-
Zhi-Yi Chen, Hui Hu, Jun Yang, Dian-Guo Xing, Xin-Yi Deng, Yang Zou, Y ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
28
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 11, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: Global warming and increasing extreme weather have become a severe problem in recent years, posing a significant threat to human health worldwide. Research exploring the link between injury as one of the leading causes of death globally and ambient temperature was lacking. Based on the hourly injury emergency ambulance dispatch (IEAD) records from 2019–2021 in the main urban area of Chongqing, this study explored the role of temperature extremes on the pathogenesis of injury by different mechanisms and identified sensitive populations for different mechanisms of injury.
Methods: In this study, we collected hourly injury emergency ambulance dispatch (IEAD) records from Chongqing Emergency Dispatch Center in the main urban area of Chongqing from 2019 to 2021, and used a distributed lagged nonlinear model (DLNM) with quasi-Poisson distribution to evaluate the association between ambient temperature and IEADs. And the stratified analysis was performed by gender, age and different injury mechanisms to identify susceptible groups. Finally, the attributable burden of ambient extreme temperatures was also investigated.
Results: The risk for total IEADs increased significantly at high temperature (32 °C) compared with optimal temperature (9 °C) (CRR: 1.210; 95%CI[1.127,1.300]). The risks of traffic accident injury (CRR: 1.346; 95%CI[1.167,1.552]), beating injury (CRR: 1.508; 95%CI[1.165,1.952]), fall-height injury (CRR: 1.871; 95%CI[1.196–2.926]) and injury of sharp penetration (CRR: 2.112; 95%CI[1.388–3.213]) were significantly increased. At low temperature (7 °C), the risk of fall injury (CRR: 1.220; 95% CI [1.063,1.400]) increased significantly. Lag for 24 hours at extreme low temperature (5 °C), the risk of 18–45 years (RR: 1.016; 95%CI[1.009,1.024]) and over 60 years of age (RR: 1.019; 95%CI[1.011,1.025]) increased significantly. The effect of 0 h delay in extreme high temperature (36 °C) on males aged 18–45 years (RR: 1.115; 95%CI[1.071,1.162]) and 46–59 years (RR: 1.069; 95%CI[1.023,1.115]) had significant impact on injury risk.
Conclusions: This study showed that ambient temperature was significantly related to the risk of injury, and different mechanisms of injury were affected differently by extreme temperature. The increasing risk of traffic accident injury, beating injury, fall-height injury and sharp penetrating injury was associated with extreme heat, while fall injury was associated with extreme cold. The risk of injury in high temperature environment was mainly concentrated in males and young adults. The results of this study can help to identify the sensitive population with different injury mechanisms in extreme temperature environment, and provide reference for public health emergency departments to respond to relevant strategies in extreme temperature environment to minimize the potential risk to the public.
View full abstract
-
Jungmi Choi, Yukiko Fujii, Zhaoqing Lyu, Hatasu Kobayashi, Tomoko Fuji ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
27
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 02, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Background: In the Great East Japan Earthquake of 11 March 2011, an earthquake and accompanying tsunami struck the Tohoku region of northeastern Japan. Buildings collapsed and the tsunami spread waste, including hazardous materials. This study aimed to determine the concentrations of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the breast milk of mothers living in the disaster-affected area of Sendai 1 year after the earthquake. Temporal trends in the POPs concentrations were evaluated by comparison with previous studies.
Methods: One hundred breast milk samples were obtained from lactating mothers at a hospital in Sendai in 2012. The results were compared with those from other years to examine whether there were changes in the POPs concentrations after the earthquake. We measured polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and organochlorine pesticides, such as chlordanes, using gas chromatography-mass spectrometer (GC-MS) with negative chemical ionization, and dichlorodiphenyl trichloroethane (DDT) and its metabolites using GC-MS with electron impact ionization.
Results: The mean total PCBs (11 congeners), total chlordane, and total DDT concentrations were 76.2 ng/g lipid, 39.8 ng/g lipid, and 73.5 ng/g lipid, respectively. For the samples collected in 2012, the concentrations of POPs in breast milk showed minimal changes compared with results from previous years for samples collected at the same hospital in Sendai.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates that 1 year after the earthquake and tsunami, the concentrations of chlorinated POPs in breast milk had not changed substantially.
View full abstract
-
Ahmed Arafa, Rena Kashima, Yoshihiro Kokubo, Masayuki Teramoto, Yukie ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
26
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 03, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: Alcohol consumption is a modifiable lifestyle, but its role in heart failure (HF) development is controversial. Herein, we investigated the prospective association between alcohol consumption and HF risk.
Methods: A total of 2,712 participants (1,149 men and 1,563 women) from the Suita Study were followed up every two years. Cox regression was applied to calculate the hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) of HF risk for heavy drinking (≥46 g/day in men or ≥23 g/day in women) and never drinking compared to light drinking (<23 g/day in men or <11.5 g/day in women). Then, we combined the results of the Suita Study with those from other eligible prospective cohort studies in a meta-analysis using the random-effects model.
Results: In the Suita Study, within a median follow-up period of 8 years, 319 HF cases (162 in men and 157 in women) were detected. In men, but not women, never and heavy drinking carried a higher risk of HF than light drinking: HRs (95% CIs) = 1.65 (1.00, 2.73) and 2.14 (1.26, 3.66), respectively. Alike, the meta-analysis showed a higher risk of HF among heavy drinkers: HR (95% CI) = 1.37 (1.15, 1.62) and abstainers: HR (95% CI) = 1.18 (1.02, 1.37).
Conclusion: We indicated a J-shaped association between alcohol consumption and HF risk among Japanese men. The results of the meta-analysis came in line with the Suita Study. Heavy-drinking men should be targeted for lifestyle modification interventions.
View full abstract
-
Risa Sonoda, Mikiko Tokiya, Kenichi Touri, Yuichi Tanomura, Kimihiro Y ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
25
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 21, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: A 4-year longitudinal study was conducted to develop a model and a point system for predicting childhood obesity.
Methods: This study included 1,504 Japanese 10-year-old children who underwent health check-ups between 2011 and 2015. Multivariable logistic regression analysis was conducted using the explanatory variables overweight and lifestyle. Obesity was defined as percentage overweight (POW) ≥ 20% calculated by the following equation: (actual weight − standard weight by height and sex)/standard weight by height and sex × 100 (%). The model was validated using the Hosmer-Lemeshow test on 10-year-olds.
