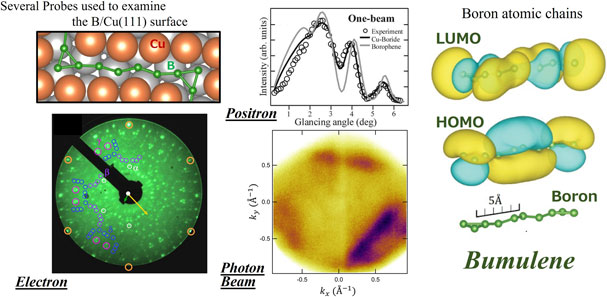
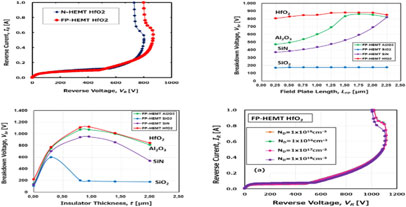
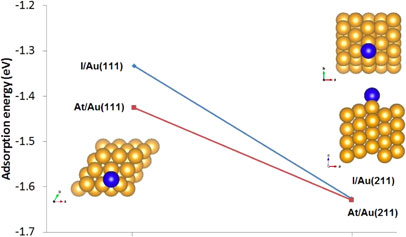
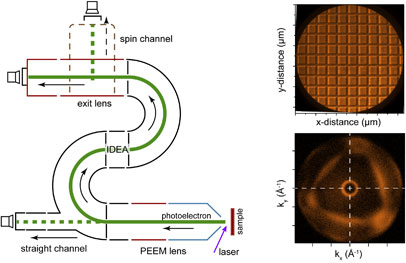
Volume 22, Issue 1
Displaying 1-11 of 11 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Review Paper
-
Article type: Review Paper
Subject area: Structure
2024 Volume 22 Issue 1 Pages 1-8
Published: September 07, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 20, 2024
Advance online publication: September 07, 2023Download PDF (4236K)
Regular Papers
-
Article type: Regular Paper
Subject area: Devices and Sensors
2024 Volume 22 Issue 1 Pages 9-15
Published: September 16, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 20, 2024
Advance online publication: September 16, 2023Download PDF (3880K) -
Article type: Regular Paper
Subject area: Electronic Properties
2024 Volume 22 Issue 1 Pages 16-24
Published: September 16, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 20, 2024
Advance online publication: September 16, 2023Download PDF (5891K) -
Article type: Regular Paper
Subject area: Nano-Materials
2024 Volume 22 Issue 1 Pages 25-31
Published: September 21, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 20, 2024
Advance online publication: September 21, 2023Download PDF (1591K) -
Article type: Regular Paper
Subject area: Thin Films
2024 Volume 22 Issue 1 Pages 32-37
Published: October 05, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 20, 2024
Advance online publication: October 05, 2023Download PDF (2009K) -
Article type: Regular Paper
Subject area: Interdisciplinary
2024 Volume 22 Issue 1 Pages 38-45
Published: October 19, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 20, 2024
Advance online publication: October 19, 2023Download PDF (4034K)
Technical Note
-
Article type: Technical Note
Subject area: Instrumentations and Techniques
2024 Volume 22 Issue 1 Pages 46-52
Published: October 12, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 20, 2024
Advance online publication: October 12, 2023Download PDF (3662K)
Conference—IVC-22—
-
Article type: Proceeding Paper
Subject area: Thin Films
2024 Volume 22 Issue 1 Pages 53-57
Published: August 17, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 20, 2024
Advance online publication: August 17, 2023Download PDF (2859K) -
Article type: Proceeding Paper
Subject area: Vacuum
2024 Volume 22 Issue 1 Pages 58-73
Published: September 07, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 20, 2024
Advance online publication: September 07, 2023Download PDF (10356K) -
Article type: Proceeding Paper
Subject area: Electronic Properties
2024 Volume 22 Issue 1 Pages 74-78
Published: September 16, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 20, 2024
Advance online publication: September 16, 2023Download PDF (4117K) -
Article type: Proceeding Paper
Subject area: Vacuum
2024 Volume 22 Issue 1 Pages 79-85
Published: September 21, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 20, 2024
Advance online publication: September 21, 2023Download PDF (4331K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|