巻号一覧

39 巻, 2 号
選択された号の論文の20件中1~20を表示しています
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Reviews
-
Hiromichi Fujino2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 149-155
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe lipid mediator prostanoids consist of prostaglandins and thromboxanes, and are synthesized from arachidonic acid by the action of cyclooxygenase. There are five major prostanoids, including prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and they are involved in a variety of biological responses such as inflammation, allergy, parturition, and tumorigenesis. These prostanoids exert their effects via activation of their cognate G protein coupled receptors, e.g., E-type prostanoid (EP) receptors for PGE2. The EP receptors are composed of four subtypes, namely EP1 to EP4. Here, breakthroughs in the last dozen years of research are introduced, with a special focus on some important findings of EP4 receptor-mediated signaling and the signaling associated with cancer development, particularly in colon cancer.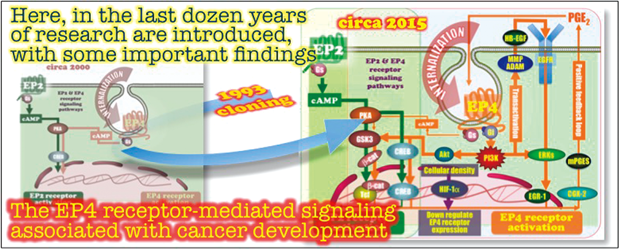 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5300K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5300K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Byung-Hwan Lee, Sun-Hye Choi, Hyeon-Joong Kim, Seok-Won Jung, Ho-Kyoun ...2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 156-162
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLLysophosphatidic acid (1-acyl-2-lyso-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidic acid; LPA) is a simple and minor phospholipid in plants. Plant LPAs are merely metabolic intermediates in de novo lipid synthesis in plant cell membranes or for glycerophospholipid storage. The production and metabolisms of LPAs in animals are also well characterized and LPAs have diverse cellular effects in animal systems; i.e., from brain development to wound healing through the activation of G protein-coupled LPA receptors. Recent studies show that various foodstuffs such as soybean, cabbage and seeds such as sesame and sunflower contain bioactive LPAs. Some LPAs are produced from phosphatidic acid during the digestion of foodstuff. In addition, herbal medicines such as corydalis tuber, and especially ginseng, contain large amounts of LPAs compared to foodstuffs. Herbal LPAs bind to cell surface LPA receptors in animal cells and exert their biological effects. Herbal LPAs elicit [Ca2+]i transient and are coupled to various Ca2+-dependent ion channels and receptor regulations via the activation of LPA receptors. They also showed beneficial effects of in vitro wound healing, in vivo anti-gastric ulcer, anti-Alzheimer’s disease, autotaxin inhibition and anti-metastasis activity. Thus, herbal LPAs can be useful agents for human health. Humans can utilize exogenous plant-derived LPAs for preventive or therapeutic purposes if plant-derived LPAs are developed as functional foods or natural medicine targeting LPA receptors. This brief review article introduces the known rich sources of herbal LPAs and herbal LPA binding protein, describes their biological effects, and further addresses possible clinical applications. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1099K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1099K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Regular Articles
-
Annisa Rahma, Muhammad Miftahul Munir, Khairurrijal, Anton Prasetyo, ...2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 163-173
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLAn electrospun fiber of polyvinyl(pyrrolidone) (PVP)–Tween 20 (T20) with curcumin as the encapsulated drug has been developed. A study of intermolecular interactions was performed using Raman spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The Raman and FT-IR studies showed that curcumin preferrably interacted with T20 and altered PVP chain packing, as supported by XRD and physical stability data. The hydroxyl stretching band in PVP shifted to a lower wavenumber with higher intenstity in the presence of curcumin and PVP, indicating that hydrogen bond formation is more intense in a curcumin or curcumin–T20 containing fiber. The thermal pattern of the fiber did not indicate phase separation. The conversion of curcumin into an amorphous state was confirmed by XRD analysis. An in vitro release study in phosphate buffer pH 6.8 showed that intermolecular interactions between each material influenced the drug release rate. However, low porosity was found to limit the hydrogen bond-mediated release. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5900K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5900K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Jianghao Zhao, Hua Tao, Wenchuan Xian, Yujie Cai, Wanwen Cheng, Mingka ...2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 174-180
