase catalytic subunit in the switch-sucrose nonfermenting (SWI/SNF) complex. However, its relationship with the pathological features of NSCLC and its prognosis remain unclear.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 2390 patients with surgically resected NSCLC, constructed tissue microarrays (TMAs) and performed immunohistochemical assays. We analyzed the correlation of SAMRCA2 with clinicopathological features and evaluated its prognostic value.
Results: Among 2390 NSCLC cases, the negative expression ratios of SAMRCA2, SMARCA4, ARID1A, ARID1B and INI1 were 9.3%, 1.8%, 1.2%, 0.4% and 0%, respectively. In NSCLC, male sex, T3 and T4 stage, moderate and poor differentiation, tumor ≥ 2 cm, Ki67 ≥ 15%, SOX-2 negative expression, middle lobe lesion and adenocarcinoma were relative risk factors affecting SMARCA2-negative expression. In lung adenocarcinomas, high-grade nuclei, histological morphology of acinar and papillary, solid and micropapillary and TTF-1-negative expression were relative risk factors affecting SMARCA2-negative expression. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis showed that the OS was shorter in the SMARCA2-negative group. Multivariate survival analysis revealed that SMARCA2-negative expression was an independent factor correlated with a poor prognosis in NSCLC.
Conclusion: In conclusion, SMARCA2-negative expression is an independent predictor of a poor outcome of NSCLC and is a potential target for NSCLC treatment.
抄録全体を表示
-
Ko Hiraoka, Tomohisa Nagata, Takahiro Mori, Hajime Ando, Ayako Hino, S ...
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
2
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/02/19
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
Background: It is important to achieve herd immunity by vaccinating as many people as possible to end the COVID-19 pandemic. We investigated the relationship between willingness to receive vaccination and sources of health information among those who did not want to be vaccinated against COVID-19.
Methods: This prospective cohort study collected data using a self-administered questionnaire survey. The baseline survey was conducted during December 22–25, 2020, and the follow-up survey during February 18–19, 2021. Participants were aged 20–65 years and worked at the time of the baseline survey (N = 33,087). After excluding 6,051 invalid responses, we included responses from 27,036 participants at baseline. In total, 19,941 people responded to the follow-up survey (74% follow-up rate). We excluded 7,415 participants who answered “yes” to the question “If a COVID-19 vaccine becomes available, would you like to get it?” in the baseline survey. We finally analyzed 12,526 participants.
Results: The odds ratio for change in willingness to be vaccinated from “no” to “yes” differed by source of health information. Compared with workers that used TV as a source of information, significantly fewer people who reported getting information from the Internet and friends/colleagues were willing to get the vaccine.
Conclusions: It is important to approach workers who do not watch TV when implementing workplace vaccination programs. It is likely that willingness to be vaccinated can be increased through an active company policy whereby the top management recommend vaccination, coupled with an individual approach by occupational health professionals.
Trial registration: Not applicable.
抄録全体を表示
-
Yuki Kuwabara, Maya Fujii, Aya Kinjo, Yoneatsu Osaki
原稿種別: Research Article
2022 年 27 巻 p.
1
発行日: 2022年
公開日: 2022/02/19
ジャーナル
オープンアクセス
HTML
電子付録
Background: Cancer prevention is a crucial challenge in preventive medicine. Several studies have suggested that voluntary health check-ups and recommendations from health professionals are associated with increased participation in cancer screening. In Japan, it is recommended that individuals aged 40–74 years should undergo annual health check-ups; however, the compliance to this recommendation is approximately <50%. According to the national survey, individuals who do not undergo annual health check-ups are at a higher risk for cancer. However, to the best of our knowledge, no previous study has investigated the association between the use of health check-ups and the incidence rate of cancer. We hypothesised that not undergoing periodic health check-ups and/or less use of outpatient medical services are predictors for advanced cancer.
Methods: To explore the relationship between health check-up or outpatient service utilisation and cancer incidence, this retrospective cohort study used data at two time points—baseline in 2014 and endpoint in 2017—from the National Health Insurance (NHI) claims and cancer registry. A multivariable logistic regression analysis was performed to investigate whether cancer diagnosis was associated with health check-up or outpatient service utilisation.
Results: A total of 72,171 participants were included in the analysis. The results of the multivariable logistic regression showed that individuals who skipped health check-ups had a higher risk of cancer diagnosis (odds ratio [OR], 1.21; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.04–1.40). Moreover, not undergoing health check-ups increased the risk of advanced-stage cancer (OR, 1.78; 95% CI, 1.29–2.44). Furthermore, increased rate of outpatient service utilisation was negatively associated with advanced cancer diagnosis.
Conclusions: This is the first study reporting that not undergoing health check-ups is a predictor of cancer diagnosis and advanced cancer stage. Primary prevention strategies for NHI members who do not undergo health check-ups must be reassessed. Moreover, future research should examine secondary prevention strategies, such as health education and recommendations from health professionals to facilitate adequate utilisation of preventive health services.
抄録全体を表示
 原稿種別: Research Article
原稿種別: Research Article 原稿種別: Research Article
原稿種別: Research Article 原稿種別: Research Article
原稿種別: Research Article 原稿種別: Research Article
原稿種別: Research Article 原稿種別: Research Article
原稿種別: Research Article 原稿種別: Review Article
原稿種別: Review Article 原稿種別: Research Article
原稿種別: Research Article 原稿種別: Research Article
原稿種別: Research Article 原稿種別: Research Article
原稿種別: Research Article