All issues

Volume 11 (2010)
- Issue 4 Pages 147-
- Issue 3 Pages 117-
- Issue 2 Pages 73-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
Volume 11, Issue 4
Displaying 1-8 of 8 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Reviews
-
Jongbin LIM, George E. INGLETT, Suyong LEE2010Volume 11Issue 4 Pages 147-152
Published: December 15, 2010
Released on J-STAGE: June 18, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe excessive dietary fat intake can result in health problems such as obesity and heart-related diseases, resulting in increased consumer demand for reduced fat foods. A number of food ingredients with fat-like functions have been developed as fat alternatives in the food industry. Especially, some fat replacers that belong to carbohydrate-based fat replacers, play multi-functional roles in foods beyond the reduction of fat and calories. They can provide beneficial physiological activity and control texture and rheology without quality loss. Also, they can promote the development of environment-friendly and natural products, make health claims on a label, and diversify the type of reduced-fat foods. Therefore, the use of multi-functional fat replacers can encourage the food industry to respond to current demand of health-conscious consumers for reduced-fat foods.View full abstractDownload PDF (328K) -
Nathalie GONTARD, Stéphane GUILBERT2010Volume 11Issue 4 Pages 153-159
Published: December 15, 2010
Released on J-STAGE: June 18, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSResearch and development efforts were in the last decades mainly dedicated to the huge development of convenient versatile petrochemical plastics, related additives, recycling processes etc. Future packaging will have to respond to the evolution of societal needs and concerns in term of health, quality, environment, cost, sustainability, worldwide raw materials availability, information etc. The present paper will focus on reasonable hypothesis on food packaging technologies development scenarios. It could be anticipated that concepts such as eco-friendly, biodegradable, active and nano-engineered materials will develop. Some examples will be briefly presented and discussed by focusing on subsequent research lines of thinking likely to facilitate the use of biopolymer for food packaging. Controlling mass transfer between the food, the food contact material (FCM) and the external atmosphere is the major key factor for the development for these new packaging solutions when considering adequacy to foods requirements and safety rules. The mass transfer control can be achieved by adjusting the FCM matrix nature and structure at different scales (macro/micro/nano). The knowledge and modeling of solute, gas, vapor and nanoparticles transfer in the packaging material can facilitate the development of efficient packaging. This approach was performed to develop different packaging food systems such as modified atmosphere packaging based on gas selective bio-materials, antimicrobial bio-packaging based on controlled release of volatile active molecules or nanocomposites packaging combined with high pressure food treatments.View full abstractDownload PDF (644K)
-
Shinya IKEDA2010Volume 11Issue 4 Pages 161-168
Published: December 15, 2010
Released on J-STAGE: June 18, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSStructures and mechanical properties of food hydrocolloids consisting of hydrated food macromolecules such as polysaccharide and protein have been reviewed. Food sols often exhibit a decrease in the viscosity with increasing flow rate (i.e., shear-thinning) due to flow-induced changes in the three-dimensional structure of food macromolecules. Relatively high viscosities at low flow rates are highly effective in slowing down the rate of floatation or sedimentation of insoluble particles. For transporting the bulk sol, the flow rate may be increased in order to decrease the viscosity to the same order of magnitude as that of water. A food sol may possess a true yield stress. If the yield stress value is sufficiently larger than the buoyancy or gravitational force, floatation or sedimentation of insoluble particles never occurs. Atomic force microscopy images of gellan gum bulk gels have revealed that the gel networks are composed of rigid rod-like strands that are crosslinked with other strands at the ends. It is unreasonable to assume that the elasticity of such a network is determined by entropic effects. A novel model for describing the concentration dependence of the elasticity has been proposed by considering the bending elasticity of rod-like network strands.View full abstractDownload PDF (1248K) -
Tomoaki HAGIWARA2010Volume 11Issue 4 Pages 169-175
Published: December 15, 2010
Released on J-STAGE: June 18, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSRecrystallization of ice crystals causes deterioration during storage and distribution in frozen foods. Therefore, the recrystallization process has been considered as an important phenomenon which should be controlled and predicted for optimal storage and distribution of frozen foods. However, a systematic understanding of the recrystallization is far from what we have expected because of its simultaneous change of size, shape, and number of ice crystals. Also, the time-consuming storage experiment to investigate the recrystallization behavior is another reason for preventing a systematic understanding of the recrystallizaton since it makes difficult to accumulate the recrystallzaiton experiments. As for the first problem, we succeeded at numerical estimation of change of ice crystal shape by using the concept of fractal. For the problem of time-consuming storage experiments, we showed that the diffusion coefficient of the water molecules in a freeze-concentrated matrix is a useful parameter for predicting recrystallization of ice crystals in model frozen foods; that means, knowing the water diffusion coefficient in a freeze-concentrated matrix would engender prediction of recrystallization rate of ice crystals and save time-consuming storage experiments. These results would help for systematical understanding of recrystallzation of ice crystals in frozen food, which may contribute to solving the global food problem and geoenvironmental issue.View full abstractDownload PDF (1787K)
Original Papers
-
Akiko TASHIRO, Keiko ONO, Atsuko HASEGAWA-TANIGOME, Hitomi KUMAGAI, Hi ...2010Volume 11Issue 4 Pages 177-185
Published: December 15, 2010
Released on J-STAGE: June 18, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe viscosity, μ, and the velocity through the pharynx of solutions prepared from commercial thickening agents were compared with “fractured yogurt” as a model bolus of yogurt to evaluate their suitability as care foods for dysphagic patients. From the shape of velocity spectra and the values of velocity, the flow property of the “fractured yogurt” was considered to be close to that of the bolus of yogurt. The value of μ for the yogurt-like thickener solution was smaller than the apparent viscosity, μapp, for the “fractured yogurt” around the shear rate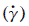 of 10 s-1. In addition, the value of Vmax, an index for the safety of care foods, for the yogurt-like and jam-like solutions was larger than that for the fractured yogurt. These results indicate that a yogurt-like solution does not necessarily have flow properties similar to those of yogurt and is less safe for dysphagic patients than yogurt.