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2015/12/03ジャーナル フリー HTMLMany anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) that mainly target ion channels or post-synaptic receptors are in clinical use, but a proportion of patients are resistant to these traditional AEDs and experience repeated severe break-out seizures. Given its involvement in the etiology of epilepsy, the neurotransmitter glycine may serve as a novel target for epilepsy treatment. Increasing evidence suggests that inhibitors of glycine transporter 1 (GlyT1) exhibit anti-seizure properties in mouse models and show potential as anti-convulsions drugs. In the present study, we investigated the effect of a highly selective GlyT1 inhibitor (named M22) on glycine transport kinetics using a radioactive substrate uptake assay and investigated the anti-seizure effects of M22 on the maximal electroshock seizure threshold (MEST) test and the timed intravenous (i.v.) pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) intravenous test. Our results demonstrate that M22 was capable of elevating the seizure threshold in the MEST test but did not alter the seizure threshold in the PTZ i.v. test. Strychnine, an inhibitor of glycine receptor activity, reversed the threshold elevation at a subconvulsive dosage (0.1 mg/kg subcutaneously) in the MEST test and did not affect M22 plasma levels in mice, suggesting that the anti-seizure effect in this model may be mediated by increased glycine receptor activity. Moreover, M22 administration did not influence motor function and coordination in mice. In combination with the previously reported excellent pharmacokinetic features of M22, our present results suggested that M22 has the potential to serve as a new anti-convulsive drug or as a lead compound for the development of AEDs.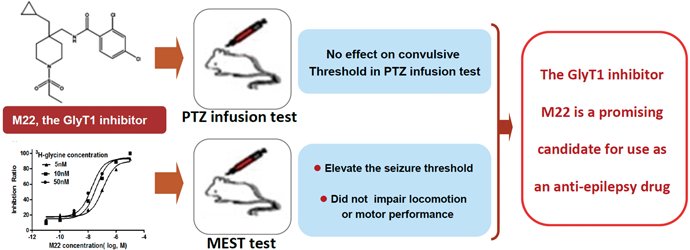 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (662K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (662K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Xiaoxuan Tian, Lianying Chang, Guangyin Ma, Taiyi Wang, Ming Lv, Zhilo ...2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 181-191
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2015/11/18ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Erigeron breviscapus has been widely used in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and its total flavonoid component is commonly used to treat ischemic stroke, coronary heart disease, diabetes and hypertension. Scutellarin is the major ingredient of E. breviscapus and scutellarein is one of the main bioactive metabolites of scutellarin in vivo, but the latter’s pharmacological activities have not been fully characterized. Provided evidence that could inhibit platelet aggregation, the effect of scutellarein on rat washed platelets and its underlying mechanisms were evaluated in our research. Scutellarein inhibited platelet adhesion and aggregation induced by multiple G protein coupled receptor agonists such as thrombin, U46619 and ADP, in a concentration-dependent manner. Furthermore, the mild effect of scutellarein on intracellular Ca2+ mobilization and cyclic AMP (cAMP) level was observed. On the other hand, the role of scutellarein as potential protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor was confirmed by PKC activity analysis and molecular docking. The phorbol myristate acetate-induced platelets aggregation assay with or without ADP implied that the scutellarein takes PKC(s) as its primary target(s), and acts on it in a reversible way. Finally, scutellarein as a promising agent exhibited a high inhibition effect on ADP-induced platelet aggregation among its analogues. This study clarifies the PKC-related signaling pathway involved in antiplatelet action of scutellarein, and may be beneficial for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1738K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1738K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Shinichiro Fuma, Masamitsu Shimazawa, Tomoyo Imamura, Yusuke Kanno, No ...2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 192-198
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe combination of timolol and latanoprost, which are ocular hypotensive agents, has a greater ocular hypotensive effect than each as monotherapy. However, the protective effect of the combination is not well understood. In the present study, we investigated whether latanoprost/timolol in combination has an additive or synergistic cytoprotective effect on neuro retinal cells (RGC-5). To investigate the protective effects of timolol/latanoprost in combination, cultured RGC-5 were treated with various concentrations of these two agents, singly or together, after which the cells were exposed to oxidative stress, serum deprivation, or endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in vitro. Cells were also treated with an Akt inhibitor, LY294002, to examine the mechanism of the protective effect. Latanoprost, timolol, and the two in combination reduced cell death induced by oxidative stress, serum deprivation, or ER stress. The latanoprost/timolol combination reduced cell death to a greater extent than monotherapy with latanoprost or timolol on serum deprivation only, and LY294002 inhibited the protective effect of their combination. These findings suggest that timolol/latanoprost in combination have a protective effect against serum deprivation only by activation of Akt signaling. Furthermore, this combination has not only an ocular hypotensive effect but also a neuroprotective effect. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (972K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (972K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Su-Hyun Chun, Hyun Ah Lee, Keon Bong Lee, Sae Hun Kim, Kun-Young Park, ...2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 199-206