Results: Our prediction model for development of childhood obesity was based on seven binary variables: sex, lack of sleep, ≥2-h use of television/ games/ smartphone, hypertension, dyslipidemia, hepatic dysfunction, and being overweight. The area under the curve of the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.803 (95% confidence interval, 0.740 to 0.866). When validated in non-obese children (n = 415), there was no significant difference between actual and predicted numbers of children with obesity (Hosmer-Lemeshow chi-square = 7.90, p = 0.18).
Conclusions: The validated prediction model and point score for obesity development were shown to be useful tools for predicting the future 4-year risk of developing obesity among 10 years-old children. The point system may be useful for reducing the occurrence of childhood obesity and promoting better health.
View full abstract
-
Mami Wakabayashi, Hirono Ishikawa, Yoshiharu Fukuda, Hiroyasu Iso, Tak ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
24
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 18, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: Little is known about the vulnerable populations and problem drinking in terms of health inequality. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between health indifference estimated by Health Interest Scale (HIS) and problem drinking identified by the Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT).
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted utilizing data from a nationwide internet survey in Japan in 2022. The number of total participants was 29,377, with 49% of them being male, and the mean age was 47.9 (±17.9) years. The participants were categorized into the following groups based on the quintiles of HIS score: health indifference (0–16), low health interest (17–20), middle health interest (21–22), middle-high interest (23–26) and high health interest (27–36) groups. Problem drinking was identified as AUDIT score of ≥8 points.
Results: The association between health indifference and problem drinking was explored through logistic regression with adjustment for various socioeconomic status, such as education, income level, and occupation; the adjusted odds ratio (aOR) was 1.72 [95% confidence interval (CI): 1.51–1.95].
Conclusion: Health indifferent or lower health interest groups were a vulnerable population for problem drinking, regardless of their socioeconomic status. It could be useful to identify the health indifferent group through HIS and to monitor the impact of health intervention for this group for the reduction of health inequality.
View full abstract
-
Qiufen Dou, Zhixiang Zhu, Liwan Zhu, Wanxin Wang, Lan Guo, Shouhang Ru ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
23
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 13, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Background: Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) is the most prevalent spinal deformity, which may have long-term negative consequences on adolescents. The research on the etiology is of great importance for identifying high-risk population and formulate tailored prevention. This study aimed to evaluate the association between academic-related factors and daily lifestyle habits and AIS.
Methods: In this population-based case-control study, 491 AIS cases and 1,346 healthy controls that frequency-matched by age and sex were recruited in Shenzhen, Southern China. AIS was diagnosed as a Cobb angle ≥ 10° on standing posteroanterior radiographs of the whole spine. The academic-related factors (e.g., reading and writing posture) and daily lifestyle habits (e.g., intake of milk and dairy products) were collected by a self-reported questionnaire. The logistic regression analysis was performed.
Results: After adjusting for potential confounding factors, multivariable logistic regression models demonstrated that academic-related factors were associated with AIS. Individuals with poor reading and writing posture were more likely to have AIS (AOR: 2.06, 95%CI: 1.58–2.68). Moreover, there was a significant association between heavy school bags and AIS (AOR: 2.22, 95%CI: 1.50–3.31). Additionally, adolescents who reported daily screen time on weekdays over 2 hours were more likely to develop AIS (P < 0.001). Regarding daily lifestyle habits, individuals without the habit of taking milk and dairy products had a higher risk of developing AIS (AOR: 1.87, 95%CI: 1.29–2.71).
Conclusions: Academic-related factors and daily lifestyle habits were associated with AIS among Chinese adolescents. Schools, families, and related facilities are recommended to take actions on developing effective prevention and management strategies that integrates “Student-Family-School-Education-Health-Sports” for AIS.
View full abstract
-
Chihiro Miyashita, Keiko Yamazaki, Naomi Tamura, Atsuko Ikeda-Araki, S ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
22
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 12, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: Concerns have been raised about the adverse health impacts of mobile device usage. The objective of this cross-sectional study was to examine the association between a child’s age at the first use of a mobile device and the duration of use as well as associated behavioral problems among school-aged children.
Methods: This study focused on children aged 7–17 years participating in the Hokkaido Study on Environment and Children’s Health. Between October 2020 and October 2021, the participants (n = 3,021) completed a mobile device use-related questionnaire and the strengths and difficulties questionnaire (SDQ). According to the SDQ score (normal or borderline/high), the outcome variable was behavioral problems. The independent variable was child’s age at first use of a mobile device and the duration of use. Covariates included the child’s age at the time of survey, sex, sleep problems, internet addiction, health-related quality of life, and history of developmental concerns assessed at health checkups. Logistic regression analysis was performed for all children; the analysis was stratified based on the elementary, junior high, and senior high school levels.
Results: According to the SDQ, children who were younger at their first use of a mobile device and used a mobile device for a longer duration represented more problematic behaviors. This association was more pronounced among elementary school children. Moreover, subscale SDQ analysis showed that hyperactivity, and peer and emotional problems among elementary school children, emotional problems among junior high school children, and conduct problems among senior high school children were related to early and long usage of mobile devices.
Conclusions: Elementary school children are more sensitive to mobile device usage than older children, and early use of mobile devices may exacerbate emotional instability and oppositional behaviors in teenagers. Longitudinal follow-up studies are needed to clarify whether these problems disappear with age.
View full abstract
-
Kimiko Tomioka, Midori Shima, Keigo Saeki
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
21
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 07, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: Civil servants and physicians play an important role in combating COVID-19. However, it is unclear whether the number of civil servants and physicians is associated with rapid COVID-19 vaccine uptake among older people (i.e., smoother rollout of priority vaccination for older people).
Methods: Using Poisson regression models of the generalized estimating equations, we examined the ecological association of the number of civil servants and physicians with prefectural-level rapid COVID-19 vaccination in older people. Prefectural-level data were based on publicly available government surveys. The outcome variable was the proportion of fully vaccinated people aged 65 and older on the day with the largest standard deviation across 47 prefectures (i.e., July 6, 2021). The explanatory variable was the number of civil servants and physicians per population by prefecture.