View full abstractDownload PDF (804K)
of 10 s-1. In addition, the value of Vmax, an index for the safety of care foods, for the yogurt-like and jam-like solutions was larger than that for the fractured yogurt. These results indicate that a yogurt-like solution does not necessarily have flow properties similar to those of yogurt and is less safe for dysphagic patients than yogurt.
View full abstractDownload PDF (804K) -
Toru SHIGEMATSU, Mina MURAKAMI, Kanako NAKAJIMA, Yoshiyuki UNO, Arata ...2010Volume 11Issue 4 Pages 189-199
Published: December 15, 2010
Released on J-STAGE: June 18, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this study, we supplied glutamic acid (Glu) into brown rice grains and allowed an enzymatic conversion from Glu to γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) due to biosynthesis induced by high pressure (HP) treatment. The distribution of free amino acids in water-soaked brown rice grains during preservation after HP treatment at 200 MPa for 10 min was analyzed. The free amino acid distribution of HP-treated samples, just after HP treatment, showed no apparent difference from that of untreated control without HP treatment. However, during 4 days preservation at 25℃ after HP treatment, certain amino acids including GABA in the HP-treated samples increased with time and showed higher concentrations than those in untreated samples. To investigate the feasibility for use of HP-treated brown rice grains as a bioreactor producing GABA, Glu was supplied into brown rice grains during water soaking and applied for HP treatment. The GABA concentrations during preservation increased with the increase in the Glu concentrations in the soaking solutions. The initial GABA production rate was accelerated by HP treatment. These results provide feasibility for a novel use of HP technology to alter the metabolic pathways in a cellular biological material and to accumulate useful metabolites.View full abstractDownload PDF (1728K) -
Hiroyuki IYOTA, Hideki SAKAI, Hiroyuki TAKASAGO, Hideya SHIMADA2010Volume 11Issue 4 Pages 203-213
Published: December 15, 2010
Released on J-STAGE: June 18, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSVisual images are one of the most important means of determining whether food has been cooked to perfection, especially while baking, which is a popular cooking method. In this study, equipment for recording the images of the food surface and image editing software were developed in order to record color images having generality and to evaluate the color change due to baking. A spherical dome with a diameter of 500 mm, whose inner surface was painted white, was used as the integrating sphere. The subject (food) was placed in the middle of the dome. Two D65 fluorescent lamps powered by a high-frequency inverter power supply were placed below the subject as the light source. Thus, the subject could be illuminated only by indirect light. The X-Rite White Balance Card and X-Rite ColorChecker were used for color correction. The colors with Munsell chroma, C, less than 5 were in a good agreement with the standard value obtained from the color chart after color correction. The color change of breadcrumbs during re-baking under 200℃ airflow is evaluated from a histogram of L* values versus the number of pixels of the corrected image as a test case.View full abstractDownload PDF (1502K) -
Yuzoh ASANO, Manabu SUZUKI, Hiroshi ARASE, Naoki YUDA, Hitoshi SAITO, ...2010Volume 11Issue 4 Pages 215-219
Published: December 15, 2010
Released on J-STAGE: June 18, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWhey protein obtained from milk product process has many nutritional values and good amino acid composition. Nevertheless, it has not been utilized so much due to protein aggregation and gel formation caused by heating. In order to improve the heat stability of whey protein, we have tried a new high shear-heating process using the thin film spinning device to denature whey protein concentrates (WPC), and the conventional low shear-heating process was used as a control test. The results showed that the product prepared with heating under high shear rate was clearly better than that prepared under low shear rate, in regard to aggregates formation and heat stability of the dispersed particles in water. It was suggested that protein heat denaturation did not contribute to the difference in the heat stability. On the other hand, the zeta-potential data of these particles in water suggested the difference in the surface of particles prepared with the high-shear method and the low-shear method. SEM images of the particles also showed the difference in the surface shape. It was suggested that the structure of the particles could cause the difference in these physical properties.View full abstractDownload PDF (1236K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|