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録The aim of this study was to determine the stimulatory effects of Maillard reaction, a non-enzymatic browning reaction on the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and phagocytic activity induced by whey protein concentrate (WPC). Glycated WPC (G-WPC) was prepared by a reaction between WPC and the lactose it contained. The fluorescence intensity of G-WPC dramatically increased after one day, and high molecular weight complexes formed via the Maillard reaction were also observed in the sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis profiles. G-WPC demonstrated immunomodulatory effects, including stimulation of increased nitric oxide production and cytokine expressions (i.e., tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6), compared to WPC. Furthermore, the phagocytic activity of RAW264.7 cells was significantly increased upon treatment with G-WPC, compared to WPC. Therefore, we suggest that G-WPC can be utilized as an improved dietary source for providing immune modulating activity.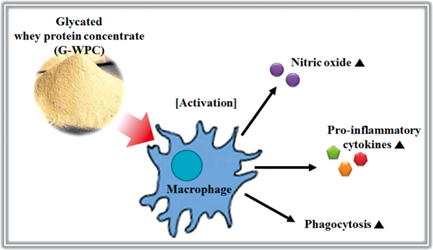 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1664K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1664K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Guping Wang, Chunlei Tang, Guijun Yan, Bainian Feng2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 207-214
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2015/11/26ジャーナル フリー HTMLHeart failure represents a major health problem. The development of new drugs to treat this condition is essential. We previously discovered that AF-001 attenuates the cardiac defects caused by heart failure in zebrafish. In this paper, we report the identification of AF-HF001, an AF-001 derivative, and its effects on live cardiomyocytes subjected to oxidative damage. The in vitro results demonstrated that AF-HF001 attenuates the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the myocardial cell apoptosis. A DNA microarray was performed to broadly analyze gene expression after H2O2 treatment with or without AF-HF001. Hierarchical clustering analysis revealed that AF-HF001 modifies the expression of certain genes (Ndufs2, Ndufb6, Ndufb8, Ndufa13, Ndufs3, Ndufs5, TPM1, MYH14, RyR1, and TIMP4) related to ROS production, cardiac contractility and extracellular matrix remodeling. AF-HF001 ameliorates oxidative damage, which may be related to the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family and the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway. Altogether, this study suggests that AF-HF001 exhibits potential as a clinical drug candidate for the treatment of heart failure. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1277K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1277K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Masami Ukawa, Yukako Fujiwara, Hidenori Ando, Taro Shimizu, Tatsuhiro ...2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 215-220
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLKupffer cells in livers bearing tumor metastases were found to have promoted tumor invasion and exacerbated the metastasis. This implies that the function of Kupffer cells might differ between animals bearing hepatic metastases and those that are healthy. Kupffer cells are considered responsible for the accumulation of liposomes in the liver. In this study, we hypothesized that the alteration in the function of Kupffer cells by hepatic metastasis would also affect the biodistribution of liposomes following intravenous administration. The hepatic accumulation and the blood concentration of PEGylated liposomes were compared between healthy mice and tumor-bearing mice. We noted that hepatic accumulation and elimination from the blood were significantly accelerated in tumor-bearing mice, indicating that our hypothesis was correct. In the tumor-bearing mice, the proportion of Kupffer cells taking up liposomes was significantly increased. Intravenous injection of oxaliplatin (l-OHP) containing PEGylated liposomes decreased the fraction of Kupffer cells, but this administration caused no injury to the hepatocytes. These results suggest that PEGylated liposomes containing l-OHP may have the potential to treat metastatic hepatic cancer—not only via the direct killing of the cancer cells but also via a reduction in tumor-supportive Kupffer cells. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (452K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (452K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Ji-Won Song, Chang-Seob Seo, Tae-In Kim, Og-Sung Moon, Young-Suk Won, ...2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 221-229