Results: After adjusting for population density, influenza vaccination coverage, socioeconomic factors, natural environmental factors, health indicators, and the number of civil servants and physicians, in all 3 models, prefectures with the highest number of civil servants and physicians had faster COVID-19 vaccine uptake than prefectures with the lowest number. A significant trend between higher staffing levels and more rapid vaccination was observed for the number of physicians in all 3 models, but for the number of civil servants only in one model.
Conclusion: We found that COVID-19 vaccine uptake among older people was more rapid in prefectures with more civil servants and physicians per population, with the number of physicians having a stronger association. This study may point the way to future areas of research on vaccine policies that include other age groups and infectious diseases.
View full abstract
-
Maho Ishihara, Hironori Imano, Isao Muraki, Kazumasa Yamagishi, Koutat ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
20
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 16, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Background: Alcohol consumption is a prevalent behavior that is bi-directionally related to the risk of type 2 diabetes. However, the effect of daily alcohol consumption on glucose levels in real-world situations in the general population has not been well elucidated. This study aimed to clarify the relationship between alcohol consumption and all-day and time-specific glucose levels among non-diabetic individuals.
Methods: We investigated 913 non-diabetic males and females, aged 40–69 years, during 2018–2020 from four communities across Japan. The daily alcohol consumption was assessed using a self-report questionnaire. All-day and time-specific average glucose levels were estimated from the interstitial glucose concentrations measured using the Flash glucose monitoring system for a median duration of 13 days. Furthermore, we investigated the association between all-day and time-specific average glucose levels and habitual daily alcohol consumption levels, using never drinkers as the reference, and performed multiple linear regression analyses after adjusting for age, community, and other diabetes risk factors for males and females separately.
Results: All-day average glucose levels did not vary according to alcohol consumption categories in both males and females. However, for males, the average glucose levels between 5:00 and 11:00 h and between 11:00 and 17:00 h were higher in moderate and heavy drinkers than in never drinkers, with the difference values of 4.6 and 4.7 mg/dL for moderate drinkers, and 5.7 and 6.8 mg/dL for heavy drinkers. Conversely, the average glucose levels between 17:00 and 24:00 h were lower in male moderate and heavy drinkers and female current drinkers than in never drinkers; the difference values of mean glucose levels were −5.8 for moderate drinkers, and −6.1 mg/dL for heavy drinkers in males and −2.7 mg/dL for female current drinkers.
Conclusions: Alcohol consumption was associated with glucose levels in a time-dependent biphasic pattern.
View full abstract
-
Yoshimitsu Shimomura, Tomotaka Sobue, Ling Zha, Tetsuhisa Kitamura, Mo ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
19
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 07, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: The association between meat, fish, or fatty acid intake and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) has been investigated in a few studies, and the results were inconsistent. In addition, most studies are mainly based on the United States and European countries, in which the dietary patterns differ from that in Asia. Therefore, the risk of AML/MDS from meat, fish, or fatty acid intake in Asia requires further exploration. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between AML/MDS incidence and meat, fish, or fatty acid intake using the Japan Public Health Center–based prospective study.
Methods: The present study included 93,366 participants who were eligible for analysis and followed up from the 5-year survey date until December 2012. We estimated the impact of their intake on AML/MDS incidence using a Cox proportional hazards model.
Results: The study participants were followed up for 1,345,002 person-years. During the follow-up period, we identified 67 AML and 49 MDS cases. An increased intake of processed red meat was significantly associated with the incidence of AML/MDS, with a hazard ratio of 1.63 (95% confidence interval, 1.03–2.57) for the highest versus lowest tertile and a Ptrend of 0.04. Meanwhile, the intake of other foods and fatty acids was not associated with AML/MDS.
Conclusion: In this Japanese population, processed red meat was associated with an increased incidence of AML/MDS.
View full abstract
-
Shinako Inaida, Atsushi Mizukoshi, Kenich Azuma, Jiro Okumura
Article type: Short Communication
2023Volume 28 Pages
18
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: March 03, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
During the recent emergence of COVID-19, an increased practice of hand hygiene coincided with the reduced incidence of the norovirus epidemic in Japan, which is similar to experience with the pandemic flu in 2009. We investigated the relationship between the sales of hand hygiene products, including liquid hand soap and alcohol-based hand sanitizer, and the trend of norovirus epidemic. We used national gastroenteritis surveillance data across Japan in 2020 and 2021 and compared the base statistics of incidence of these two years with the average of the previous 10 years (2010–2019). We calculated the correlations (Spearman’s Rho) between monthly sales of hand hygiene products and monthly norovirus cases and fitted them to a regression model. In 2020, there was no epidemic, and the incidence peak was the lowest in recent norovirus epidemics. In 2021, the incidence peak was delayed for five weeks to the usual epidemic seasons. Correlation coefficients between monthly sales of liquid hand soap and skin antiseptics and norovirus incidence showed a significantly negative correlation (Spearman’s Rho = −0.88 and p = 0.002 for liquid hand soap; Spearman’s Rho = −0.81 and p = 0.007 for skin antiseptics). Exponential regression models were fitted between the sales of each hand hygiene product and norovirus cases, respectively. The results suggest hand hygiene using these products is a potentially useful prevention method against norovirus epidemics. Effective ways of hand hygiene for increasing the prevention of norovirus should therefore be studied.
View full abstract
-
Jie Tang, Jingjing Wang, Yifei Pei, Shiferaw Blen Dereje, Qian Chen, N ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
17
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 22, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Background: There has been minimal research on the role of benevolent childhood experiences (BCEs) and how such events may offer protection from the insidious effects of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) or later in life.
Objectives: This research aims to learn how BCEs and ACEs interact to affect adolescents’ psychological distress.
Methods: Cross-sectional survey was conducted in three cities (Xuzhou, Nanjing, and Wuhan) in China from March 2021 to May 2021. Latent class analysis (LCA) was used to classify the patterns of ACEs and BCEs. We adopted hierarchical multivariable regression to examine the influences of ACEs and BCEs on depression and suicidal ideation.
