抄録
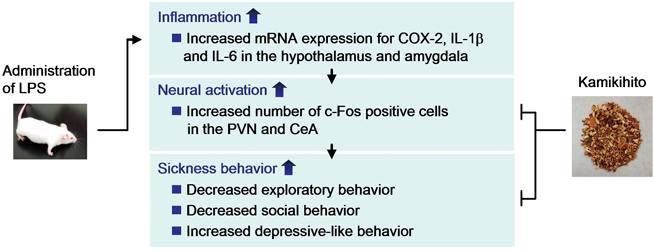
Sickness behavior is a series of behavioral and psychological changes that develop in those stricken with cancers and inflammatory diseases. The etiological mechanism of sickness behavior is not known in detail, and consequently there are no established standard therapies. Kamikihito (KKT), a Kampo (traditional Japanese herbal) medicine composed of 14 herbs, has been used clinically to treat psychiatric dysfunction. Previously, we found that KKT ameliorated sickness behavior in mice inoculated with murine colon 26 adenocarcinoma cells. In this study, we examined the effects of KKT on bacterial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced sickness behavior in mice. The administration of LPS caused the emotional aspects of sickness behavior, such as loss of object exploration, social interaction deficit, and depressive-like behavior. LPS also induced mRNA expression for cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6, and increased the number of c-Fos immunopositive cells in the hypothalamus and amygdala. KKT ameliorated the behavioral changes and reversed the increases in c-Fos immunopositive cells in the two brain regions, but did not influence the mRNA expression. These results suggest that KKT ameliorates sickness behavior via the suppression of neural activation without anti-inflammatory effects, and that KKT has the potential to treat sickness behavior.