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2015/12/02ジャーナル フリー HTMLManassantin A, a neolignan isolated from Saururus chinensis, is a major phytochemical compound that has various biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, neuroleptic, and human acyl-CoA : cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitory activities. In this study, we investigated the protective effects of manassantin A against ethanol-induced acute gastric injury in rats. Gastric injury was induced by intragastric administration of 5 mL/kg body weight of absolute ethanol to each rat. The positive control group and the manassantin A group were given oral doses of omeprazole (20 mg/kg) or manassantin A (15 mg/kg), respectively, 1 h prior to the administration of absolute ethanol. Our examinations revealed that manassantin A pretreatment reduced ethanol-induced hemorrhage, hyperemia, and epithelial cell loss in the gastric mucosa. Manassantin A pretreatment also attenuated the increased lipid peroxidation associated with ethanol-induced acute gastric lesions, increased the mucosal glutathione (GSH) content, and enhanced the activities of antioxidant enzymes. The levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-1β were clearly decreased in the manassantin A-pretreated group. In addition, manassantin A pretreatment enhanced the levels of cyclooxygenase (COX)-1, COX-2, and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and reduced the inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) overproduction and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) phosphorylation. Collectively, these results indicate that manassantin A protects the gastric mucosa from ethanol-induced acute gastric injury, and suggest that these protective effects might be associated with COX/PGE2 stimulation, inhibition of iNOS production and NF-κB activation, and improvements in the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory status.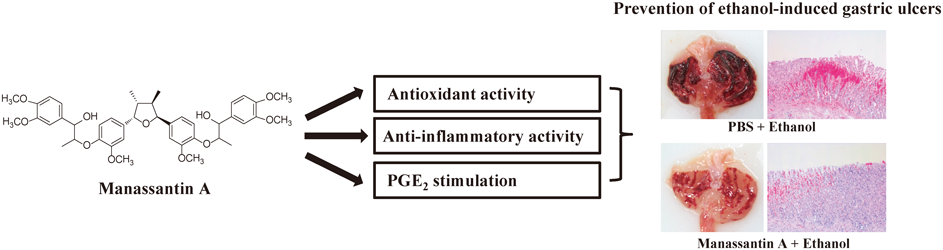 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1737K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1737K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Shinichi Harada, Wataru Matsuura, Masaoki Takano, Shogo Tokuyama2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 230-238
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThis article has been deleted at the request of the authors from this journal. The Editorial Committee of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan (September 17, 2019)抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1636K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Magda Ismail Marzouk, Soheir Ahmad Shaker, Aisha Ali Abdel Hafiz, Khal ...2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 239-251
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録The acetohydrazide derivative reacted with carbon electrophiles such as acid chlorides, acetylacetone, ethyl acetoacetate and aromatic aldehydes to give some interesting heterocyclic compounds. The hydrazide derivative reacted with acetophenone which in turn underwent Vielsmeier–Haack reaction. Also, the phthalazinethione has been synthesized and its behavior towards hydrazine hydrate, oxidizing agent and ethyl chloroacetate has been investigated. The newly synthesized compounds were characterized by spectroscopic data. The antimicrobial, the cytotoxic, and the antioxidant activities of some of the synthesized products were evaluated. Some of the tested compounds showed very strong cytotoxic activity with respect to the standard. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1046K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1046K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Akihiro Michihara, Asaki Oda, Mayuko Mido2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 252-258
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLWe previously demonstrated that the high levels of oxidative stress in the brains of ten-week-old stroke-prone hypertensive rats (SHRSP) were attributable to intrinsic, not extrinsic factors (Biol. Pharm. Bull., 33, 2010, Michihara et al.). The aim of the present study was to determine whether increases in the enzymes producing reactive oxygen species (ROS), reductions in the enzymes and proteins removing ROS, or increases in an enzyme and transporter removing antioxidants promoted oxidative stress in the SHRSP cerebrum. No significant decreases were observed in the mRNA levels of enzymes that remove ROS between SHRSP and normotensive Wistar Kyoto rats. The activity of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase (NOX) and the protein and mRNA levels of NOX3, an enzyme that produces ROS, were significantly increased in the SHRSP cerebrum. These results suggested that the high expression levels of NOX3 increased oxidative stress in the SHRSP cerebrum. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (446K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (446K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Hee-Sung Chae, Hunseung Yoo, Young Hee Choi, Won Jun Choi, Young-Won C ...2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 259-266