Results: To explore the relationship between childhood experience and suicidal ideation and depression, LCA revealed three patterns of ACEs: (1) emotional abuse (10.57%); (2) high ACEs (0.55%); and (3) low ACEs classes (88.88%). Adolescents with emotional abuse (depression: OR = 3.82, 95%CI = 2.80–5.22, P < 0.001; suicidal ideation: OR = 5.766, 95%CI = 3.97–8.38, P < 0.001) and high ACEs class (suicidal ideation: OR = 5.93, 95%CI = 1.19–29.66, P < 0.05) had an increased risk of psychological distress (reference: low ACEs). LCA revealed four patterns of BCEs: (1) relationship support (14.54%); (2) low BCEs (4.85%); (3) high BCEs (55.34%); and (4) high quality of life classes (25.28%). Adolescents with a high quality of life (depression: OR = 0.09, 95%CI = 0.05–0.16, P < 0.001; suicidal ideation: OR = 0.22, 95%CI = 0.12–0.40, P < 0.001) and high BCEs (depression: OR = 0.05, 95%CI = 0.03–0.09, P < 0.001; suicidal ideation: OR = 0.15, 95%CI = 0.09–0.26, P < 0.001) protected the mental health of adolescents (reference: low BCEs).
Conclusions: High ACEs and emotional abuse classes were significantly associated with poorer mental health symptoms, including suicidal ideation and depression. In contrast, high BCEs and high quality of life classes were associated with better mental health. These findings point out that it is more necessary to identify and support victims of ACEs, and it is urgent to increase BCEs in early childhood.
View full abstract
-
Shigeto Yoshida, Shu Tanaka, Masafumi Okada, Takuya Ohki, Kazumasa Yam ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
16
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 15, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: Previous cardiovascular risk prediction models in Japan have utilized prospective cohort studies with concise data. As the health information including health check-up records and administrative claims becomes digitalized and publicly available, application of large datasets based on such real-world data can achieve prediction accuracy and support social implementation of cardiovascular disease risk prediction models in preventive and clinical practice. In this study, classical regression and machine learning methods were explored to develop ischemic heart disease (IHD) and stroke prognostic models using real-world data.
Methods: IQVIA Japan Claims Database was searched to include 691,160 individuals (predominantly corporate employees and their families working in secondary and tertiary industries) with at least one annual health check-up record during the identification period (April 2013–December 2018). The primary outcome of the study was the first recorded IHD or stroke event. Predictors were annual health check-up records at the index year-month, comprising demographic characteristics, laboratory tests, and questionnaire features. Four prediction models (Cox, Elnet-Cox, XGBoost, and Ensemble) were assessed in the present study to develop a cardiovascular disease risk prediction model for Japan.
Results: The analysis cohort consisted of 572,971 invididuals. All prediction models showed similarly good performance. The Harrell’s C-index was close to 0.9 for all IHD models, and above 0.7 for stroke models. In IHD models, age, sex, high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein, cholesterol, and systolic blood pressure had higher importance, while in stroke models systolic blood pressure and age had higher importance.
Conclusion: Our study analyzed classical regression and machine learning algorithms to develop cardiovascular disease risk prediction models for IHD and stroke in Japan that can be applied to practical use in a large population with predictive accuracy.
View full abstract
-
Hitomi Matsuura, Yoko Hatono, Isao Saito
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
15
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 07, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: Individual-level social capital is an important determinant of older adults’ long-term care needs; however, there is scant evidence regarding community-level social capital. Therefore, we investigated the association between community-level social capital and the prevalence of the need for long-term care among older adults.
Methods: Between January and February 2018, a cross-sectional survey was conducted among all older adults (n = 13,558) aged 65 to 74 years in a rural municipality in Japan (total population, n = 72,833). A self-reported questionnaire was used to identify community-level social capital, comprising civic participation, social cohesion, and reciprocity. A multilevel logistic regression analysis was performed to estimate the odds ratios of the need for long-term care and a decline in social activity competence as assessed by instrumental activities of daily living. For the analysis, the community levels were divided into 76 voting districts and adjusted for daily life, lifestyle, socioeconomic status, health conditions, and the three social capital subscale scores at the individual level.
Results: After adjusting for the covariates, we observed a tendency that a higher community level of reciprocity was associated with a lower prevalence of long-term care needs (OR: 0.86, 95% confidence interval: 0.75–1.00), whereas a high community level of social cohesion was associated with a significantly reduced decline in instrumental activities of daily living (OR per standard deviation increase: 0.87, 95% confidence interval: 0.79–0.96). No significant association was found with civic participation. Similarly, individual-level social capital was associated with the need for long-term care and decline in instrumental activities of daily living.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that good community-level reciprocity or social cohesion as well as good individual social capital status may help prevent the need for long-term care among older adults.
View full abstract
-
Yasuaki Saijo, Eiji Yoshioka, Yukihiro Sato, Yuki Kunori
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
14
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 03, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: Internal medicine (IM) doctors in Japan play the role of primary care physicians; however, the shortage of rural physicians continues. This study aims to elucidate the association of age, sex, board certification, type of work, and main clinical work with the retention or migration of IM doctors to rural areas.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included 82,363 IM doctors in 2010, extracted from the national census data of medical doctors. The explanatory variables were age, sex, type of work, primary clinical work, and changes in board certification status. The outcome was retention or migration to rural areas. The first tertile of population density (PD) of municipalities defined as rural area. After stratifying the baseline ruralities as rural or non-rural areas, the odds ratios (ORs) of the explanatory variables were calculated using generalized estimation equations. The analyses were also performed after age stratification (<39, 40–59, ≥60 years old).
Results: Among the rural areas, women had a significantly higher OR for retention, but obtaining board certification of IM subspecialties had a significantly lower OR. Among the non-rural areas, physicians who answered that their main work was IM without specific subspecialty and general had a significantly higher OR, but obtaining and maintaining board certification for IM subspecialties had a significantly lower OR for migration to rural areas. After age stratification, the higher OR of women for rural retention was significant only among those aged 40–59 years. Those aged under 40 and 40–59 years in the non-rural areas, who answered that their main work was IM without specific subspecialty had a significantly higher OR for migration to rural areas, and those aged 40–59 years in the rural areas who answered the same had a higher OR for rural retention.
Conclusions: Obtaining and maintaining board certification of IM subspecialties are possible inhibiting factors for rural work, and IM doctors whose main work involves subspecialties tend to work in non-rural areas. Once rural work begins, more middle-aged female IM doctors continued rural work compared to male doctors.
