Volume 20, Issue 4
Displaying 1-13 of 13 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Regular Papers
-
Article type: Regular Paper
Subject area: Instrumentations and Techniques
2022Volume 20Issue 4 Pages 196-201
Published: July 07, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: November 26, 2022
Advance online publication: July 07, 2022Download PDF (1521K) -
Article type: Regular Paper
Subject area: Devices and Sensors
2022Volume 20Issue 4 Pages 202-206
Published: July 07, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: November 26, 2022
Advance online publication: July 07, 2022Download PDF (998K) -
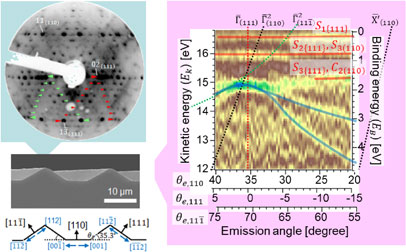
Article type: Regular Paper
Subject area: Micro- and Nano-Fabrication
2022Volume 20Issue 4 Pages 207-213
Published: July 14, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: November 26, 2022
Advance online publication: July 14, 2022Download PDF (4188K) -
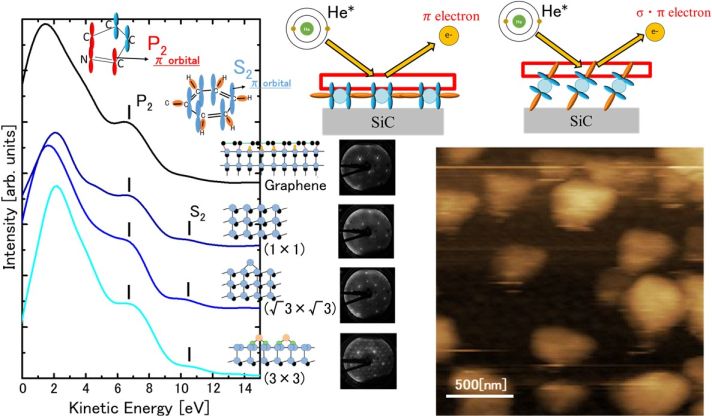
Article type: Regular Paper
Subject area: Nano-Science and -Technology
2022Volume 20Issue 4 Pages 214-220
Published: July 28, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: November 26, 2022
Advance online publication: July 28, 2022Download PDF (3003K) -
Article type: Regular Paper
Subject area: Electronic Properties
2022Volume 20Issue 4 Pages 221-225
Published: July 28, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: November 26, 2022
Advance online publication: July 28, 2022Download PDF (1935K) -
Soft X-ray Absorption/Emission Spectroscopy and Atomic Hydrogen Irradiation Effect of Ammonia BoraneArticle type: Regular Paper
Subject area: Nano-Science and -Technology
2022Volume 20Issue 4 Pages 226-231
Published: August 06, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: November 26, 2022
Advance online publication: August 06, 2022Download PDF (1200K) -
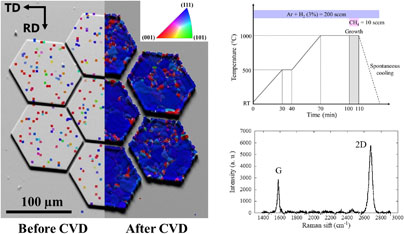
Article type: Regular Paper
Subject area: Crystal growth
2022Volume 20Issue 4 Pages 232-236
Published: August 25, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: November 26, 2022
Advance online publication: August 25, 2022Download PDF (2526K) -
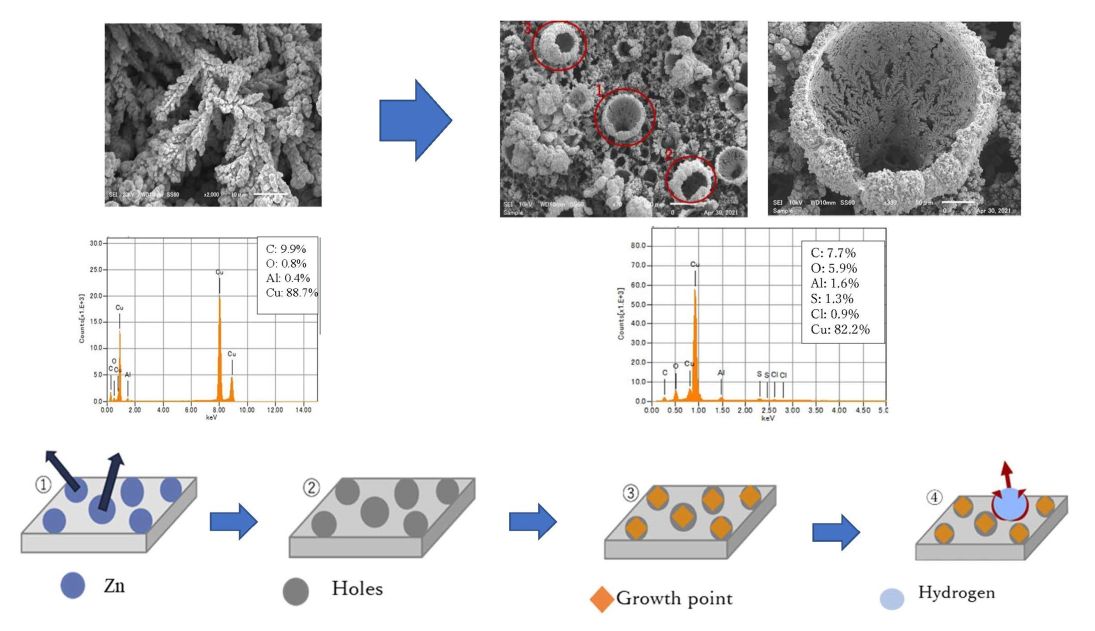
Article type: Regular Paper
Subject area: Environmental and Energy Technology
2022Volume 20Issue 4 Pages 237-242
Published: October 08, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: November 26, 2022
Advance online publication: October 08, 2022Download PDF (2713K)
Conference—ISSS-9—
-
Article type: Proceeding Paper
Subject area: Nano-Science and -Technology
2022Volume 20Issue 4 Pages 243-247
Published: July 07, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: November 26, 2022
Advance online publication: July 07, 2022Download PDF (1223K) -
Article type: Proceeding Paper
Subject area: Nano-Science and -Technology
2022Volume 20Issue 4 Pages 248-251
Published: July 16, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: November 26, 2022
Advance online publication: July 16, 2022Download PDF (1374K) -
Article type: Proceeding Paper
Subject area: Thin Films
2022Volume 20Issue 4 Pages 252-256
Published: July 16, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: November 26, 2022
Advance online publication: July 16, 2022Download PDF (951K) -
Article type: Proceeding Paper
Subject area: Thin Films
2022Volume 20Issue 4 Pages 257-260
Published: August 04, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: November 26, 2022
Advance online publication: August 04, 2022Download PDF (1218K) -
Article type: Proceeding Paper
Subject area: Structure
2022Volume 20Issue 4 Pages 261-265
Published: August 06, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: November 26, 2022
Advance online publication: August 06, 2022Download PDF (1548K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|