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Maackiapterocarpan B, one of the pterocarpan analogs found in Sophora tonkinensis, is known to display pharmacological activities. However, the anti-inflammatory effects of maackiapterocarpan B and its molecular mechanism have yet to be clearly elucidated. In the present study, the effects of maackiapterocarpan B on macrophage-mediated inflammation in vitro were assessed. Maackiapterocarpan B inhibited the production of nitric oxide, the expression of tumor necrosis factor α, colony stimulating factor 2, interleukin-1β and interleukin-6, and the activation of nuclear factor-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinases in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. These observations suggest the potential of maackiapterocarpan B in the treatment of inflammatory diseases.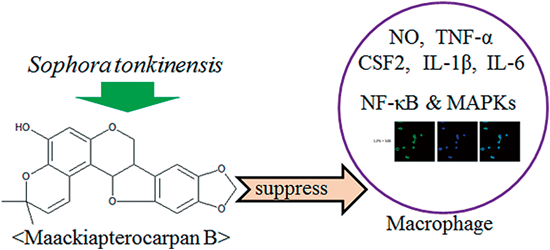 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1453K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1453K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Lin An, Li-li Han, Zu-jian Wang, Tong-hui Huang, Hui-dong Zhu2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 267-271
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2015/12/03ジャーナル フリー HTMLIn this work, the catalytic activity of calix[8]arene sulfonic acid was successfully investigated for the famous Biginelli reaction. Under ultrasonic irradiation, calix[8]arene sulfonic acid could efficiently catalyzed the three-component reaction of aldehydes with ethyl acetoacetate and urea or thiourea in ethanol to afford the corresponding 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones/thiones in 46–93%. The advantages of this method are the easy isolated procedure, short reaction time and low cost of the catalyst. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (361K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (361K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Takeshi Matsuoka, Kohta Kurohane, Wakana Suzuki, Erina Ogawa, Kamiyu K ...2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 272-277
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2015/12/02ジャーナル フリー HTMLDi-n-butyl phthalate (DBP), a phthalate ester, has been shown to have an adjuvant effect on fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-induced contact hypersensitivity (CHS) mouse models. Di-n-butyl maleate (DBM), widely used as a plasticizer for industrial application, has been reported to cause dermatitis in humans. DBM is a butyl alcohol ester of di-carboxylic acid that represents a part of the DBP structure, while di-n-butyl fumarate (DBF) is a trans isomer of DBM. We examined whether DBM or DBF exhibits an adjuvant effect like DBP does. When BALB/c mice were epicutaneously sensitized with FITC in the presence of DBM or DBF, the FITC-specific CHS response was enhanced, as we have observed for DBP. As to underlying mechanisms, DBM and DBF facilitated the trafficking of FITC-presenting CD11c+ dendritic cells (DCs) from skin to draining lymph nodes and increased the cytokine production by draining lymph nodes. In conclusion, DBM and DBF may have an effect that aggravates contact dermatitis through a skin sensitization process. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (795K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (795K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Yohei Tatematsu, Hiroki Hayashi, Ryo Taguchi, Haruhi Fujita, Atsushi Y ...2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 278-284
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLHepatotoxicity is a known side effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). In the present study, the effects of N-phenylanthranilic acid (NPA) scaffold NSAIDs on rat liver mitochondria were examined. Mefenamic acid (MEF, 200 µM) induced mitochondrial swelling, which was inorganic phosphate (Pi)-dependent and suppressed by cyclosporin A (CsA, 2.5 µM), similar to calcium-induced swelling. Mitochondrial swelling was also observed following the addition of 200 µM flufenamic acid (FLU), meclofenamic acid (MCL), and tolfenamic acid (TOL). Less swelling was observed with the addition of 200 µM diclofenac (DIC) or NPA. Diphenylamine (DPA)-induced swelling occurred in a Pi-independent manner and was not sensitive to CsA. The mechanism by which DPA interacted with the mitochondrial inner membrane differed from those of the other NPA scaffold NSAIDs. The addition of 50 µM MEF, MCL, TOL, and FLU had uncoupling effects in mitochondrial inner membrane. These NSAIDs dose-dependently obstructed electron transport in the respiratory chain. NSAIDs are known to have various dynamic structures, and the solvation free energies (dGWs: an index of stereo-hydrophobicity) of the conformers obtained were determined using a molecular orbital analysis. The relationship between the dynamic structures and swelling induced by NPA scaffold NSAIDs was also examined. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (862K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (862K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Notes
-