View full abstract
-
Tomohiro Ishimaru, Toru Yoshikawa, Makoto Okawara, Michiko Kido, Yoshi ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
13
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 03, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic may have increased the rate of presenteeism among front-line physicians. Presenteeism is the term used to describe attendance at work despite ill health that would normally prompt rest or absence from work. This study aimed to examine the associations between COVID-19 clinical practice and presenteeism among physicians.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted from December 2021 to January 2022. The questionnaires were distributed to 21,737 employed physicians who were members of the Japan Medical Association. Presenteeism was measured by the Work Functioning Impairment Scale. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to evaluate the association between COVID-19 clinical practice and presenteeism.
Results: Overall, 3,968 participants were included in the analysis, and presenteeism was observed in 13.9% of them. The rate of presenteeism significantly increased with both the number of COVID-19 patients treated and the percentage of work time spent treating these patients (both P values for trend < 0.001). In comparison to those not currently engaged in the treatment of COVID-19 patients, presenteeism was significantly higher among front-line (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 1.71, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.16–2.53) and second-line physicians supporting those in the front-line (aOR = 1.45, 95% CI: 1.17–1.78). There was no association between involvement in COVID-19 vaccination services and presenteeism.
Conclusions: The burden on front-line and second-line physicians in COVID-19 clinical practice must be minimized. Employed physicians also need to recognize the importance of communicating with their workplaces about presenteeism.
View full abstract
-
Mina Hayama-Terada, Yuri Aochi, Satoyo Ikehara, Takashi Kimura, Kazuma ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
12
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 03, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: Few prospective studies have investigated the association between paternal occupational exposures and risk of infant congenital heart defects (CHDs). We investigated the associations between paternal occupational exposures, frequency of use, and concurrent or sequential exposure to a mixture of compounds and the risk of infant CHDs.
Methods: Our study examined 28,866 participants in the Japan Environment and Children’s Study. Logistic regression analysis was used to estimate odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) associated with paternal occupational exposures during the 3 months until pregnancy was noticed after adjustment for potential confounding factors of the infant CHDs. CHD diagnosis was ascertained from medical record.
Results: In total, 175 were diagnosed with infant CHDs. The number of fathers who were exposed to the following substances at least once a month were: 11,533 for photo copying machine/laser printer, 10,326 for permanent marker, 8,226 for soluble paint/inkjet printer, 6,188 for kerosene/petroleum/benzene/gasoline, 4,173 for organic solvents, 3,433 for chlorine bleach/germicide, 2,962 for engine oil, 2,931 for insecticide, 2,460 for medical sterilizing disinfectant, 1,786 for welding fumes, 1,614 for dyestuffs, 1,247 for any products containing lead-like solder, 986 for herbicide, 919 for radiation/radioactive substances/isotopes, 837 for lead-free solder, 341 for microbes, 319 for formalin/formaldehyde, 301 for agricultural chemical not listed above or unidentified, 196 for general anesthetic for surgery at hospital, 171 for anti-cancer drug, 147 for chromium/arsenic/cadmium, 88 for mercury and 833 for other chemical substances. Paternal occupational exposure regularly to photo copying machine or laser printer and soluble paint/inkjet printer were associated with higher risks of infant CHDs: the adjusted ORs (95%CIs) were 1.38 (1.00–1.91) and 1.60 (1.08–2.37), respectively. The higher risks were also observed for occasional exposure to engine oil, any products containing lead-like solder lead-free solder, and microbes; the adjusted ORs (95%CIs) were 1.68 (1.02–2.77), 2.03 (1.06–3.88), 3.45 (1.85–6.43), and 4.51, (1.63–12.49), respectively.
Conclusions: Periconceptional paternal occupational exposure was associated with a higher risk of infant CHDs. Further studies using biomarkers of the association between paternal occupational exposure and infant CHDs are warranted.
View full abstract
-
Mari Tanaka, Hironori Imano, Mina Hayama-Terada, Isao Muraki, Kokoro S ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
11
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 03, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Background: Sex- and age-specific impacts of cardiovascular risk factors on the development of dementia have not been well evaluated. We investigated these impacts of smoking, overweight/obesity, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus on the risk of disabling dementia.
Methods: The study participants were 25,029 (10,134 men and 14,895 women) Japanese aged 40–74 years without disabling dementia at baseline (2008–2013). They were assessed on smoking status (non-current or current), overweight/obesity (body mass index ≥25 kg/m2 and ≥30 kg/m2, respectively), hypertension (systolic blood pressure ≥140 mmHg, diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mmHg or any antihypertensive medication use), and diabetes mellitus (a fasting serum glucose ≥126 mg/dL, non-fasting glucose ≥200 mg/dL, hemoglobin A1c ≥6.5% by the National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program or glucose-lowering medication use) at baseline. Disabling dementia was identified as the level of care required ≥1 and cognitive disability grade ≥IIa according to the National Long-term Care Insurance Database. We used a Cox proportional regression model to estimate hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) of disabling dementia according to the cardiovascular risk factors and calculated the population attributable fractions (PAFs).
Results: During a median follow-up of 9.1 years, 1,322 (606 men and 716 women) developed disabling dementia. Current smoking and hypertension were associated with a higher risk of disabling dementia in both sexes, whereas overweight or obesity was not associated with the risk in either sex. Diabetes mellitus was associated with a higher risk only in women (p for sex interaction = 0.04). The significant PAFs were 13% for smoking and 14% for hypertension in men and 3% for smoking, 12% for hypertension, and 5% for diabetes mellitus in women. The total PAFs of the significant risk factors were 28% in men and 20% in women. When stratified by age, hypertension in midlife (40–64 years) was associated with the increased risk in men, while diabetes mellitus in later-life (65–74 years) was so in women.
Conclusions: A substantial burden of disabling dementia was attributable to smoking, and hypertension in both sexes and diabetes mellitus in women, which may require the management of these cardiovascular risk factors to prevent dementia.
View full abstract
-
Daisuke Hori, Tsukasa Takahashi, Yudai Kaneda, Akihiko Ozaki, Takahiro ...
Article type: Short Communication
2023Volume 28 Pages
10
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 02, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: Before the COVID-19 vaccine became available, many Japanese people were undecided about whether or not to receive them. Their decisions were keys to achieving herd immunity. The impact of the type of information source on the COVID-19 vaccine uptake decision-making process remains unclear. We aimed to investigate the association between information source usage on COVID-19 and subsequent vaccine uptake status among those who have yet to decide whether to receive vaccines from non-prioritized people for vaccination.
