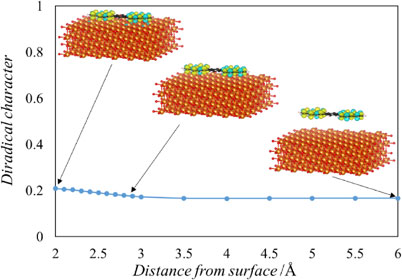
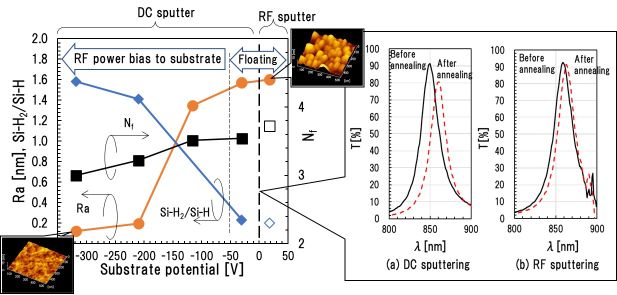
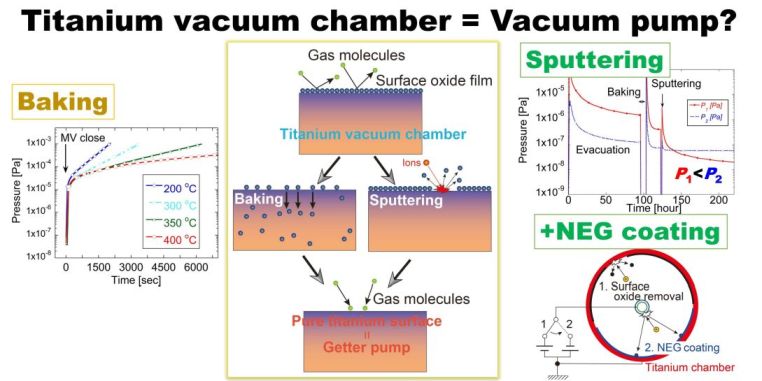
20 巻, 2 号
選択された号の論文の9件中1~9を表示しています
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Regular Papers
-
原稿種別: Regular Paper
専門分野: Electronic Properties
2022 年 20 巻 2 号 p. 59-67
発行日: 2022/03/19
公開日: 2022/05/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2022/03/19PDF形式でダウンロード (6122K) -
原稿種別: Regular Paper
専門分野: Thin Films
2022 年 20 巻 2 号 p. 68-75
発行日: 2022/03/24
公開日: 2022/05/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2022/03/24PDF形式でダウンロード (1678K) -
原稿種別: Regular Paper
専門分野: Structure
2022 年 20 巻 2 号 p. 76-84
発行日: 2022/03/24
公開日: 2022/05/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2022/03/24PDF形式でダウンロード (4921K) -
原稿種別: Regular Paper
専門分野: Crystal Growth
2022 年 20 巻 2 号 p. 85-89
発行日: 2022/04/02
公開日: 2022/05/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2022/04/02PDF形式でダウンロード (1659K) -
原稿種別: Regular Paper
専門分野: Bio-Science and -Technology
2022 年 20 巻 2 号 p. 90-97
発行日: 2022/04/21
公開日: 2022/05/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2022/04/21PDF形式でダウンロード (2849K) -
原稿種別: Regular Paper
専門分野: Bio-Science and -Technology
2022 年 20 巻 2 号 p. 98-106
発行日: 2022/04/21
公開日: 2022/05/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2022/04/21PDF形式でダウンロード (2514K) -
原稿種別: Regular Paper
専門分野: Vacuum
2022 年 20 巻 2 号 p. 107-118
発行日: 2022/05/07
公開日: 2022/05/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2022/05/07PDF形式でダウンロード (4563K) -
原稿種別: Regular Paper
専門分野: Catalysis
2022 年 20 巻 2 号 p. 119-123
発行日: 2022/05/12
公開日: 2022/05/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2022/05/12PDF形式でダウンロード (1437K)
Technical Note
-
原稿種別: Technical Note
専門分野: Instrumentations and Techniques
2022 年 20 巻 2 号 p. 124-127
発行日: 2022/05/14
公開日: 2022/05/28
[早期公開] 公開日: 2022/05/14PDF形式でダウンロード (1662K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|