Hirokazu Nakayama, Kensuke Usuki, Hirotoshi Echizen, Ryuichi Ogawa, Ta ...2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 285-288
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLEculizumab given bi-weekly is widely recommended for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). We undertook a retrospective analysis on the medical records of 763 dosings of 14 PNH patients to investigate whether a threshold would exist in dosing intervals associated with breakthrough hemolysis. We identified 12 events of breakthrough hemolysis in 4 patients. Multivariate logistic regression and receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis revealed a significant association between increased risk of breakthrough hemolysis and prolonged dosing intervals of 17 days or more and concomitant inflammation: odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were 1.6 (1.3–2.0, p<0.01) and 5.5 (1.3–22.8, p=0.02), respectively. ROC analysis showed that the best cut-off dosing interval discriminating breakthrough hemolysis was 16.5 days. We consider that eculizumab dosing intervals longer than 17 days may be associated with an increased risk for developing breakthrough hemolysis in patients with PNH. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (266K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (266K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Ryota Araki, Shoji Nishida, Yosuke Hiraki, Feng Li, Kinzo Matsumoto, T ...2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 289-294
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Sickness behavior is a series of behavioral and psychological changes that develop in those stricken with cancers and inflammatory diseases. The etiological mechanism of sickness behavior is not known in detail, and consequently there are no established standard therapies. Kamikihito (KKT), a Kampo (traditional Japanese herbal) medicine composed of 14 herbs, has been used clinically to treat psychiatric dysfunction. Previously, we found that KKT ameliorated sickness behavior in mice inoculated with murine colon 26 adenocarcinoma cells. In this study, we examined the effects of KKT on bacterial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced sickness behavior in mice. The administration of LPS caused the emotional aspects of sickness behavior, such as loss of object exploration, social interaction deficit, and depressive-like behavior. LPS also induced mRNA expression for cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6, and increased the number of c-Fos immunopositive cells in the hypothalamus and amygdala. KKT ameliorated the behavioral changes and reversed the increases in c-Fos immunopositive cells in the two brain regions, but did not influence the mRNA expression. These results suggest that KKT ameliorates sickness behavior via the suppression of neural activation without anti-inflammatory effects, and that KKT has the potential to treat sickness behavior.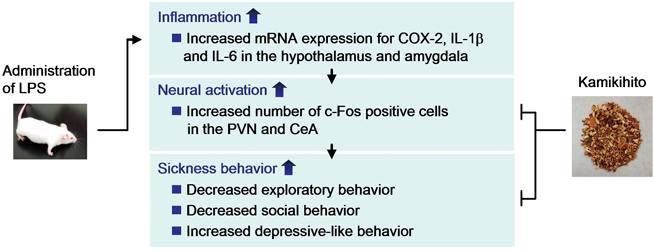 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (692K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (692K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Naoto Okada, Shuji Fushitani, Momoyo Azuma, Shingen Nakamura, Toshimi ...2016 年 39 巻 2 号 p. 295-300
発行日: 2016/02/01
公開日: 2016/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe therapeutic effects of anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) agents, vancomycin (VCM), teicoplanin (TEIC), and arbekacin (ABK), depend on their concentrations in blood. Therefore, therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is important when these antibiotics are used. In the hematological ward at Tokushima University Hospital, pharmacists have ordered the measurement of blood VCM, TEIC, and ABK concentrations to promote the use of TDM in accordance with an agreed protocol since 2013. Moreover, the infection control team includes several medical disciplines and has advised on the optimal treatment using VCM, TEIC, and ABK since 2013. This study aimed to investigate the clinical effectiveness of these pharmacist interventions. We retrospectively studied 145 cases in which patients were treated with VCM, TEIC, or ABK between January 2012 and December 2013 in the hematological ward at Tokushima University Hospital. The patients were divided into a control group (71 cases) and an intervention group (74 cases), and their clinical outcomes were compared. The rate of achievement of effective drug concentrations significantly increased in the intervention group (74%), compared to the rate in the control group (55%). Moreover, univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression revealed that pharmacist intervention and appropriate concentrations of anti-MRSA agents were independent factors associated with reduced hospitalization periods in patients with lymphoma. Our study revealed that proactive pharmacist intervention may improve the therapeutic effect of anti-MRSA agents in hematology ward patients.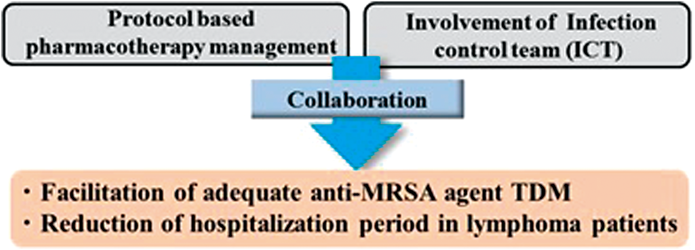 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (650K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (650K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|