Methods: Prospective cohort online self-administered surveys were conducted in February 2021 (T1), before the start of the mass vaccination program, and September–October 2021 (T2), when the vaccines were available to all citizens. The survey’s target population was registered monitors of an Internet research company. Participants who answered “I want to get vaccinated after waiting to see how it goes.” at T1 were eligible for analysis. The outcome variable was the COVID-19 vaccine uptake status in T2, and the predictors were 20 types of information sources, categorized based on people (family members, etc.), institutions (governments, etc.), or media (TV news, etc.). Adjusted odds ratio and 95% confidence intervals were estimated using logistic regression adjusted for possible confounders.
Results: The 5,139 respondents, mean age and standard deviation was 42.8 ± 12.5, 55.7% female, were eligible for analysis. 85.7% completed vaccination (including reserved/intended people) in T2. In the multivariate logistic analysis, odds ratios (95% confidence interval) for vaccine uptake were 1.49 (1.18–1.89) for workplaces/schools, 1.81 (1.33–2.47) for LINE, 0.69 (0.55–0.86) for Internet news and 0.62 (0.48–0.82) for video sharing sites.
Conclusions: The type of information source usage played an important role in the decision to vaccinate against COVID-19. Although caution is needed in interpreting the results, obtaining information from workplaces/schools and LINE was influential in promoting immunization.
View full abstract
-
Keiko Murakami, Shinichi Kuriyama, Hideki Hashimoto
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
9
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 28, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: There is substantial evidence on the association between lower education and unhealthy behaviors. However, the mechanism underlying this association remains unclear. This study aimed to examine whether income, health literacy, and social support mediate the association between education and health-related behaviors.
Methods: A questionnaire survey was conducted in metropolitan areas in Japan from 2010 to 2011 among residents aged 25–50 years. Data from 3663 participants were used in this study. Health literacy was measured using the Communicative and Critical Health Literacy scale. Health-related behaviors were current smoking, poor dietary habits, hazardous drinking, and lack of exercise. Poisson regression analyses with robust variance estimators were conducted to examine the associations between education and these health-related behaviors. Multiple mediation analyses were conducted to estimate the magnitudes of the mediating effects of income, health literacy, and social support on these associations.
Results: Less educated participants had higher risks of all unhealthy behaviors. Income mediated the associations of education with smoking (6.4%) and exercise (20.0%). Health literacy mediated the associations of education with dietary habits (15.4%) and exercise (16.1%). Social support mediated the associations of education with dietary habits (6.4%) and exercise (7.6%). The education–drinking association was mediated by income in the opposite direction (−10.0%). The proportions of the total effects mediated by income, health literacy, and social support were 9.8% for smoking, 24.0% for dietary habits, −3.0% for drinking, and 43.7% for exercise.
Conclusions: These findings may provide clues for designing effective interventions to reduce educational inequalities in health-related behaviors.
View full abstract
-
Yeaeun Kim, Jongho Park, Jae-Hyun Park
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
8
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 26, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Background: Health screening is a preventive and cost-effective public health strategy for early detection of diseases. However, the COVID-19 pandemic has decreased health screening participation. The aim of this study was to examine regional differences in health screening participation between before and during COVID-19 pandemic and vulnerabilities of health screening participation in the regional context.
Methods: Administrative data from 229 districts consisting of 16 provinces in South Korea and health screening participation rate of each district collected in 2019 and 2020 were included in the study. Data were then analyzed via descriptive statistics and geographically weighted regression (GWR).
Results: This study revealed that health screening participation rates decreased in all districts during COVID-19. Regional vulnerabilities contributing to a further reduction in health screening participation rate included COVID-19 concerns, the population of those aged 65+ years and the disabled, lower education level, lower access to healthcare, and the prevalence of chronic disease. GWR analysis showed that different vulnerable factors had different degrees of influence on differences in health screening participation rate.
Conclusions: These findings could enhance our understanding of decreased health screening participation due to COVID-19 and suggest that regional vulnerabilities should be considered stringent public health strategies after COVID-19.
View full abstract
-
Kimiko Tomioka, Kenji Uno, Masahiro Yamada
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
7
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 21, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
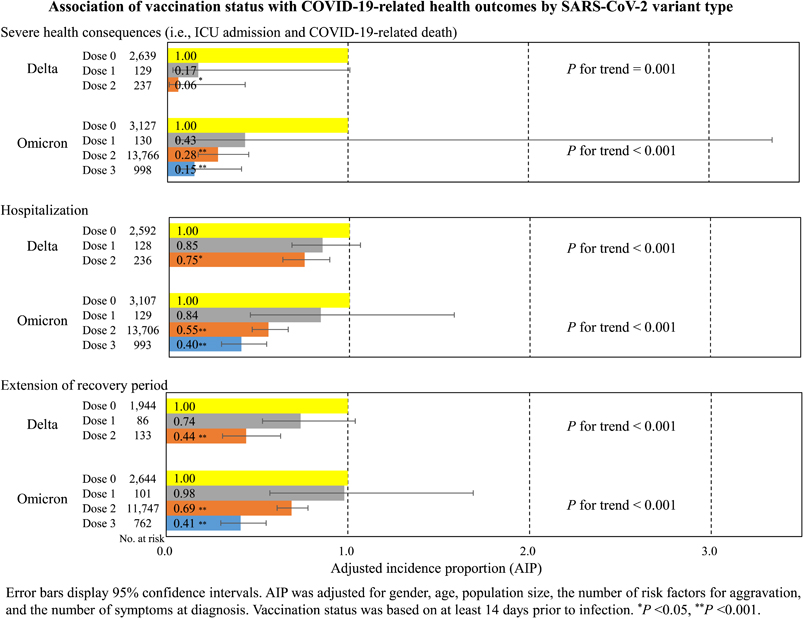
Background: Many previous studies have reported COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness, but there are few studies in Japan. This community-based, retrospective observational study investigated the association between vaccination status and COVID-19-related health outcomes in COVID-19 patients by SARS-CoV-2 variant type.
Methods: The study participants were 24,314 COVID-19 patients aged 12 or older whose diagnoses were reported to the Nara Prefecture Chuwa Public Health Center from April 2021 to March 2022, during periods when the alpha, delta, and omicron variants of COVID-19 were predominant. The outcome variables were severe health consequences (SHC) (i.e., ICU admission and COVID-19-related death), hospitalization, and extension of recovery period. The explanatory variable was vaccination status at least 14 days prior to infection. Covariates included gender, age, population size, the number of risk factors for aggravation, and the number of symptoms at diagnosis. The generalized estimating equations of the multivariable Poisson regression models were used to estimate the adjusted incidence proportion (AIP) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for each health outcome. We performed stratified analyses by SARS-CoV-2 variant type, but the association between vaccination status and COVID-19-related health outcomes was stratified only for the delta and omicron variants due to the small number of vaccinated patients during the alpha variant.
Results: Of the 24,314 participants, 255 (1.0%) had SHC; of the 24,059 participants without SHC, 2,102 (8.7%) were hospitalized; and of the 19,603 participants without SHC, hospitalization, and missing data on recovery period, 2,960 (15.1%) had extension of recovery period. Multivariable Poisson regression models showed that regardless of SARS-CoV-2 variant type or health outcome, those who received two or more vaccine doses had significantly lower risk of health outcomes than those who did not receive the vaccine, and there was a dose-response relationship in which the AIP for health outcomes decreased with an increased number of vaccinations.
Conclusion: A higher number of vaccinations were associated with lower risk of COVID-19-related health outcomes, not only in the delta variant but also in the omicron variant. Our findings suggest that increasing the number of COVID-19 vaccine doses can prevent severe disease and lead to early recovery of patients not requiring hospitalization.
View full abstract
-
Takafumi Takase, Mizuho Nagao, Rei Kanai, Takahiro Nishida, Tomoyuki A ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
6
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 21, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: Recent studies indicate that the timing of introduction of potentially allergenic food is crucial for the development of food allergy in children. This cross-sectional study aimed to clarify the reality of allergen food intake in a general population of young children in Japan.
Methods: A questionnaire survey of caregivers was conducted at health checkups for 1.5-year (18-month)-old and 3-year-old children in the fall of 2020. The caregivers were asked about (1) the presence/absence of allergic disease symptoms based on the ISAAC questionnaire, and (2) foods that caregivers avoided giving their children. Ordinal logistic regression analyses were periformed to determine factors associated with food avoidance.
Results: Questionnaires were distributed to 1720 caregivers, and 1603 (93%) responded. The responders consisted of 771 and 832 caregivers who participated in 1.5-year-old and 3-year-old checkups, respectively. The prevalence of allergic diseases was comparable to recent epidemiological studies in Japan, indicating that the population may be representative. At 1.5 years old, more than 50% of the children were not exposed to peanuts, tree nuts, fish eggs, shellfish, and buckwheat. At 3 years old, the avoidance rates of the foods had decreased but were still between 18.8% and 32.0%. On the other hand, the avoidance rates of chicken egg and cow’s milk, the top 2 common allergenic foods in Japan, were much lower at 2.8% and 1.5% at 1.5 years, and they decreased to 1.4% and 0.7% at 3 years old, respectively. Ordinal logistic analysis showed that avoidance of chicken egg, cow’s milk, and wheat was associated with food allergy diagnosis and chicken egg avoidance with eczema, but avoidance of other foods showed no associations with any risk factors for food allergy.
Conclusion: Caregivers avoided giving various foods, independent of allergy risk factors, to their young children. Since delayed introduction of an allergenic food has been reported to increase the risk of developing an allergy to the food, the results warrant future investigation of the development of food allergies in relation to current eating habits and recommendations.
View full abstract
-
Ai Hori, Takahiro Tabuchi, Naoki Kunugita
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
5
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 18, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: Heated tobacco product (HTP) use has increased substantially between 2016 and 2017 in Japan. This study aims to clarify how HTP use (IQOS, Ploom, and glo) spread across the different combustible cigarette smoking statuses during 2015–16 and 2017–18 in Japan.
Methods: We compared the two periods of (i) 2015 to 2016 (N = 5,366) and (ii) 2017 to 2018 (N = 3,422) from a longitudinal study randomly sampling members from the Japan “Society and New Tobacco” Internet Survey (JASTIS). Multivariable logistic regression models for current HTP use in the previous 30 days by combustible cigarette smoking status in the previous year were used adjusting for socio-demographic factors.
Results: HTP use increased by 10 times in the 2017–18 cohort compared with the 2015–16 cohort according to the adjusted odds ratio (95% confidence interval) for current HTP use as 10.2 (7.03–14.8). According to smoking status, significantly higher adjusted ORs (95% CIs) of current HTP use for the after period were observed: 2.60 (1.37–4.94) for never smokers, 7.82 (3.64–16.8) for former smokers, 21.1 (5.73–77.9) for current smokers with intention to quit, and 17.0 (9.58–30.3) for current smokers without intention to quit.
Conclusion: During 2015 to 2018 in Japan, HTP use dramatically increased in all subgroups except for never smokers.
View full abstract
-
Zhao Ma, Weiqin Li, Jicui Yang, Yijuan Qiao, Xue Cao, Han Ge, Yue Wang ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
4
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 13, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: Congenital heart disease (CHD) is one of the most common congenital malformations in humans. Inconsistent results emerged in the existed studies on associations between air pollution and congenital heart disease. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the association of gestational exposure to air pollutants with congenital heart disease, and to explore the critical exposure windows for congenital heart disease.
Methods: The nested case-control study collected birth records and the following health data in Tianjin Women and Children’s Health Center, China. All of the cases of congenital heart disease from 2013 to 2015 were selected matching five healthy controls for each case. Inverse distance weighting was used to estimate individual exposure based on daily air pollution data. Furthermore, the conditional logistic regression with distributed lag non-linear model was performed to identify the association between gestational exposure to air pollution and congenital heart disease.
Results: A total of 8,748 mother-infant pairs were entered into the analysis, of which 1,458 infants suffered from congenital heart disease. For each 10 µg/m3 increase of gestational exposure to PM2.5, the ORs (95% confidence interval, 95%CI) ranged from 1.008 (1.001–1.016) to 1.013 (1.001–1.024) during the 1st–2nd gestation weeks. Similar weak but increased risks of congenital heart disease were associated with O3 exposure during the 1st week and SO2 exposure during 6th–7th weeks in the first trimester, while no significant findings for other air pollutants.
Conclusions: This study highlighted that gestational exposure to PM2.5, O3, and SO2 had lag effects on congenital heart disease. Our results support potential benefits for pregnancy women to the mitigation of air pollution exposure in the early stage, especially when a critical exposure time window of air pollutants may precede heart development.
View full abstract
-
Jiayu He, Yuanyuan Liu, Ai Zhang, Qianfeng Liu, Xueli Yang, Naixiu Sun ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
3
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 11, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: Weather conditions are a possible contributing factor to age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of irreversible loss of vision. The present study evaluated the joint effects of meteorological factors and fine particulate matter (PM2.5) on AMD.
Methods: Data was extracted from a national cross-sectional survey conducted across 10 provinces in rural China. A total of 36,081 participants aged 40 and older were recruited. AMD was diagnosed clinically by slit-lamp ophthalmoscopy, fundus photography, and spectral domain optical coherence tomography (OCT). Meteorological data were calculated by European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) reanalysis and were matched to participants’ home addresses by latitude and longitude. Participants’ individual PM2.5 exposure concentrations were calculated by a satellite-based model at a 1-km resolution level. Multivariable-adjusted logistic regression models paired with interaction analysis were performed to investigate the joint effects of meteorological factors and PM2.5 on AMD.
Results: The prevalence of AMD in the study population was 2.6% (95% CI 2.42–2.76%). The average annual PM2.5 level during the study period was 63.1 ± 15.3 µg/m3. A significant positive association was detected between AMD and PM2.5 level, temperature (T), and relative humidity (RH), in both the independent and the combined effect models. For PM2.5, compared with the lowest quartile, the odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) across increasing quartiles were 0.828 (0.674,1.018), 1.105 (0.799,1.528), and 2.602 (1.516,4.468). Positive associations were observed between AMD and temperature, with ORs (95% CI) of 1.625 (1.059,2.494), 1.619 (1.026,2.553), and 3.276 (1.841,5.830), across increasing quartiles. In the interaction analysis, the estimated relative excess risk due to interaction (RERI) and the attributable proportion (AP) for combined atmospheric pressure and PM2.5 was 0.864 (0.586,1.141) and 1.180 (0.768,1.592), respectively, indicating a synergistic effect between PM2.5 and atmospheric pressure.
Conclusions: This study is among the first to characterize the coordinated effects of meteorological factors and PM2.5 on AMD. The findings warrant further investigation to elucidate the relationship between ambient environment and AMD.
View full abstract
-
Mengxi Zhai, Zhizhou Duan, Jiawei Tian, Qingqing Jiang, Biao Zhu, Chen ...
Article type: Research Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
2
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 11, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Background: Men who have sex with men (MSM) have become a high risk population of HIV infection due to their risky sexual behaviors. The latent pattern of psychosocial characteristics plays an important effect in HIV-related risky behaviors among HIV-negative MSM.
Method: Participants were recruited from Wuhan, Nanchang, and Changsha city from September 2017 to January 2018. Social support was assessed by the multidimensional scale of social support, Connor-Davidson Resilience scale-10 items for reliance, the assessment of Stigma towards Homosexuality for sexual minority stigma, the Likert subscale of nondisclosure for identity concealment, the ACE questionnaire-Kaiser-CDC for adverse childhood experience, the Centers for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale for depression. Latent profile analysis (LPA) and multivariate regression were used to analyze the data.
Results: Three psychosocial characteristic patterns were revealed by the LPA. “Social support and resilience group” (SR group), “Identity concealment group” (IC group) and “Adverse childhood experience” (ACE group) were identified, respectively. In comparison with “SR group”, “IC group” have a higher likelihood of one-night male partners (AOR = 2.74, 95%CI = [1.54, 4.90]), both fixed and one-night male partners (AOR = 2.01, 95%CI = [1.34, 3.01]) and HIV-unsure male partner (AOR = 2.12, 95%CI = [1.44, 3.13]). Similarly, “ACE group” were more likely having inconsistent condom use (AOR = 2.58, 95%CI = [1.41, 4.73]), and having sex with HIV-positive male partner (AOR = 4.90, 95%CI = [1.95, 12.30]) with comparison of “SR group”. In addition, we further revealed that “ACE group” had a higher ratio (90.0%) of inconsistent condom use among MSM whose male partners were HIV-positive.
Conclusions: Six important psychosocial factors were divided into three latent pattern classes. Compared with “SR group”, “IC group” and “ACE group” were more likely to engage in HIV-related risky sexual behaviors. Further research may pay more attention to “IC group” and “ACE group” for targeted intervention.
View full abstract
-
Sani Rachman Soleman, Zhaoqing Lyu, Takuya Okada, Mariko Harada Sassa, ...
Article type: Review Article
2023Volume 28 Pages
1
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 07, 2023
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material
Background: Healthcare workers (HCWs) employed personal protective equipment (PPE) during the COVID-19 pandemic, crucial to protecting themselves from infection. To highlight the efficacy of PPE in preventing environmental infection among HCWs, a systematic review was conducted in line with PRISMA guidance.
Methods: A search of the PubMed and Web of Science databases was conducted from January 2019 to April 2021 using pre-defined search terms. Articles were screened by three researchers. The approved papers were read in full and included in this review if relevance was mutually agreed upon. Data were extracted by study design and types of PPEs.
Results: 47 of 108 identified studies met the inclusion criteria, with seven reviews and meta-analyses, seven cohort, nine case-control, fifteen cross-sectional studies, four before and after, four case series, and one modeling studies. Wearing PPE offered COVID-19 protection in HCWs but required adequate training. Wearing surgical masks provided improved protection over cloth masks, while the benefit of powered air-purifying respirators is less clear, as are individual gowns, gloves, and/or face shields.
Conclusions: Wearing PPE, especially facial masks, is necessary among HCWs, while training in proper use of PPE is also important to prevent COVID-19 infection.
View full abstract
 Article type: Research Article
Article type: Research Article Article type: Research Article
Article type: Research Article Article type: Research Article
Article type: Research Article Article type: Research Article
Article type: Research Article Article type: Research Article
Article type: Research Article